Supplementary Information (doc 56K)
advertisement

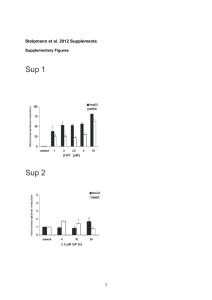
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1 Increase of rhoB mRNA expression after UV treatment. Relative rhoB mRNA expression was analyzed by qRT-PCR 8 h after UV (60 J/m2) treatment. Data are presented as mean +/- SD (n=3). *, P < 0.05. Figure S2 Translation of rhoB mRNA is regulated upon UV exposure. Lysates prepared from HaCat cells UV-irradiated (60 J/m2 ; 8 hr) or left untreated were fractionated through a sucrose gradient and the relative distribution (%) of actin mRNA (top) and rhoB mRNA (bottom) was studied by qRT-PCR analysis in each of the 17 gradient fractions. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Figure S3 Analysis of reporter construct expression in human primary keratinocytes isolated from two different donors. The RLuc activities of the indicated transfected constructs, normalized to the FLuc activities of a cotransfected FLuc construct are shown. The values are averages from at least three transfections +/- SD. Figure S4 Transfection of a miR-19b synthetic oligonucleotide leads to an increase in endogenous miR19b levels. miR-19b expression was analyzed by qRT-PCR. Data are presented as mean +/SD (n=3). ***, P < 0.005. 1 Figure S5 Relative expression of the indicated miRNAs was determined by qRT-PCR 8 h after UV treatment. Data are presented as mean +/- SD (n=3). Figure S6 HuR was immunoprecipitated from crosslinked HaCat cells. Igg1 loaded beads were used as a control. The endogenous rhoB mRNAs was isolated from HuR immunoprecipitates (IP) and reverse transcribed. The levels of HuR-associated mRNAs were quantified by qRT-PCR relative to gapdh mRNA. For each HuR IP sample, relative mRNA levels were normalized to the corresponding input samples. The values are averages from at least three transfections ± SD. **, P < 0.01. Figure S7 Relocalization of HuR from the nucleus to the cytoplasm upon UV treatment of HaCat cells as described in the supplementary materials and methods section. The slides were incubated with the anti-HuR monoclonal primary antibody (3A2) or with mouse IgG (immunoglobulin G). The merged images (merge) show the presence of HuR outside the nucleus in UV treated cells. Figure S8 (a) Proteins from nuclear (Nuc.) and cytoplasmic (Cyto.) extracts of UV-treated or control HaCat cells were immunoblotted with anti-HuR, anti-Tubulin, anti-Topoisomerase I, anti CFI68 and anti-hnRNP C1/C2 antibodies. hnRNP C1/C2, CFI68 and topoisomerase I are predominantly nuclear, whereas tubulin is predominantly cytoplasmic, as expected for a good nuclear/cytoplasmic fractionation. (b) HuR was immunoprecipitated from HaCat cytoplasmic 2 extracts. Igg1 loaded beads were used as a control. The endogenous rhoB mRNAs was isolated from HuR immunoprecipitates (IP) and reverse transcribed. The levels of HuRassociated mRNAs were quantified by qRT-PCR relative to gapdh mRNA. For each HuR IP sample, relative mRNA levels were normalized to the corresponding input samples. The values are averages from at least three transfections ± SD. **, P < 0.01. Figure S9 HuR represses RhoB expression. UV-treated or control HaCat cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs. 48 h later, proteins were extracted and immunoblotted with anti-RhoB, anti-HuR or anti-actin antibodies. Figure S10 HaCat cells, transfected with a miR-19b synthetic oligonucleotide or mock-transfected were UV irradiated. HuR and Ago2 were immunoprecipitated from HaCat cells. Igg1 loaded beads were used as a control. The endogenous rhoB mRNAs was isolated from HuR or Ago2 immunoprecipitates (IP) and reverse transcribed. The levels of HuR-associated mRNAs