Part A: Male Reproductive System
advertisement

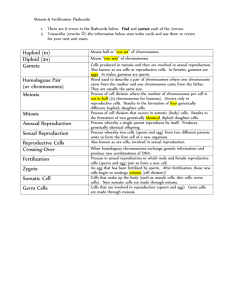
Name: ____________________________________________ Unit 13: Reproductive System Per. ___ Part A: Male Reproductive System testes scrotum urethra penis ejaculation Part B: Female Reproductive System ovaries o follicles o ovulation fallopian tubes uterus cervix vagina Part C: Menstrual Cycle menstruation negative feedback mechanism Part D: Fertilization and Development fertilization zygote differentiation placenta umbilical cord prenatal care fraternal twins identical twins 1 female male gonad hormones ovaries estrogen & progesterone testes testosterone secondary sex characteristics development of breasts changes in body form growth of body hair growth of beard and body hair changes in body form lowered voice pitch Part A: Male Reproductive System production of sperm deposition of sperm inside the female reproductive tract testes- production of sperm scrotum sac that holds testes outpocketing of the abdominal wall keeps testes one or two degrees cooler than normal body temperature lower temperature necessary for sperm production and storage tubes to the urethra penis glands secrete fluids provide perm with proper alkaline pH (basic) & glucose for energy sperm able to swim (adaptation for life on land) semen- fluid + sperm ejaculation- process by which sperm pass out of the body 2 gametes eggs sperm Part B: Female Reproductive System produce eggs site of fertilization & embryonic development ovaries- production of eggs follicles- tiny cavities surrounded by cells ovulation- release of a mature egg from a follicle fallopian tube (oviduct) uterus- development of embryo cervix- lower end of uterus vagina- muscular tube receives semen during intercourse Part C: The Menstrual Cycle series of events that prepare the uterus for pregnancy lining of uterine wall thickens and fills with blood vessels uterine lining breaks down and gets expelled from body during menstruation four stages o follicle stage o ovulation o corpus luteum stage o menstration controlled by different hormones secreted by the pituitary gland & the ovaries o negative feedback mechanism cycle stops during pregnancy 3 Practice: 1. The diagram represents the human male reproductive system. Which 1. 2. 3. 4. activity would be prevented by blockages at X and Y? transport of urine out of the body passage of testosterone to the female to stimulate egg production movement of sperm out of the body movement of testosterone to the testes to stimulate sperm production 2. The diagram represents a system in the human body. The primary function of structure X is to 1. produce energy needed for sperm to move 2. provide food for the sperm to carry to the egg 3. produce and store urine 4. form gametes that may be involved in fertilization 3 The diagram below represents structures found in a human female. Which X? 1. 2. 3. 4. process results in the formation of structure mitosis meiosis recombination cloning 4. The human female reproductive system is represented in the diagram to the right. Production of gametes and support of the fetus normally occur in structures 1. 1 and 2 2. 2 and 4 3. 3 and 5 4. 4 and 5 5. Which hormones most directly influence the uterus during pregnancy? 1. testosterone and insulin 2. progesterone and testosterone 3. estrogen and insulin 4. progesterone and estrogen 4 6. The diagram represents the human female reproductive system. Exposure to radiation or certain chemicals could alter the genetic information in the gametes that form in structure 1. A 2. B 3. C 4. D 7. As women age, their reproductive cycles stop due to decreased 1. digestive enzyme production 2. production of ATP 3. levels of specific hormones 4. heart rate Base your answers to 8 through 11 on the diagram. 8. In humans, which structures are normally presented in pairs? 1. structures A, C, K, and I 3. structures D, E, G, and H 2. structures B, D, J , and H 4. structures F, C, I , and G 9. Ovulation occurs within 1. structure G 2. structure I 3. structure H 4. structure J 10. Which structure provides the optimum temperature for sperm production? 1. structure A 3. structure G 2. structure F 4. structure D 11. Hormones that regulate the development of secondary sex characteristics are produced within 1. structures E and G 3. structures F and J 2. structures C and K 4. structures A and H 12. Gamete cells are produced within 1. structures A and J 2. structures B and I 3. structures E and G 4. structures D and H 5 Part D: Fertilization and Development pregnancy/ prenatal development- period of time before birth sexual intercourse penis transfers sperm into the vagina sperm cells swim through the female reproductive tract and enter the oviducts (fallopian tubes) sperms meet egg and may fuse fertilization- fusion of sperm cell nucleus & an egg cell nucleus zygote- fertilized egg if egg is not fertilized within about 24 hours after ovulation, it breaks down and disappears cleavage begins in fallopian tube (rapid cell divisions) embryo implants in the thickened, spongy uterine wall 6 to 10 days later differentiation- changing of unspecialized cells into specialized cells/tissues/organs developing embryonic membranes become part of the placenta and umbilical cord o embryo able to obtain nutrients and oxygen, get rid of metabolic wastes o materials exchanged between fetal & maternal blood through diffusion o NOT exchange of blood gestation- time between fertilization of egg and the birth o humans- approximately 9 months, or 266 days 6 8 weeks after development of embryo… you now have a fetus! prenatal care o low birth weight, fetal alcohol syndrome and other birth defects caused by: alcohol tobacco drugs baby forced from the uterus by muscular contractions controlled by a hormone from pituitary gland Multiple Births fraternal twins- two eggs are released at one time, each fertilized by different sperm identical twins- from one zygote that separates in half early in cleavage What I MUST know because I care about doing well: Male Reproductive System 1. be familiar with the front and side views 2. testes- produce sperm (meiosis) 3. urethra has both reproductive & excretory functions 4. how sperm is released Female Reproductive System 1. be familiar with the front and side views 2. ovaries- produce eggs (meiosis) 3. fallopian tube- site of fertilization 4. uterus- develops fetus 5. how egg travels 7 Development zygote- single cell when sperm + egg combine (fertilization… restore chromosome number) zygote starts going through mitosis (cell division) and eventually develop organs (differentiation) since we started off with a single cell, all our cells in our body has the same exact DNA you get different kinds of cells because some genes are turned on, some are turned off! (gene expression) fetus gets nutrients & gets wastes removed through the placenta (diffusion) mother & fetus’ blood don’t get exchanged directly alcohol, tobacco, and drugs can cause low birth weight Practice: 1. Which sequence represents the order of some events in human development? 