Activity 2.1.4 AOI Logic Analysis
advertisement

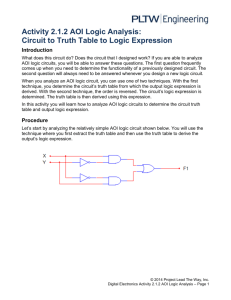
Activity 2.1.4 AOI Logic Analysis Introduction What does this circuit do? Does the circuit that I designed work? If you are able to analyze AOI logic circuits, you will be able to answer these questions. The first question frequently comes up when you need to determine the functionality of a previously designed circuit. The second question will always need to be answered whenever you design a new logic circuit. When you analyze an AOI logic circuit, you can use one of two techniques. With the first technique, you determine the circuit’s truth table from which the output logic expression is derived. With the second technique, the order is reversed. The circuit’s logic expression is determined. The truth table is then derived using this expression. In this activity you will learn how to analyze AOI logic circuits to determine the circuit truth table and output logic expression. Equipment Paper and Pencil Calculator Procedure Let’s start by analyzing the relatively simple AOI logic circuit shown below. You will use the technique where you first extract the truth table and then use the truth table to derive the output’s logic expression. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2010 DE – Unit 2 – Lesson 2.1 – Activity 2.1.4 – AOI Logic Analysis – Page 1 1. Using the test points that have been assigned (TP1-TP4), complete the following truth table. TP1 TP2 TP4 TP3 X Y F1 TP1 TP2 TP3 TP4 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 2. Using the truth table, write out the Minterms for every location that contains a (1) in the F1 column. F1=X’Y+XY’+XY 3. Using the Minterm(s), write the logic expression for the output F1. F1=X’Y+XY’+XY Re-analyze the simple AOI logic circuit using the technique where you first extract the logic expression for the output and then use the logic expression to derive the truth table. 1. Using the circuit diagram below, write the logic expression at the output of each gate until you reach the output of the circuit. F1=X’Y’+XY’+X’Y+XY 2. Using the logic expression, complete the truth table shown below. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2010 DE – Unit 2 – Lesson 2.1 – Activity 2.1.4 – AOI Logic Analysis – Page 2 X Y F1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 How do the logic expressions and truth tables obtained from the two techniques compare? Are they the same? They should be. If they are not, review your work and correct any mistakes. Let’s analyze a more complex circuit. Complete the following steps for the three input AOI logic diagram shown below. 1. Using the analysis technique where you first extract the truth table and then use it to derive the output’s logic expression, analyze the circuit. Record your results below. F2=R’ST’+R’S’T’+R’ST+RST’ Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2010 DE – Unit 2 – Lesson 2.1 – Activity 2.1.4 – AOI Logic Analysis – Page 3 R S T F2 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 F2 = R’ST’+R’S’T’+R’ST+RST’ 2. Now, using the analysis technique where you first extract the logic expression for the output and then use it to derive the truth table, analyze the circuit. Record your results below. R S T F2 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 F2 = R’ST’+R’S’T’+R’ST+RST’ 3. How do the truth tables obtained from the two techniques compare? Are they the same? They should be. If they are not, review your work and correct any mistakes. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2010 DE – Unit 2 – Lesson 2.1 – Activity 2.1.4 – AOI Logic Analysis – Page 4 4. How do the logic expressions obtained from the two techniques compare? Are they the same? All answers had matched accurately between the two techniques. They are not the same but equal to one another They are NOT the SAME, but they are EQUAL. In later activities we will learn how to use Boolean algebra to simplify logic expressions like these and prove that they are equal. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2010 DE – Unit 2 – Lesson 2.1 – Activity 2.1.4 – AOI Logic Analysis – Page 5 Conclusion 1. In your own words, describe the process used to analyze a logic circuit where you first extract a truth table and then derive the logic expression. First off you must look at the types of switches found within the circuit. Then according to the type of switch found within a circuit you can derive weather or not the given circuit will be a 0 or a 1 (on or off positions) Then based upon the combination of 1’s and 0’s you can figure out whether the output at the end of the circuit will become toggled. Then through this process of trial and order you can begin formulating a Truth Table and thus through filling this table out you can piece together a logical expression for a given circuit. 2. Again, in your own words, describe the process used to analyze a logic circuit where you first extract the logic expression and then derive the truth table. First off you must look at the types of switches found within the circuit. Then according to the type of switch found within a circuit you can derive whether or not the given circuit will be a 0 or a 1 (on or off positions) Then based upon the combination of 1’s and 0’s you can figure out whether the output at the end of the circuit will become toggled. Then through this process of trial and order you can begin formulating a Truth Table and thus through filling this table out you can piece together a logical expression for a given circuit. 3. Did you find one of the processes easier than the other? Which one and why? I found the 2nd method to be easiest due to the monitoring of different outputs as well as the generalized form of the 1st method. Not having to keep track of TP1, TP2, etc makes life a whole lot easier. 4. What is the difference between two logic equations being equal versus two logic equations being equivalent? By equal it means that they are the same. By equivalent it means that they consist of different items or values but they add up to the same end sum or value Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2010 DE – Unit 2 – Lesson 2.1 – Activity 2.1.4 – AOI Logic Analysis – Page 6