were quantified by qRT-PCR relative to gapdh mRNA. For each HuR or Ago2 IP sample, relative mRNA levels were normalized to the corresponding input samples. The values are averages from at least three transfections ± SD. *, P < 0.05. Figure S11 miR-19b increases UV-induced apoptosis. (a) UV-treated or control HaCat cells were transfected with a miR-19b synthetic oligonucleotide or a miR-24 synthetic oligonucleotide or an siRNA against RhoB. 8 h later, apoptotic cells were detected by the TUNEL assay method using the ApopTag Fluorescein direct in situ apoptosis detection kit (Millipore) according to 3 the manufacturer’s instructions. 600 cells were counted for each experiment. (b) Quantification of TUNEL positive cells is shown. Data are presented as mean +/- SD (n=3). *, P < 0.05. **, P < 0.01. SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS Cell culture. Normal human epidermal keratinocytes (primary keratinocytes, NEHK) were grown in keratinocyte-SFM medium (KSFM) (Invitrogen) supplemented with bovine pituitary extract (25µg/ml) and EGF (1,5 ng/ ml). Immunofluorescence HaCat cells grown on sterilized glass overslips, were treated with UVC (60 J/m2), cultured for 8h, fixed with 3,7% formaldehyde for 20 min and permeabilized with PBS 0,1% BSA (Bovine Serum Albumin) 0,5 % Triton 100-X for 5 min. After washes, the slides were incubated overnight with the anti-HuR monoclonal primary antibody (3A2 ; Santa Cruz Biotechnology ; 1/200) or with immunoglobulin G mouse (Sigma ; 1/200) and stained with Alexa-488 coupled donkey anti-mouse secondary antibody (Invitrogen ; 1 /2000) for 45 min. Cell were examined with a fluorescence microscope (Nikon Eclipse 90i) at 40X magnification. Subcellular Fractionation Subcellular fractionation was performed as in (Lewis, Mol Biol Cell 2007). HaCat cells (30 million) were washed in ice-cold PBS, resuspended in 400µl of buffer A (10 mM HEPES-KOH, pH 7.5 ; 10 mM KCl ; 1mM DTT; 1mM PMSF) containing protease inhibitors (Roche), and incubated on ice for 15 min. Nonidet P-40 was added to a final concentration of 0,3% and cells were incubated for an additional 10 min on ice. Nuclei were pelleted by centrifugation at 1,500g x for 5 min and the cytoplasmic fraction was collected to a new tube and clarified by centrifugation at 13,000g x for 15 min. The nuclei pellet was washed two times with 1 ml of buffer A, then resuspended in 50µl of buffer 4 B (20 mM HEPES-KOH, pH 7.5 ; 400 mM NaCl ; 1 mM DTT ; 1mM PMSF) containing protease inhibitors, and incubated on ice for 30 min, with mixing every 5 min. Nuclear debris was pelleted at 13,000 x g for 5 min. In vivo Crosslink RNA immunoprecipitation HaCat cells (30 million) were crosslinked for 10 min with 0,5% V/V formaldehyde (Sigma), inactivated for 5 min with 250mM glycine pH7. Cells were washed four times with PBS and lysed in 1 ml RIPA 150mM NaCl (50 mM Tris–HCl ph 7,4 ; 1% NP40 ; 0,5% Nadesoxycolate ; 0,05% SDS ; 1mM EDTA ; 150 mM NaCl ; protease inhibitor mixture (Roche); RNAsin (Promega)) for 30min at 4°C. Extracts were precleared for 30 min at 4°C by using 20 µl of Protein A/G+ agarose beads (Sigma) that had been previously blocked with yeast tRNA (invitrogen) and RNAse-free BSA (Ambion). Beads were incubated (16h at 4°C) with 15 µg of anti-Ago2 (clone 2E12-1C9 ; Abnova) antibody or anti-HuR (3A2 ; Santa Cruz biotechnology) antibody and next overnight at 4°C with 1 mg of cell lysate. After extensive washes with RIPA 0,8 M NaCl, beads were resuspended with 100µl H20 and reverse crosslink was performed by adding 100 µl 2X rev Buffer (50 mM TRIS HCL pH7 ; 5mM EDTA ; 10mM DTT ; 1% SDS) (45 min at 70°C). Then RNA were extracted using TRIzol LS Reagent (Invitogen). 5