Part A: Multiple Choice. Circle the letter corresponding to the correct
advertisement

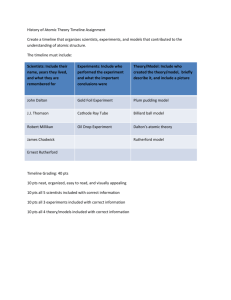
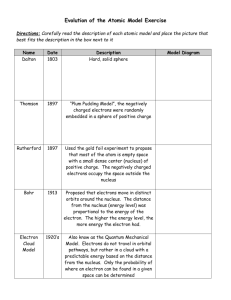
Chemistry 11 Unit 1: Atomic Theory Test 1 Chemist __________________________ Part A: Multiple Choice. Circle the letter corresponding to the correct response. (1 point each) 1. A vertical arrangement of elements on the periodic table is known as a) an octet b) a period c) a group d) a row e) a series 2. A horizontal arrangement of elements on the periodic table is known as a) a group b) a family c) a period d) an octet e) a column 3. Which of the following elements has the largest radius? a) carbon b) beryllium c) nitrogen d) oxygen e) neon 4. In the periodic table, the elements are arranged according to a) increasing atomic number b) no particular order c) decreasing atomic mass d) increasing ionization energy e) decreasing nuclear charge 5. In the periodic table, the halogens are located a) in the middle b) in group 15 d) in group 17 e) along the bottom c) down the left-hand side 6. Most non-metals are located in the periodic table a) on the right hand side b) as the first twenty elements c) in the center d) on the left hand side e) scattered throughout the table 7. In general, which of the following properties does NOT increase across a row from left to right? a) atomic number b) atomic radius c) nuclear charge d) ionization energy e) electron affinity 8. Which of the following properties decreases from top to bottom in a column? a) ionization energy b) atomic mass c) atomic number d) atomic size e) number of electrons 9. The amount of energy needed to remove an electron from an atom in the gaseous state is called a) electron affinity b) ionization energy c) electronegativity d) shielding effect e) nuclear charge 10. If element ‘X’ is in the same group as fluorine and chlorine, then element ‘X’ is: a) a metal b) a transition element c) a noble gas d) none of these e) more reactive than chlorine 1 11. Which of the following does not have the same number of electrons as one of the noble gases? a) Na + b) Kr c) Ca 2+ d) I e) Cl 12. Which one of the following statements about the periodic table is FALSE? a) Elements in a vertical column constitute a family of elements having many similar properties b) The elements on the left side of the table form negative ions readily. c) Hydrogen has properties which distinguish it from any single chemical family. d) Elements in any row have widely varying chemical and physical properties. e) The elements on the right side of the table form negative ions readily. 13. Element ‘X’ readily loses 1 electron. It probably a) belongs to group 1 b) is a metal d) belongs to the noble gases e) forms X – ions c) is nonreactive 14. Which of the following does not explain the trends observed in the periodic table: a) shielding b) nuclear charge c) quantum number d) atomic number e) electrostatic forces 15. Analysis of an atom indicates that there are five electrons in the third energy level. The element is a) nitrogen b) phosphorus c) potassium d) silicon e) chlorine 16. An element has the following electron configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p4. It belongs to the same family as a) nitrogen b) carbon c) chlorine d) oxygen e) sodium Questions 16-20 are based on these electron configurations: A B C D E 1s22s22p5 1s22s22p63s1 1s22s22p1 1s22s22p6 1s22s22p63s2 17. Which configuration represents an alkali metal? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) E 18. Which configuration represents an atom with two valence electrons? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) E 19. Configuration D represents which neutral atom? a) Mg b) Ne c) Na d) N e) some other element 20. Which configuration represents an atom with the maximum allowed number of valence electrons? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) E 2 21. The lowest energy level is known as: a) excited state b) ground state c) valence electron d) p sublevel e) d sublevel 22. He used cathode ray tubes, a current, and an electrical field to determine the nature of electrons: a) Bohr b) Rutherford c) Schrodinger d) Dalton e) Thomson 23. He further developed the ideas of the Greek philosophers and supported that atoms of elements are Identical: a) Bohr b) Rutherford c) Schrodinger d) Dalton e) Thomson 24. He proposed that the nucleus was a dense, compact structure surrounded by mostly empty space a) Bohr b) Rutherford c) Schrodinger d) Dalton e) Thomson 25. He used a mathematical equation to determine the probability of finding an electron within a region a) Bohr b) Rutherford c) Schrodinger d) Dalton e) Thomson 26. He proposed the “planetary model” or orbits of electrons a) Bohr b) Rutherford c) Schrodinger d) Dalton e) Thomson Part B: Short answer. 1. Complete the table below. (8 pts) Atomic number 18 Mass number 40 27 # of protons # of neutrons # of electrons Element Al 3+ 2. Natural neon contains 90.9% 20Ne, 0.3% 21Ne, and 8.8% 22Ne. What is the average atomic mass for neon? (All work must be shown.) (3 pts) 3. List all the orbital types found in the third principal energy level, and the maximum number of electrons the third energy level can hold. (2 pts) 3 4. Give the full electron configuration for copper. (2 pts) 5. Give the full electron configuration for nickel. Circle the orbitals containing the valence electrons, and state the number of valence electrons. (3 pts) 6. a) Provide the electron configuration for Mg2+. (1 pt) b) What other neutral element has the same electron configuration as Mg2+? (1 pt) 7. Draw an energy level diagram for iron. (3 pts) 8. What is the noble gas shorthand electron configuration for strontium? (2 pt) 10. What charge do halogens typically take on when they form ions, and why? (2 pts) 4 11. State whether ionization energy increases or decreases as you go down a family in the periodic table, and explain why. (2 pts) 12. How many unpaired electrons are there in the following ions? (2 pts) a. V3+ b. Sn4+ 13. Which of the four atoms Na, P, Cl, or K: (3 pts) a. has the largest atomic radius? b. has the highest ionization energy? c. is the most electronegative? 14. List the following species in order of increasing radius. (2 pts) a. Ni, Ni2+, Ni3+ b. Br, Br-, I15. Explain in your own words: (2 pts) a. the Pauli exclusion principle b. Hund’s rule 16. Main group elements wish to become like what chemical family? Why? (2 pts) 5