Study Guide for Climate
advertisement
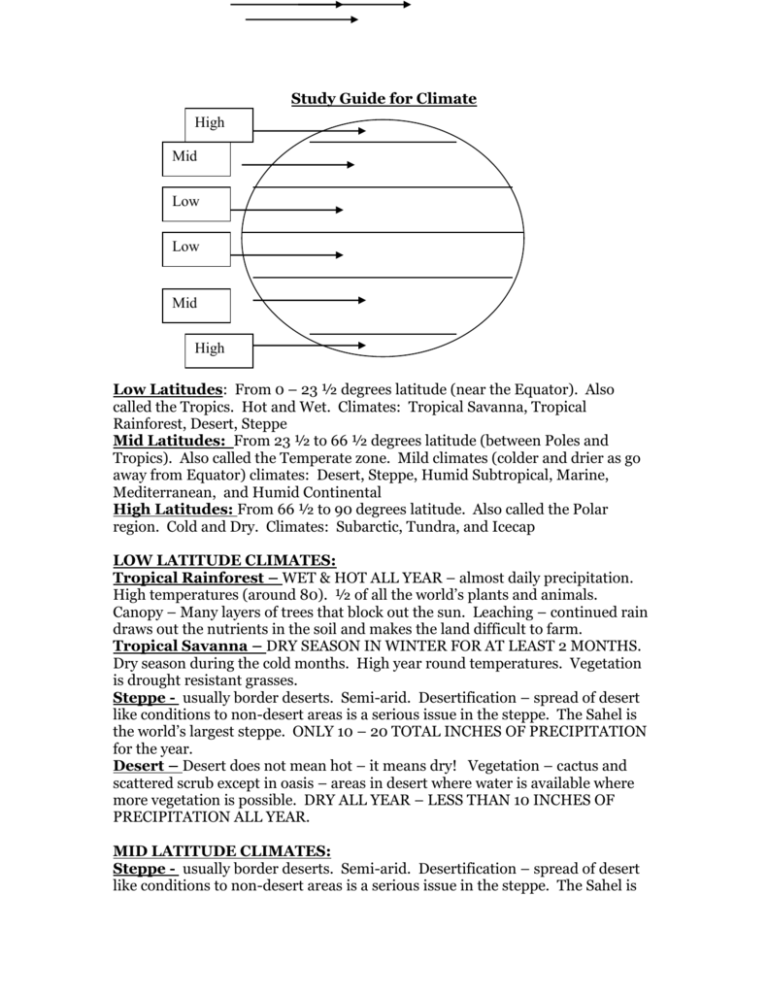
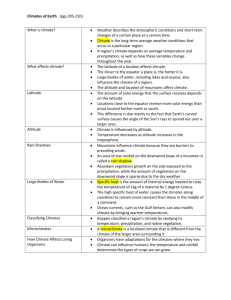
Study Guide for Climate High Mid Low Low Mid High Low Latitudes: From 0 – 23 ½ degrees latitude (near the Equator). Also called the Tropics. Hot and Wet. Climates: Tropical Savanna, Tropical Rainforest, Desert, Steppe Mid Latitudes: From 23 ½ to 66 ½ degrees latitude (between Poles and Tropics). Also called the Temperate zone. Mild climates (colder and drier as go away from Equator) climates: Desert, Steppe, Humid Subtropical, Marine, Mediterranean, and Humid Continental High Latitudes: From 66 ½ to 90 degrees latitude. Also called the Polar region. Cold and Dry. Climates: Subarctic, Tundra, and Icecap LOW LATITUDE CLIMATES: Tropical Rainforest – WET & HOT ALL YEAR – almost daily precipitation. High temperatures (around 80). ½ of all the world’s plants and animals. Canopy – Many layers of trees that block out the sun. Leaching – continued rain draws out the nutrients in the soil and makes the land difficult to farm. Tropical Savanna – DRY SEASON IN WINTER FOR AT LEAST 2 MONTHS. Dry season during the cold months. High year round temperatures. Vegetation is drought resistant grasses. Steppe - usually border deserts. Semi-arid. Desertification – spread of desert like conditions to non-desert areas is a serious issue in the steppe. The Sahel is the world’s largest steppe. ONLY 10 – 20 TOTAL INCHES OF PRECIPITATION for the year. Desert – Desert does not mean hot – it means dry! Vegetation – cactus and scattered scrub except in oasis – areas in desert where water is available where more vegetation is possible. DRY ALL YEAR – LESS THAN 10 INCHES OF PRECIPITATION ALL YEAR. MID LATITUDE CLIMATES: Steppe - usually border deserts. Semi-arid. Desertification – spread of desert like conditions to non-desert areas is a serious issue in the steppe. The Sahel is the world’s largest steppe. ONLY 10 – 20 TOTAL INCHES OF PRECIPITATION for the year. Desert – Desert does not mean hot – it means dry! Vegetation – cactus and scattered scrub except in oasis – areas in desert where water is available where more vegetation is possible. DRY ALL YEAR – LESS THAN 10 INCHES OF PRECIPITATION ALL YEAR. 2 types of desert – reg (the majority of deserts) – “desert pavement” of sand, gravel, and rocks. Erg – sand dunes Marine – precipitation all year because on Westerlies. SMALL TEMPERATURE VARIATION between summer and winter ( about 30 degrees difference) 40 low and 60 high. MILD SUMMERS AND WINTERS with precipitation every month. Temperate rainforest in this climate. Mediterranean – PRECIPITATION IN THE WINTER and much DRIER SUMMERS. Hot sunny summers and mild, rainy winters. Chaparral vegetation – short trees, underbrush, woody bushes (scrub) Humid Subtropical – Houston. SHORT MILD WINTERS AND HOT SUMMERS WITH YEAR ROUND PRECIPITATION. Hurricanes and typhoons. Mixed forests – both deciduous and coniferous trees. Humid Continental – HAS FOUR DISTINCT SEASONS – hot summer, cold winter. Continentality plays a large roll in this climate – far away from water. Agriculture has replaced prairie grass. HIGH LATITUDE CLIMATES: Subarctic – WIDEST TEMPERATURE RANGE BETWEEN SUMMER AND WINTER TEMPERATURES. Short, cool summers (high around 70) and very cold winters (below freezing). Permafrost – permanently frozen soil. Only the top layer of the soil ever thaws. Taiga – Russian world for forest. Short pine trees. Tundra – 9 MONTHS OR MORE BELOW FREEZING. Rarely gets above 50 degrees. Permafrost. Low bushes, very short grass, mosses, lichen, and permafrost bogs in summer. Icecap – coldest temperatures on earth. NO MONTHS ABOVE FREEZING. Polar night – 6 months of the year are dark because the Pole is tilted away from the sun. Polar desert – too cold to precipitate. Covered in ice and snow up to 2 miles thick. HIGHLANDS: Orographic Effect – clouds too heavy to get over the mountains. Leeward side is dry and windward side is moist. Every 1,000 feet up the mountain the temperature decreases 3.5 degrees. VERTICAL CLIMATE: Tierra Caliente – hot land. 0-2,500 ft, banana, sugar cane, banana, cacao Tierra Templada – Temperate land. 2,500-6,500 ft, coffee, cotton, tobacco Tierra Fria – cold land. 6,500-10,000 ft. grains, apples, potatoes Paramo – grassland. 10,000 – 14,000 ft. grazing sheep, alpacas, and llamas Tierra Helada – above snow line. Nothing grows here.