Public relations competencies
advertisement
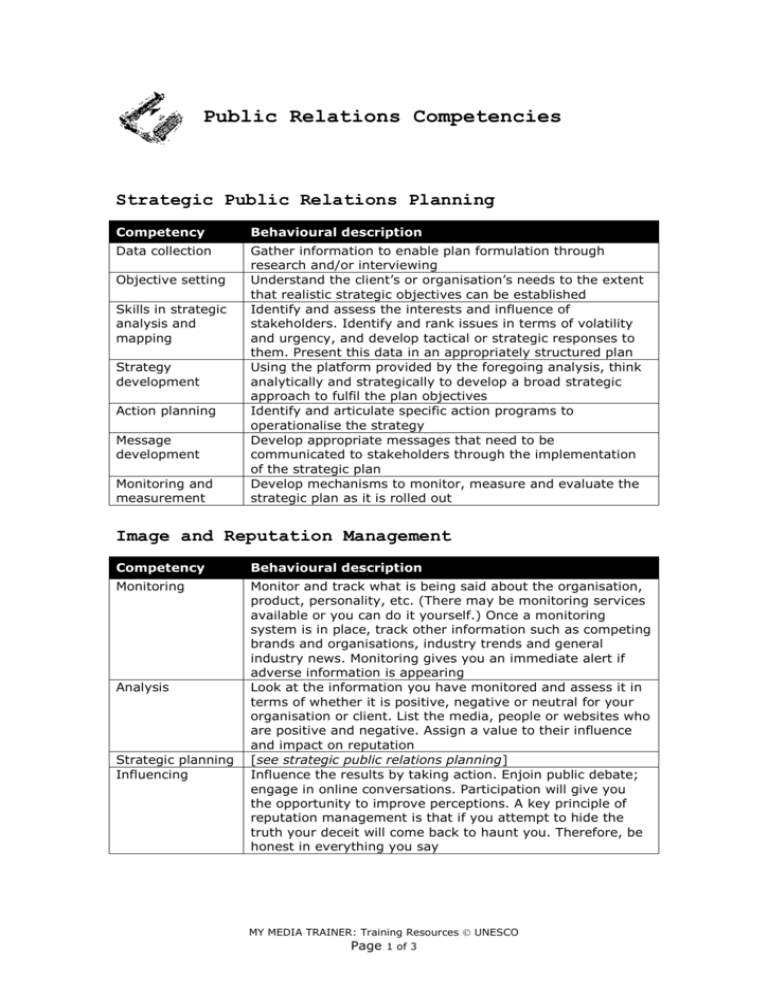
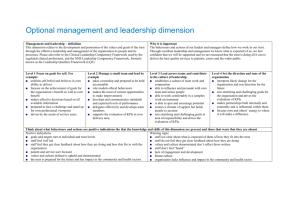
Public Relations Competencies Strategic Public Relations Planning Competency Behavioural description Data collection Gather information to enable plan formulation through research and/or interviewing Understand the client’s or organisation’s needs to the extent that realistic strategic objectives can be established Identify and assess the interests and influence of stakeholders. Identify and rank issues in terms of volatility and urgency, and develop tactical or strategic responses to them. Present this data in an appropriately structured plan Using the platform provided by the foregoing analysis, think analytically and strategically to develop a broad strategic approach to fulfil the plan objectives Identify and articulate specific action programs to operationalise the strategy Develop appropriate messages that need to be communicated to stakeholders through the implementation of the strategic plan Develop mechanisms to monitor, measure and evaluate the strategic plan as it is rolled out Objective setting Skills in strategic analysis and mapping Strategy development Action planning Message development Monitoring and measurement Image and Reputation Management Competency Behavioural description Monitoring Monitor and track what is being said about the organisation, product, personality, etc. (There may be monitoring services available or you can do it yourself.) Once a monitoring system is in place, track other information such as competing brands and organisations, industry trends and general industry news. Monitoring gives you an immediate alert if adverse information is appearing Look at the information you have monitored and assess it in terms of whether it is positive, negative or neutral for your organisation or client. List the media, people or websites who are positive and negative. Assign a value to their influence and impact on reputation [see strategic public relations planning] Influence the results by taking action. Enjoin public debate; engage in online conversations. Participation will give you the opportunity to improve perceptions. A key principle of reputation management is that if you attempt to hide the truth your deceit will come back to haunt you. Therefore, be honest in everything you say Analysis Strategic planning Influencing MY MEDIA TRAINER: Training Resources UNESCO Page 1 of 3 Writing Competency Behavioural description Mechanics of writing Understand aspects of writing through which content is effectively expressed: spelling, grammar, syntax, vocabulary, etc Place related ideas in a meaningful sequence to clarify their logical relationships to one another In response to a stimulus, express thoughts and feelings related to the stimulus. Interpret personal experiences, opinions and values in words Understand through directed attention. Take notes about the observation. Draw conclusions through interpretation of what has been observed Break a whole into its constituent parts so relationships between parts and the whole are understandable and consequences are clarified Provide a concrete example of an abstract concept to clarify or explain it, typically, using an example from every day life Find answers or information using a systematic method of inquiry Support a thesis by presenting a sequence of logically related ideas backed up by relevant and reliable evidence Compare a specific case to an abstract set of principles or standards in order to determine the quality of the case Combine two or more subordinate ideas in a more general idea that unifies them Organisation Reaction Observation Analysis Application Research Argument Criticism Synthesis Public Relations Measurement and Evaluation Competency Behavioural description Planning for research Ensure that specific measurable communications objectives have been set so there is something to measure. Be guided by the basic communications research mantra: who says what, to whom, how and with what effect. Who refers to the sources or disseminators of information; what to the messages being disseminated; to whom to the target audiences; how to the channels of communications; with what effect to the outputs and outcomes of the communications effort Establish research objectives. Identify the group or sample to be researched. Decide content of research. Determine research methodology [see below]. Structure research instrument (questionnaire) and prepare clear and unambiguous questions Somewhat subjective but in-depth studies that use a probing, open-end format. Main forms: focus groups (group under guidance of trained moderator discusses specific topics), depth interviewing (probing, open-ended, structured interviews where respondents talk freely and in detail), convenience poll (unscientific non-probability study sometimes referred to as informal or quick-and-dirty) Research design Understanding qualitative data collection methodologies MY MEDIA TRAINER: Training Resources UNESCO Page 2 of 3 Understanding quantitative data collection methodologies Measuring communications outputs Measuring institutional outcomes To obtain highly objective insight, use closed-end, forcedchoice questionnaires. These studies tend to rely heavily on statistics and numerical measures. Collect data by email, websites, mail, face-to-face interviews or panels Know how to measure outputs which are the results of a communications program. They measure how well an organisation presents itself or the amount of exposure it receives. Outputs also might be an assessment of a specific event, a direct mail campaign, the number of people who participated in an activity, how an organisation’s executives are perceived or the appearance and contents of a brochure Relate communications outputs to institutional goals such as increasing market penetration, improving market share, meeting recruitment expectations, etc MY MEDIA TRAINER: Training Resources UNESCO Page 3 of 3