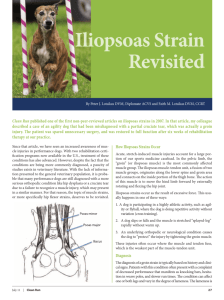
Iliopsoas Muscle
advertisement

Groin and Low back Pain Caused by the Iliopsoas Muscle By Juliette Woodruff The term iliopsoas refers to a group of muscles which primarily bend the hip. Iliopsoas is comprised of three muscles: the psoas major, psoas minor, and iliacus. These muscles attach to both the spine and thigh bone and work in opposition to the gluteal (buttock) muscles. These muscles in balance provide the basic strength required for hip movement activities like walking, as well as playing a significant role in maintaining upright posture. Tightness or shortening of this muscle can produce groin, and low back pain, as well as creating a series of other symptoms. What causes iliopsoas pain? An overactive iliopsoas muscle: When your spine and legs are continuously in a flexed position (e.g., sitting at a desk or in a vehicle for prolonged periods of time or from repeatedly lifting heavy objects, etc.) the iliopsoas muscle may shorten and the gluteal muscles at the back of the hip may stretch. Pain is caused from the over activity in the iliopsoas muscle and the alterations to the body’s movement patterns resulting in a variety of musculoskeletal conditions. Iliacus Tunnel Syndrome: This usually occurs after surgery to the pelvis (e.g. hernias, etc.) causes a shortening of the muscles (contracture) and a build up of scar tissue in the iliopsoas muscle. Sometimes this scar tissue can trap the femoral nerve and cause iliacus tunnel syndrome causing feeling to be lost from the inner thigh down to the foot. If may also become difficult to straighten the knee due to a lack of strength in the thigh muscles. Meralgia Paresthetica: is a condition that irritates the sensory nerve called the Lateral Cutaneous. This results in a loss of sensation or burning along the outer aspect of the thigh. Tight clothing, direct trauma (e.g. seat belt trauma), abdominal surgery, obesity, or deep bruising are all common causes which can lead to a shortening of the iliopsoas muscle (contracture) and tension on the Lateral Cutaneous nerve. Over the long term compression of this nerve can cause skin changes as well as a loss of hair on the affected leg. What are symptoms of an over active iliopsoas muscle? Pain in your groin area when executing thigh muscle intensive activities (e.g., walking, hockey, soccer, running, gymnastics, ballet, etc.) Pain across your back or down the front of your leg A feeling of heaviness in your legs Clicking or pain in your groin Difficulty straightening your leg Pain after sitting for long periods of time How should iliopsoas pain be treated? Physiotherapy and massage treatment are beneficial to rehabilitate the gluteal muscles and to reduce the reoccurrence of tight psoas muscle. Exercises should be directed at building the abdominal muscles to stabilize the spine. Massage therapy assists in the rehabilitation although injury occurs due to an imbalance of structures, strengthening the muscles that are weak are an essential part of recovery. The specific structures which should be addressed are dependant on the condition and the strength of the muscles. Treatment of a tight Iliopsoas can also benefit other conditions (e.g., degenerative disc disease, lordosis, scoliosis, faulty posture, etc.). The lengthening of this muscle helps to re-align the spine, allowing the hip to extend more fully and to reduce faulty posture. Massage can aid in a quicker recovery from injury and decrease pain. It allows the client to perform exercises in less discomfort which enables them to move better and have an increase in range due to the lengthening of the tissue. Massage therapy can also allow the muscle to gain power if the trigger points (irritable area within a muscle) are worked out of the muscle. Many athletes as well as other clients can get a physiological aspect to their injuries such as depression which will have a negative impact on their healing process. Massage therapy treatments aid in reducing stress and improving tissue quality. is beneficial to enhance circulation to assist in the healing process, increase range of motion, decrease pain and reduce adhesion formation in the injured tissue. For further information on massage therapy and iliopsoas treatment please contact Juliette Woodruff R.M.T who has over five years experience.