Elementary French
advertisement

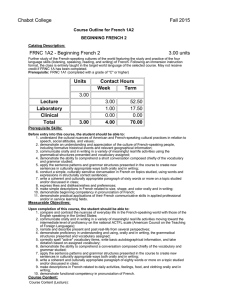
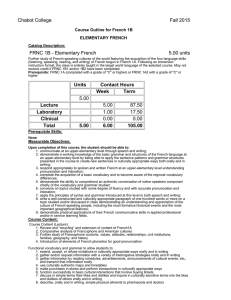
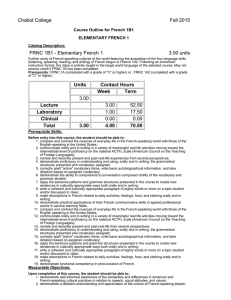
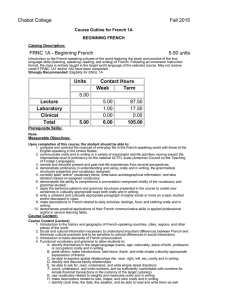
Chabot College Fall 2009 Replaced Fall 2010 Course Outline for French 1B ELEMENTARY FRENCH Catalog Description: 1B – Elementary French 5 units Further study of French-speaking cultures of the world featuring the acquisition of the four language skills (listening, speaking, reading, and writing) of French begun in French 1A. Prerequisite: French 1A (completed with a grade of “C” or higher). 5 hours lecture, 1 hour laboratory. [Typical contact hours: lecture 87.5, laboratory 17.5] Prerequisite Skills: Before entering the course the student should be able to: 1. compare and contrast American and French-speaking cultural practices in relation to speech, social attitudes, and values; 2. demonstrate an understanding and appreciation of the culture of French-speaking people, including formative historical events and relevant geographical information; 3. demonstrate proficiency in understanding and using, orally and in writing, the grammatical structures listed in the French 1A course outline; 4. correctly spell common vocabulary to write basic autobiographical information and simple dialogues; 5. demonstrate the ability to comprehend short conversations on common topics; 6. apply the sentence patterns and grammar structures presented in French 1A to create new sentences in culturally appropriate ways both orally and in writing; 7. conduct a simple, culturally sensitive conversation in French on everyday topics, using words and expressions in structurally correct sentences; 8. write a coherent and culturally appropriate paragraph of sixty words or more on a topic studied and/or discussed a first semester French class; 9. make simple descriptions in French related to size, shape, and color orally and in writing; 10. pronounce his or her French sufficiently well to be understood by a sympathetic native listener. Expected Outcomes for Students: Upon completion of the course the student should be able to: 1. demonstrate well-informed awareness of the similarities and differences in American and Frenchspeaking cultural practices in relation to speech, social attitudes, and values; 2. demonstrate a detailed understanding and appreciation of the culture of French-speaking people, including the most formative historical events and the most important geographical features; 3. demonstrate the ability to comprehend an authentic conversation of native speakers composed chiefly of the vocabulary and grammar studied; 4. show proficiency in applying the sentence patterns and grammar structures presented in the course to create new sentences in culturally appropriate ways both orally and in writing 5. converse on topics studied with some degree of fluency and with accurate pronunciation and intonation; 6. apply the principles of syntax and grammar introduced at this level in both speech and writing; 7. write a well-constructed and culturally appropriate paragraph of one hundred words or more on a topic studied and/or discussed in class. Course Content (Lecture): 1. Review “recycling” and extension of content of French1A 2. Development of conversation skills 3. Functional vocabulary and grammar to allow students to: a. extend, accept, or refuse invitations in culturally appropriate ways orally and in writing b. gather and/or request information with a variety of interrogative strategies orally and in writing c. gather information by reading schedules, advertisements, announcements of cultural events, etc., and transmit that information orally d. use culturally authentic maps and timetables e. make purchases in stores and perform transactions in culturally appropriate ways Chabot College Course Outline for French 1B, Page 2 Fall 2009 f. function successfully in basic cultural interactions that involve buying tickets g. discuss in simple terms their likes and dislikes and inquire in culturally sensitive terms into the likes and dislikes of others orally and in