4×6 mod 4 drugs cards
advertisement
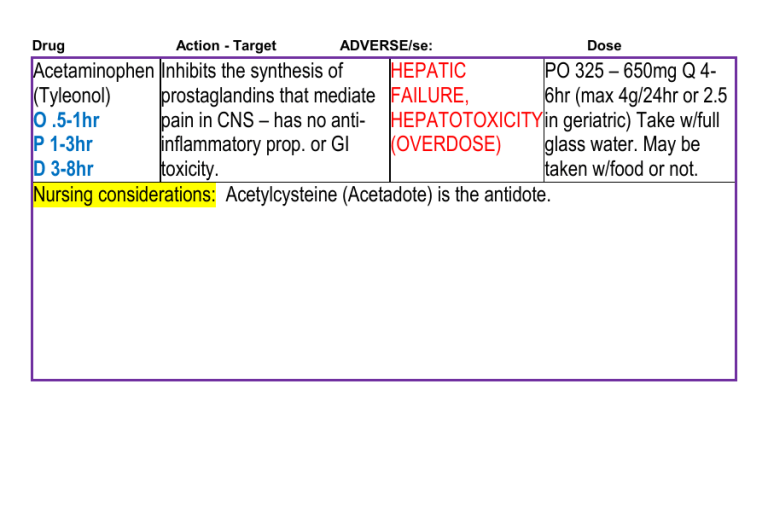
Drug Action - Target ADVERSE/se: Dose Acetaminophen Inhibits the synthesis of HEPATIC PO 325 – 650mg Q 4(Tyleonol) prostaglandins that mediate FAILURE, 6hr (max 4g/24hr or 2.5 O .5-1hr pain in CNS – has no anti- HEPATOTOXICITY in geriatric) Take w/full P 1-3hr inflammatory prop. or GI (OVERDOSE) glass water. May be D 3-8hr toxicity. taken w/food or not. Nursing considerations: Acetylcysteine (Acetadote) is the antidote. Drug Action - Target ADVERSE/se: diphenhydrAMINE antihistamines/relief of allergic drowsiness, (Benadryl ) symptoms. Antagonizes the anorexia, dry R O P D effects of histamine at mouth P 15-60 2-4 4-8 hr receptor sites. CNS O min hr depressant and anticholinergic IM 20-30 2-4 4-8 hr properties. min hr IV rapid UK 4-8 hr N Dose PO 25-50mg q 4-6 hr, MAX 300mg/day. w/meals/milk IM, IV 25-50mg q 4 hr (may need 100mg – MAX 300mg/day) Nursing considerations: May cause sedation and confusion due to increased sensitivity to anticholinergic effects. Monitor carefully, assess for confusion, delirium, other anticholinergic side effects and fall risk. Institute measures to prevent falls. PO: Administer with meals or milk to minimize GI irritation. Capsule may be emptied and contents taken with water or food. IM: Administer 50 mg/ml into well-developed muscle. Avoid SQ injections. Drug Corticosteroids Action - Target ADVERSE/se: Dose antiasthmatic, PEPTIC ULCERATION, PO Immunosupressant. THROMBOEMBOLISM, depression, Dependent upon type of depending on type of euphoria, hypertension, anorexia, corticosteroid – Use corticosteroid: nausea, acne, decreased wound Drug book systemically and locally in healing, ecchymosis, fagility, wide variety of chronic hirsutism, Petechiae, adrenal diseases: Inflammatory, suppression, muscle wasting, Allergic, Hematologic, osteoporosis, cushingoid Neoplastic, Autoimmune appearance disorders. Nursing Implications: Instruct patient to inform health care professional promptly if severe abdominal pain or tarry stools occur Do not double doses. immunosuppression and may mask symptoms of infection. Discuss possible effects on body image. Lab Test Considerations: Monitor serum electrolytes and glucose. May cause hyperglycemia, especially in persons with diabetes. May cause hypokalemia. Patients on prolonged therapy should routinely have CBC, serum electrolytes, and serum and urine glucose evaluated. May ↓ WBCs. May cause hyperglycemia, especially in persons with diabetes. May ↓ serum potassium and calcium and ↑ serum sodium concentrations. Drug Epinephrine R O PP D IN 1 U 1-3 hr HL min K N SQ 5-10 20 <1-4 hr min mi n IM 6-12 U <1-4 hr min K N IV rapi 20 20-30 d mi min n Action - Target Antiasthmatic, bronchodilator, vasopressor./ inhibits release of mediators of immediate hypersensititivy reactions from mast cells and results in accum. of cAMP ADVERSE/se: Dose nervousness, SQ, IM (anaphylactic reactions/asthma restlessness, 0.1 – 0.5 mg. may repeat q 10-15 min tremor, (anaphylactic react. or q 20 min – 4 hr angina, (asthma) arrhythmias, IV Severe anaphylaxis 0.1-0.25 mg q hypertension, 5-15 min; may be followed by 1-4 tachycardia