5. Mendelian Genetics II
advertisement

Biology 212 General Genetics
Spring 2007
Lecture 5: "Mendelian Genetics II"
Reading: Chap. 3 pp. 45-51
Lecture outline:
1. Dihybrid cross
2. Mendel’s law of independent assortment
3. Chromosomal basis of heredity
Lecture:
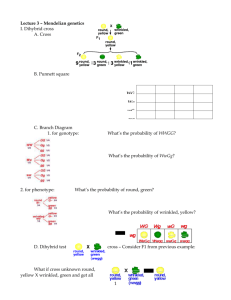
1. Dihybrid cross
Cross between individuals varying in two characters
How are two traits inherited?
Trait 1: Seed color
Yellow=G
Green=g
Trait 2: Seed shape
Round=W
Wrinkled=w
Cross: P1 true-breeding round yellow x
true-breeding wrinkled green
F1 round yellow x F1 round yellow
F2
Round yellow
Round green
Wrinkled yellow
Wrinkled green
#
315
108
101
32
See Fig. 2.12
Round is dominant to wrinkled
Yellow is dominant to green
P1
WWGG
x
wwgg
1
fraction
9/16
3/16
3/16
1/16
ratio
9
3
3
1
F1
F2
WwGg
WG
WWGG
WWGg
WwGG
WwGg
WG
Wg
wG
wg
x
WwGg
Wg
WWGg
WWgg
WwGg
Wwgg
wG
WwGG
WwGg
wwGG
wwGg
wg
WwGg
Wwgg
wwGg
wwgg
F2 progeny
Genotypes
1/16
2/16
2/16
4/16
WWGG
WWGg
WwGG
WwGg
Phenotypes
9/16 round yellow
1/16 wwGG
2/16 wwGg
3/16 wrinkled yellow
1/16 WWgg
2/16 Wwgg
3/16 round green
1/16 wwgg
1/16 wrinkled green
Figures 2.11 and 2.12
How does this experiment demonstrate Mendel's laws of
(1) segregation
(2) independent assortment
Principle of Segregation: The two alleles for a gene are separated during gamete
formation.
W separates from w
G separates from g
2. Principle of Independent Assortment: Two genes and their alleles assort
independently in gamete formation.
Behavior of W/w gene is independent of G/g gene.
Testcrosses can be used to show the result of independent assortment.
2
Testcross: Cross with homozygous recessive individual to determine how one or
more genes are inherited.
Cross F1 heterozygote (dihybrid) with homozygous recessive
F1
WwGg
x
wwgg
F2 progeny:
wg
WwGg
Wwgg
wwGg
wwgg
WG
Wg
wG
wg
1/4 round yellow
1/4 round green
1/4 wrinkled yellow
1/4 wrinkled green
Fig. 2.14
3. Probability
Use of principles of probability for solving genetics problems.
Addition Rule: The probability of one or the other of two mutually exclusive
probabilities is the sum of their probabilities.
Example: For cross
Round
Ww
x
Round
Ww
What is probability of the round phenotype in F1 generation?
Round offspring can be WW and Ww
Probability {WW or Ww} = Prob. WW + Prob. Ww
= 1/4 + 1/2 = 3/4
Multiplication Rule: The probability of two independent events occurring
simultaneously is the product of their separate probabilities.
Examples of independent events. Fig. 2.16
(1) independent segregation of alleles
In cross of two round heterozygotes
Ww
3
x
Ww
Ww gametes are 1/2 W
and
1/2 w
Probability of genotypes is product of allele probabilities
1/2 W x 1/2 W
1/2 W x 1/2 w
1/2 w x 1/2 W
1/2 w x 1/2 w
=
=
=
=
1/4 WW
1/4 Ww
1/4 wW
1/4 ww
(2) each offspring is due to an independent fertilization event
probability of a girl
probability of a boy
= 1/2
= 1/2
probability of having 5 girls = 1/2 x 1/2 x 1/2 x 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/32
4
½ Ww