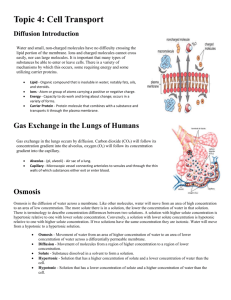
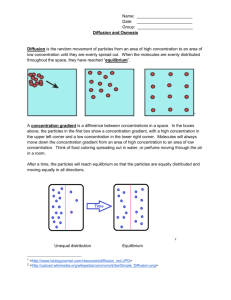
Osmosis Bingo Q & A
advertisement
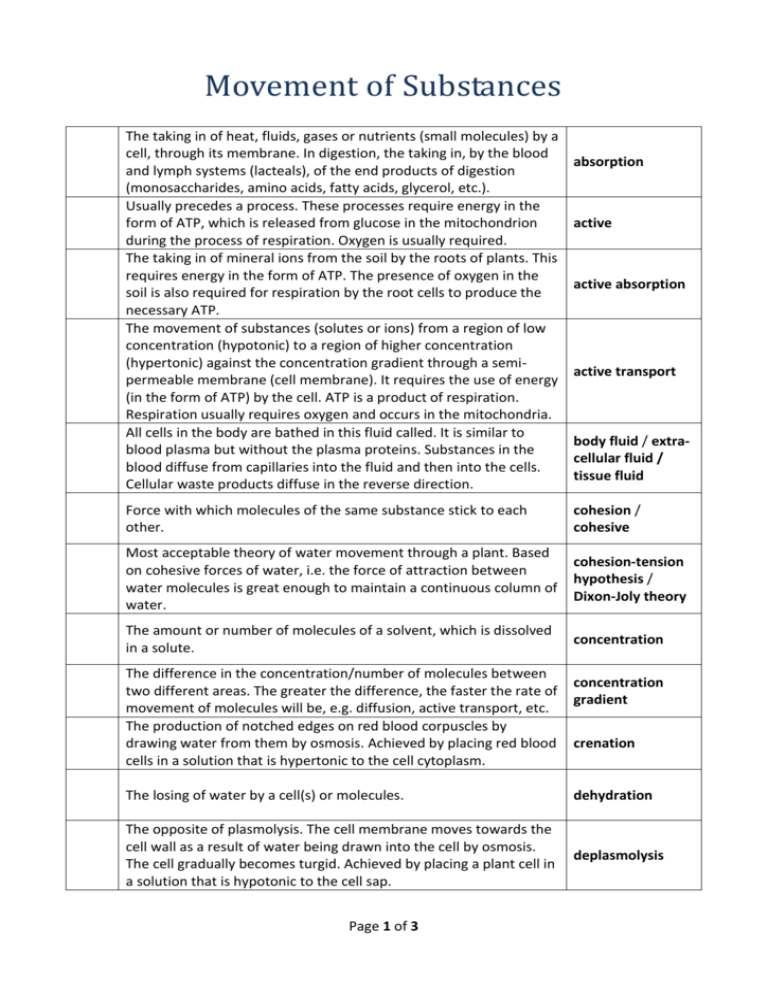
Movement of Substances The taking in of heat, fluids, gases or nutrients (small molecules) by a cell, through its membrane. In digestion, the taking in, by the blood and lymph systems (lacteals), of the end products of digestion (monosaccharides, amino acids, fatty acids, glycerol, etc.). Usually precedes a process. These processes require energy in the form of ATP, which is released from glucose in the mitochondrion during the process of respiration. Oxygen is usually required. The taking in of mineral ions from the soil by the roots of plants. This requires energy in the form of ATP. The presence of oxygen in the soil is also required for respiration by the root cells to produce the necessary ATP. The movement of substances (solutes or ions) from a region of low concentration (hypotonic) to a region of higher concentration (hypertonic) against the concentration gradient through a semipermeable membrane (cell membrane). It requires the use of energy (in the form of ATP) by the cell. ATP is a product of respiration. Respiration usually requires oxygen and occurs in the mitochondria. All cells in the body are bathed in this fluid called. It is similar to blood plasma but without the plasma proteins. Substances in the blood diffuse from capillaries into the fluid and then into the cells. Cellular waste products diffuse in the reverse direction. absorption active active absorption active transport body fluid / extracellular fluid / tissue fluid Force with which molecules of the same substance stick to each other. cohesion / cohesive Most acceptable theory of water movement through a plant. Based on cohesive forces of water, i.e. the force of attraction between water molecules is great enough to maintain a continuous column of water. cohesion-tension hypothesis / Dixon-Joly theory The amount or number of molecules of a solvent, which is dissolved in a solute. concentration The difference in the concentration/number of molecules between two different areas. The greater the difference, the faster the rate of movement of molecules will be, e.g. diffusion, active transport, etc. The production of notched edges on red blood corpuscles by drawing water from them by osmosis. Achieved by placing red blood cells in a solution that is hypertonic to the cell cytoplasm. concentration gradient crenation The losing of water by a cell(s) or molecules. dehydration The opposite of plasmolysis. The cell membrane moves towards the cell wall as a result of water being drawn into the cell by osmosis. The cell gradually becomes turgid. Achieved by placing a plant cell in a solution that is hypotonic to the cell sap. deplasmolysis Page 1 of 3 The movement of solute from a region of high solute concentration to a region of lower solute concentration. No permeable or semipermeable membrane is necessary for this process to occur. No diffusion energy used by the cell in this process, i.e. it is passive. Examples are: gaseous exchange in alveoli; absorption