mcg/min continuous infusion. cardio res 1mg q 3-5 min Bradycardia 2-10 mcg/min Inhaln 1 inhalation (160-250 mcg) repeated after 1-2 min. Nursing Implications: Assess lung sounds/rep patt/pulse /BP. Lab Test Considerations: May cause transient ↓ in serum potassium concentrations with nebulization or at higher than recommended doses. Drug Action - Target ADVERSE/se: Dose May cause an ↑ in blood glucose and serum lactic acid concentrations. Toxicity and Overdose: Symptoms of overdose include persistent agitation, chest pain or discomfort, decreased blood pressure, dizziness, hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, seizures, tachyarrhythmias, persistent trembling, and vomiting. Treatment includes discontinuing adrenergic bronchodilator and other beta-adrenergic agonists and symptomatic, supportive therapy. Cardioselective beta blockers are used cautiously, because they may induce bronchospasm. For anaphylactic shock, volume replacement should be administered concurrently with epinephrine. Antihistamines and corticosteroids may be used in conjunction with epinephrine. Use a tuberculin syringe with a 26-gauge 1/2-in. needle for subcut injection to ensure that correct amount of medication is administered. Prior to administration, have second practitioner independently check original order, dose calculations, concentration, route of administration, and infusion pump settings. IM, Subcut: Medication can cause irritation of tissue. Rotate injection sites to prevent tissue necrosis. Massage injection sites well after administration to enhance absorption and to decrease local vasoconstriction. Avoid IM administration in gluteal muscle. Drug Furosemide RO P D P 30-60 1-2 6-8 O min hr hr I 10-30 UK 4-8 M min N hr I 5 min 30 2 hr V min Action - Target ADVERSE/se: loop diuretic/inhibits APLASTIC ANEMIA, the reabsorption of AGRANULOCYTOSIS, sodium an dchloride dehydration, from the loop of hypochloremia, Henle and distal renal hypokalemia, tubule. Increases hypomagnesemia, renal excretion of hyponatremia, water, sodium, hypovolemia, metabolic chloride, Mg, K, Ca. alkalosis. Dose Edema PO 20-80 mg/day sinele dose, may repeat 6-8hr, may increase by 20-40 mg q 6-8 hr until desired response. hypertension – 40 twice daily initially Hypercalcemia – 120 mg/day in 1-3 doses May be taken w/food/milk to reduce GI irritation. IM, IV 20-40mg Nursing Implications: NSAIDS decrease effects. Many commopn drug interactions-check book! Assess fluid status, weight, I/O amount/location of edema, lung sounds, skin Turgor and mucous membranes. BP, P before and after. Assess fall risk in geriatrics. Assess for tinnitus and hearing loss. Lab Test Considerations: Monitor electrolytes, renal and hepatic function, serum glucose, and uric acid levels before and periodically throughout therapy. Commonly ↓ serum potassium. May cause ↓ serum sodium, calcium, and magnesium concentrations. May also cause ↑ BUN, serum glucose, creatinine, and uric acid levels. Caution patient to change positions slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension. Advise diabetic patients to monitor blood glucose closely; may cause increased blood glucose levels.