1. zygote → sperm → tissues → egg 3. zygote → tissues → organs → fetus 2. fetus → tissues → zygote → egg 4. sperm → zygote → organs → tissues Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below which represents some stages in the development of an embryo. 2. The arrow labeled X represents the process of 1. meiosis 2. recombination 3. differentiation 4. cloning 3. If cell A has 46 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will most likely be found in each cell of stage G? 1. 23 2. 46 3. 69 4. 92 4. Essential materials needed for development are transported to a human fetus through the 1. reproductive hormones 3. placenta 2. egg cell 4. ovaries 5. German measles is a disease that can harm an embryo if the mother is infected in the early stages of pregnancy because the virus that causes German measles is able to 1. be absorbed by the embryo from the mother’s milk 2. be transported to the embryo in red blood cells 3. pass across the placenta 4. infect the eggs 6. A pathogen passing from a mother to her fetus could cause 1. a decrease in the chromosome number of the fetus 2. an increase in milk production in the mother 3. gamete production to increase 4. an infection in the fetus 7. In most mammals, the placenta is essential to the embryo for the processes of 1. meiosis and excretion 3. nutrition and excretion 2. milk production and digestion 4. blood exchange and digestion 8 8. Which situation involves a risk to a fetus due to the mother smoking during pregnancy? 1. decreased digestive activity in the stomach of the fetus 2. a decrease in the amount of oxygen in the ovary of the mother 3. inhalation of secondhand smoke by the fetus 4. toxins in the bloodstream of the mother 9. The diagram represents a process that occurs during normal human development. Which 1. 2. 3. 4. statement is correct regarding the cells and DNA? All the cells have identical DNA. The DNA of the fertilized egg differs from the DNA of all the other cells. The DNA of the fertilized egg differs from some, but not all, of the other cells. Only the fertilized egg contains DNA. 10. All cells in an embryo have the same DNA. However, the embryonic cells form organs, such as the brain and the kidneys, which have very different structures and functions. These differences are the result of 1. having two types of cells, one type from each parent 2. rapid mitosis causing mutations in embryo cells 3. new combinations of cells resulting from meiosis 4. certain genes being expressed in some cells and not in others 11. Research has shown that certain body cells, known as stem cells, can develop into a variety of specialized cells. Various factors can cause stem cells to develop into different types of mature cells. These different types of mature cells result from 1. different antibodies and mitotic cell division 2. identical genetic codes and meiotic cell division 3. different environments of the cells and the functioning of different parts of the genetic code 4. similar steps in the development of the cells and a reduction in the number of chromosomes in each cell 12. The characteristics of a developing fetus are most influenced by 1. gene combinations and their expression in the embryo 2. hormone production by the father 3. circulating levels of white blood cells in the placenta 4. milk production in the mother 13. The reproductive cycle of a human is usually regulated by 1. gametes 2. hormones 3. natural selection 4. immune responses 14. Which reproductive structure is correctly paired with its function? 1. uterus - usual site of fertilization 3. testis - usual location for egg development 2. ovary - delivers nutrients to the embryo 4. sperm - transports genetic material 15. The human brain, kidney, and liver all develop from the same zygote. This fact indicates that cells formed by divisions of the zygote are able to 1. differentiate 2. mutate 3. undergo cloning 4. be fertilized 16. The process of meiotic cell division in a human male usually forms 1. one diploid cell, only 2. four diploid cells 3. one monoploid cell, only 4. four monoploid cells 9 17. The development of an embryo is represented in the diagram. These changes in the form of the embryo are a direct result of 1. uncontrolled cell division and mutations 2. differentiation and growth 3. antibodies and antigens inherited from the father 4. meiosis and fertilization 18. A temporary suspension of the menstrual cycle normally occurs during 1. menstruation 3. pregnancy 2. ovulation 4. menopause 19. The diagram represents processes involved in human reproduction. Which row in the chart below correctly identifies the processes represented by the letters in the diagram? Row A B C D 1. mitosis meiosis fertilization differentiation 2. meiosis meiosis fertilization differentiation 3. meiosis mitosis differentiation fertilization 4. mitosis differentiation mitosis fertilization Base your answers to questions 20 through 22 on the diagram below. 20. Which structures secrete hormones that regulate the development of secondary sex characteristics? 1. A and J 2. F and I 3. D and H 4. E and G 21. After sperm cells are deposited inside the female, the pathway they follow to reach the egg is 1. H to I to K 2. J to K to H 3. K to I to H 4. G to H to I 22. Which structures in the diagrams are directly affected by hormones involved in the menstrual cycle? 1. C and E 2. A and D 3. G and I 4. I and J 10