through villi of small intestine. The bursting of red blood corpuscles with the release of haemoglobin. Achieved by placing red blood corpuscles in a solution, haemolysis which is hypotonic to the cell sap. A solution with a higher solute concentration than the surrounding solution. hypertonic A solution with a lower solute concentration than the surrounding solution. hypotonic Cannot be penetrated by particles of solids or liquids. impermeable A solution with the same solute concentration as another solution. isotonic A special case of diffusion. It is the movement of solvent (always water) from a region of high solvent concentration to a region of lower solvent concentration through a semi-permeable membrane, until both concentrations are equal. No energy used by the cell for osmosis osmosis to take place, i.e. it is a passive process. Examples are: water entering root hair cell; water moving from cell to cell in transpiration. The entry of water into a cell by osmosis exerts an outward pressure. osmotic pressure The pressure necessary to prevent osmosis is ... Not requiring the use of energy, e.g. diffusion and osmosis, or brought about by outside forces. passive The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. No energy is required for the process. (passive) diffusion Movement of substances across the cell membrane which does not involve the use of energy by the cell, e.g. diffusion and osmosis. passive transport Refers to a membrane; allows molecules or ions of a certain maximum size to pass through. The cell wall allows all molecules and ions to pass through irrespective of size. The shrinking of the plasma membrane (cell membrane) away from the cell wall with the loss of turgidity as a result of water being drawn out of the cell by osmosis. This does not normally occur in nature but is achieved by placing a plant cell in a solution, which is hypertonic to the cell sap. A cell will become flaccid before becoming plasmolysed. Page 2 of 3 (fully) permeable plasmolysis Refers to the cell membrane. Allows certain molecules or ions to pass through but prevents others. semi- / selectively / partially permeable e.g. cell membrane, visking tubing. Certain molecules or ions can pass through but others cannot, depending on size. semi-permeable membrane Substance that is dissolved in a liquid. solute A mixture of a solute and a solvent. Solute is the substance that will be dissolved and solvent is the liquid that will do the dissolving, usually water. solution A liquid in which the solute is dissolved. solvent Inflated by pressure from within as a result of water been drawn into the cell by osmosis. Achieved by placing a plant cell in a solution that is hypotonic to the cell sap. Water flows in and is collected in the vacuoles and the cells swell and push out against the cell walls. turgid State of a plant cell due to pressure built up in the cell; exerted outwards and caused by the cell taking in water by osmosis. turgor pressure Pressure exerted inwards by the cell wall in response to turgor pressure. This prevents a plant cell from bursting. wall pressure Page 3 of 3