What is ecology activity guide
advertisement

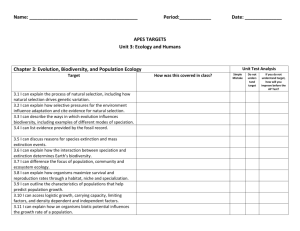
Unit 1: Introduction to Sustainability What is ecology? activity guide Developed by This project was funded by the Department of Sustainability and Environment. This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 Australia licence. This information pack is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 Australia licence. A copy of this licence is available at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.5/au/Page or by 1 writing of 5 to info@creativecommons.org.au. However logos are protected by copyright Unit 1: Introduction to sustainability ‘What is ecology?’ activity guide Estimated duration: 25 minutes Aim To develop a definition of ecology and biodiversity based on students’ existing knowledge, instinct and guess work. Outcome By the end of this session, students will: Develop a basic understanding of ecology and its role in environmental sustainability Consider the role of biodiversity in sustainable communities Resources Whiteboard Texta PowerPoint presentation: “What is ecology?” Activity description 1. Wood chipper brainstorm Teacher asks: How many people here are familiar with the term ‘ecology’? How many people know what ecology means? Ask students to form pairs. I am going to allocate you two minutes to work in pairs to develop a definition of what you think ecology is. If you don’t know then make a definition of what you feel it might be – your gut instinct…. To give them a hint write it on the board and underline ecology After two minutes, invite students to return to the main group with their definition. Page 2 of 5 Teacher explains: I am going to work like a wood chipper. I’m going to collect your definition and put it in the chipper. It will then be broken down into key words or terms that are pitched upon the board. Teacher collates the key words on the board, while reinforcing students’ individual and shared insight into the concept of ecology. While some of us might be coming to this class with little understanding about environmental concepts or theories, it is interesting to observe how much knowledge we can offer each other. Now tell the students there is a short presentation on this and we should see the words you have come up with 2. PowerPoint Presentation Presenter notes are included below, and also in the notes section of the PowerPoint file. Teacher displays the PowerPoint slide 2 (of a river gum) and explains: Ecology is the study of the living organisms and their environment. The environment of an organism includes both physical properties, such as sunlight, climate and the earth, as well as the other organisms that share its habitat. This ancient river gum provides homes for lots of animals, birds and bugs. It has lived through droughts and floods for hundreds of years. It is part of an ecosystem which has sustained communities of plants, animals, and microorganisms. Nature demonstrates that sustainable systems are possible. Slide 3: River gum branch Teacher explains: There is no “waste” in nature. Everything that is produced and discarded by one organism is used up gratefully by something else. We need to try to make human systems mimic natural systems. The ants and termite here use the wood as food. And other animals use the hollow as a home. Slide 4: No individual organism can exist in isolation Animals depend on the photosynthesis of plants for their energy needs; plants depend on the carbon dioxide produced by animals and on the nitrogen fixed by bacteria at their roots. Together plants, animals and microrganisms regulate the entire biosphere and maintain conditions conductive to life. This is a profound lesson we need to learn from nature. Page 3 of 5 Slide 5: Biodiversity – coral reefs A diverse ecosystem is one with lots of different types of plants, animals and organisms. A diverse ecosystem will be a resilient one because it contains many species with overlapping ecological functions that can partially replace one another if one dies out or is affected by changing conditions. When a particular species is destroyed by a severe disturbance a diverse community will be able to survive because other links can at least partially fulfil the function of the destroyed species. Slide 6: Biodiversity – mangroves There are many types of different systems that suit different areas. Mangroves have adapted to suit the area they are located in. Slide 7: Biodiversity – arid zones As have plants and animals in the bush and desert regions. Slide 8: Biodiversity – cities? Do cities have biodiversity? Depending on what you look at they do. Naturewise it might be limited but in terms of things made by humans, you could say it does. There are lots of different types of buildings to suit different uses. There are different types of shops, types of work. Slide 9: Human biodiversity In human communities, ethnic and cultural diversity may play a similar role to biodiversity in an ecosystem. Diversity means that many different relationships, values and experiences can offer many different approaches to the same problem. Values, knowledge, language, and world views associated with culture impact on the way issues connected to sustainability are dealt with in a community context. So sharing stories from the each other creates an opportunity for us to think critically about the factors that shape our vision and expectations of the future. Slide 10: Monoculture On the other hand communities lacking diversity remain vulnerable to destruction if a pest threatens a single species. For example a monoculture such as wheat or corn can be wiped out within hours. So it is important that we have diversity. As we begin to learn more about the environment we will get to see that one size does not fit all. When things are going well it is because a number of different groups work together, not apart. That when one thing fails there is something similar to come along and take its place. But if we disrupt the environment too much we lose that diversity and the ability to bounce back. We begin to put all our eggs in one basket. Page 4 of 5 Student Roles and Responsibilities Participate in agreed tasks Contribute to class discussions Level of Teacher Support Facilitate discussion Organise materials and equipment Present slideshow Assessment To use these learning activities as assessment tasks, collect evidence such as: Teacher checklist and observation Student research notes and report Copies of student materials and worksheets Student notes Page 5 of 5