What the assessment focuses mean in practice
advertisement

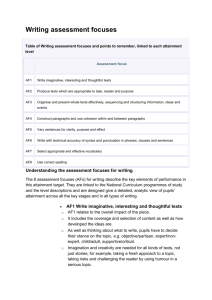
What the assessment focuses mean in practice Some pairings of the assessment focuses can be helpful when looking for evidence, for example AF3&4; AF5&6; AF7&8. However when making a judgement of pupils’ overall attainment in writing, you need to consider how all the different strands combine to make an effective piece when judged against the criteria for AF1&2. AF1 Write imaginative, interesting and thoughtful texts This AF relates to the overall impact of the piece. It includes the coverage and selection of content and how well thought out the ideas are. Imagination and creativity are needed for all kinds of texts, not just stories; for example, taking a fresh approach to a topic taking risks and challenging the reader by using humour in a serious topic. Pupils need opportunities to develop as independent writers, choosing topics, forms and purposes that interest them. AF2 Produce texts that are appropriate to task, reader and purpose This AF covers adaptation, viewpoint and style. Pupils need to be set tasks that prompt them to make use of their knowledge of different text types in adventurous ways (adaptation). In refining their purposes pupils need to decide their stance on the topic eg objective/partisan, expert/non expert, child/adult, supportive/critical (viewpoint). Help pupils to understand how specifying a ‘reader’ suggests they need to make decisions about eg levels of formality, choice of vocabulary, form of writing (style). AF3 Organise and present whole texts effectively, sequencing and structuring information, ideas and events This AF is about the overall coherence of texts and includes layout, use of subheadings, pictures in print and digital texts. There are underlying ways to think about text organisation in non-fiction eg logical order, chronology, moving AF4 from general to specific points. There are similar choices in fictional writing – strict chronology is not always needed. In stories, endings matter – both plot and theme have to be resolved. Information texts also need endings, whether these are signalled by the last in a series of numbers or by a brief conclusion. Construct paragraphs and use cohesion within and between paragraphs This AF is about the ways paragraphs hang together as a sequence as well as connect internally. Within paragraphs, pupils should try different ways of developing topics within paragraphs, grouping related content, developing details around main ideas, writing topic sentences. Pupils need to experiment with different ways to make links between paragraphs, eg by time, by reason, by subject, by importance. AF5 Vary sentences for clarity, purpose and effect This AF is about the purposeful variation of sentence structure. More able writers use varied sentence structures as a way of packaging meaning into sentences with little redundancy Pupils need to work on both endings and beginnings in complex sentences to achieve different effects When writing poetry, pupils need to construct and select different types of sentences to fit a rhyme or rhythmic scheme AF6 Write with technical accuracy of syntax and punctuation in phrases, clauses and sentences This AF is about using accurate grammar and punctuation in sentences. Effective punctuation creates clarity and meaning and can be helpfully linked to understanding of grammar. As pupils reach for more complex sentence construction, their punctuation often does not keep pace. AF7 Select appropriate and effective vocabulary This AF is relevant to all kinds of writing and supports the other AFs. Vivid writing, whether fiction and non-fiction, is achieved by choices of nouns, verbs and adverbs, not just adjectives. In non fiction writing, the use of technical and precise vocabulary is vital to conveying content accurately and giving the sense that the writers know what they are talking about. AF8 Use correct spelling This AF is developed in two ways in APP so that distinctions can be made between correct/incorrect spelling of grammatical function words (a small set of items) and the larger pool of content words that carry most of the meaning. In learning to spell, pupils need help with both phonemes and word structure (morphemes). Spelling accuracy is an important focus, but does not necessarily correlate with achievement at sentence and text level.



![afl_mat[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005387843_1-8371eaaba182de7da429cb4369cd28fc-300x300.png)