writing h. describe, orally and in writing, simple physical ailments to pharmacists and doctors i. narrate simple events in past, present, and future orally and in writing j. make physical descriptions of people and things orally and in writing 4. The following aspects of French grammar: a. the irregular verbes dire, lire, écrire, savoir, connaître, ouvrir, couvrir, découvrir, offrir, souffrir, vivre, suivre, conduire, construire, détruire, produire, réduire, and traduire. b. the imperfect, past perfect (plus-que-parfait), and future tenses of verbs and their present conditional mood and present and past subjunctive mood. c. verb complements used with prepositions (the construction conjugated verb + preposition + infinitive) d. the sequence of tenses and moods associated with “if” (si) clauses e. direct and indirect discourse f. the negative constructions ne… rien, ne… personne, rien… ne, and personne… ne g. the uses of depuis and pendant with appropriate complements h. impersonal expressions followed by infinitives i. the formation and placement of adverbs j. the comparative and superlative forms of adjectives and adverbs k. use of prepositions with geographical nouns l. relative pronouns and clauses m. demonstrative pronouns 5. An introduction to French phonetics that includes accentuation, rhythm, linking (la liaison), and the schwa (l’e instable). Course Content (Laboratory): 1. Activate lecture content using interactive audio and audiovisual programs on CDs, DVDs, CD ROMS, target language websites, etc., featuring culturally authentic and contextual guided speaking, reading, and writing activities such as cued repetition of native speech, dictations, cued oral responses, listening comprehension, and interactive realia (culturally authentic texts). 2. Organized laboratory activities including conversation groups. 3. Fundamentals of pronunciation: a. The consonant /R/ (all symbols between slashes are International Phonetic Alphabet symbols) b. The consonants /s/, /z/, /∫/, and /j/ (voiced /∫/) c. Aspirated and non-aspirated h d. The consonant /nj/ (spelled gn) e. The consonant /l/ (French light l contrasted to English light and heavy l’s) f. Liaison: required, optional, and forbidden g. Interrogative inflection. h. The schwa (the silent e, or l’e instable) and the law of three consonants i. accentuation j. equality of rhythm Methods of Presentation: 1. 2. 3. 4. Lecture/discussion in target language Choral/individual repetition of model speech Re-creation of dialogues and improvisation Small group activities leading to skits, dialogues, etc. Assignments and Methods of Evaluating Student Progress: 1. Typical Assignments a. Prepare a skit in which one person accepts an invitation and the other declines an invitation; both use culturally appropriate expressions curriculum 0809 dk 11/12/08 Chabot College Course Outline for French 1B, Page 3 Fall 2009 b. Laboratory Assignment: After studying the silent e, make a recording Paul Verlaine's "II pleure dans mon coeur" c. Prepare a travel itinerary to five different French-speaking cities on five different continents to demonstrate proper use of prepositions with numerous geographical names d. Write a composition comparing and contrasting two actors, musicians, athletes or celebrities. 2. Methods of Evaluating Student Progress a. Tests, quizzes, and interviews to evaluate the four language skills in relation to material presented b. Student participation in class activities c. Oral reports (without notes) on geographical regions, French holidays, art, films or an aspect of French popular culture d. Homework assignments e. Recordings from the language laboratory to evaluate pronunciation skills f. Final examination Textbook(s) Typical: Débuts, An Introduction to French, second edition, H. Jay Siskin, Ann Williams, and Thomas T. Field, McGraw Hill, 2007. Workbook/Laboratory Manual Part 1 to accompany Débuts: An Introduction to French, second edition, H. J. Siskin, Anne Williams, Nancy Virtue, and Elise C. Leahy, Jr., McGraw-Hill 2007. Special Student Materials: None curriculum 0809 dk 11/12/08