Browse through information on these map projection websites:

EPSc 409 Assignment 1. Part 1.
Name:
Assignment 1.
This assignment is intended to make sure everyone is familiar with certain properties of maps. Links to a number of good online sources of information are provided; you may or may not need to consult with them depending on the amount of experience you’ve had..
Map projections: http://go.owu.edu/~jbkrygie/krygier_html/geog_222/geog_222_lo/geog_222_lo13.html http://www.colorado.edu/geography/gcraft/notes/mapproj/mapproj.html
http://www.uncc.edu/lagaro/cwg/mapproj/intro_mp.html
Using UTM coordinates:
Many field scientists use UTM coordinates for plotting locations on maps in the field. Most USGS topographic maps have UTM grids on them, as do many foreign maps. We will mostly use UTM coordinates to refer to points on maps. http://www.maptools.com/UsingUTM/
Reading topographic maps: http://www.cis.ksu.edu/~dha5446/topoweb/guide.html
Map projection questions: (more than one “right” answer possible; just explain your reasoning)
(2) The area of drainage basins is an important variable in geomorphic studies; what projection would you use to make one map on which you could easily measure and compare drainage basin areas for the world’s major rivers (e.g., Mississippi, Yangtze, Amazon, Nile, etc)? Explain.
(2) What if you wanted to make a map which you could use to navigate on Great Lakes in your boat and not get lost?
(4) Go to http://lorenz.mur.csu.edu.au/cgi-bin/gis/Map , and type in 0/40/50/75 for the minimum bounding rectangle and hit “enter” (or the “plot map” button). You should see Scandinavia, with an X-Y plot (default: latitude and longitude values simply plotted on an X-Y grid). Take a look at the shapes of the countries, then select “mercator” from the map projections and hit “plot” map.
Compare this map to the first, then select “Albers (centre, parallels)” from the map projections list, type 20/60 into the “centre” field, and 50/70 into the “Standard Parallel/s” field…and plot the map.
*Briefly* discuss the main differences in what you see on the three maps, and relate them to what you know about the projections used.
Coordinate system and topo map questions (use PDF file):
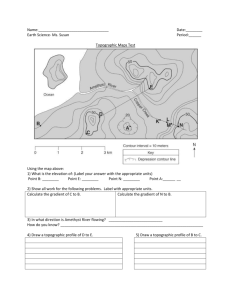
(2)Look at the topo map on page 1 of the PDF (for all topo maps, red= 50 m contour, blue= 75 m, and green = 100m; north is toward the top of the page). Describe in a few sentences the major features of this landscape (nothing technical, just something like: “there is one main ridge running
NE-SW, with 2 major valleys on the NW side”)
Compare the maps of the same section of land on pages 1 (contour interval 5 m), 2 (contour interval
10 m), 3 (contour interval 25 meters), 4 (digital elevation model-DEM- with elevations categorized and represented by different colors) 5(hillshade model of topography), and 6 (semi-transparent classified DEM over hillshade).
Which map is best suited for (and why):
(1) Visualization of the landscape
(1) Quantitative comparison of slope (gradients) at different locations
(1) Quick identification of highest and lowest points in the landscape
Focusing specifically on the three different topographic maps; much geomorphological analysis involves comparing quantitative topographic parameters from different regions; sometimes comparable topographic data (i.e. same scale, same contour interval) is not available from each area of interest. For each of the following parameters, would you expect higher resolution (smaller contour interval) maps to over- or underestimate values for a particular region relative to lower resolution
(larger contour interval) maps (if you can’t tell, say why).
(2) Gradient
(2) total sum valley length for drainage system including all visible tributaries
(2) Valley floor area (defined by noticeable break in slope between (steeper) valley walls and
(flatter) valley floor
(3) What would you do if you needed to measure and compare “contour-interval sensitive” parameters for two areas, but a 5m contour interval map was only available for one area, with a 25 m contour interval map being the best available for the other region?
Finally, take a look at the gridded map on page 7; the grid over the map is a UTM grid.
(2) Your GPS says 474605, 1420217. Describe where you’re standing and give the elevation.
(2) What are the UTM coordinates for the orange x on the map?
(2) What’s the approximate horizontal scale of the map? How did you determine this?