File
advertisement

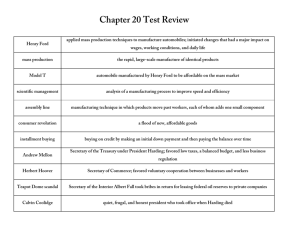
Chapter 11 – THE TWENTIES 1919-1929 Chapter 11.1 – BOOMING ECONOMY Note specific economic changes of the 1920. MASS PRODUCTION INCREASED WAGES ECONOMY OF THE 1920s INSTALLMENT BUYING ADVERTISING BULL MARKET FOCUS QUESTIONS: Answer each question completely. How did the booming economy of the 1920s lead to changes in American life? The workweek shortened to 40 hours and allowed people extra leisure time. People used credit to buy new machines and stocks. Many prosperous Americans relied on cars for transportation and moved to the suburbs where they could enjoy more space. Chapter 11.2 – THE BUSINESS OF GOVERNMENT Note the similarities and differences between Presidents Harding and Coolidge. HARDING • Fun-loving BOTH COOLIDGE • Serious • Republican • Not Intellectual • Not particularly moral • Raised tariffs • Laissez-faire approach to business • Quiet • Pro-business • Honest • Opposed to social reform laws • Frugal FOCUS QUESTIONS: Answer each question completely. How did domestic and foreign policy change direction under Harding and Coolidge? Both men refused to use legislation to make social changes. Unlike the Progressives, their economic policies favored big business. Both Presidents also maintained isolationist stances in world affairs. Chapter 11.3 – SOCIAL AND CULTURAL TENSIONS As you read, look for issues that divided Americans in the 1920s. DIFFERING VIEWPOINTS Education View Point 1 – Urban Americans tended to value education highly. View Point 2 – Rural Americans placed less value on formal education. View Point 1 – Fundamentalists opposed the theory of evolution. Evolution Immigration View Point 2 – Modernists stressed the importance of science, including the theory of evolution, and secular life. View Point 1 – Nativists sought to limit immigration. View Point 2 – Others viewed immigration as essentially American. View Point 1 – Fundamentalists tend to oppose social change. Social Change View Point 2 – Modernists tended to accept social change. View Point 1 – “Drys” supported Prohibition. Prohibition View Point 2 – “Wets” opposed Prohibition. FOCUS QUESTIONS: Answer each question completely. How did Americans differ on major social and cultural issues? Many rural Americans were more religious and traditional, and many urban Americans were more interested in science and modernity. Rural Americans often opposed evolution and new roles for women, and supported Prohibition. Chapter 11.4 – A NEW MASS CULTURE Look for ways in which culture changed during the 1920s. MASS MEDIA SOCIAL TRENDS CHANGING CULTURE Radio Flappers Movies Phonographs F. Scott Fitzgerald ART, LITERATURE, and THOUGHT Ernest Hemingway Women Challenging Boundaries National Heroes Psychologist Sigmund Freud Modernist Painters As you read, classify the various types of changes that took place in women’s lives in the 1920s. WOMEN IN THE 1920s SOCIAL CHANGES • Wore shorter skirts POLITICAL CHANGES • Won the right to vote ECONOMIC CHANGES • Joined the workforce • Tended to live longer, marry later, and have fewer children • Ran for political office • Challenged boundaries • Enjoy more leisure time as new appliances reduce housework • Enlarged their intellectual world FOCUS QUESTIONS: Answer each question completely. How did the new mass culture reflect technological and social changes? Movies, radio, and records all reached a national audience, and created celebrities and trends at the same time across the country. The new American society was reflected in action movies and radio shows, and fast dance music on records. Chapter 11.5 – THE HARLEM RENAISSANCE As you read, identify the main ideas. I. New “Black Consciousness” A. New Chances, New Challenges 1. Migration to North continues 2. Migrants seek better opportunities and social advancement 3. Many African Americans are drawn to Harlem B. Garvey Calls for Racial Pride 1. Urges blacks to support black-run businesses 2. Calls for blacks to separate from whites 3. Promotes “Back to Africa” movement II. The Jazz Age A. A Unique American Music Emerges 1. Jazz migrates from the South to the North 2. Musicians Louis Armstrong and Bessie Smith find success. B. Jazz Wins Worldwide Popularity III. The Harlem Renaissance A. African American Literature Flowers with Works from Claude McKay, Langston Hughes, and Zora Neale Hurston B. The Harlem Renaissance Defines African American Culture. FOCUS QUESTIONS: Answer each question completely. How did African Americans express a new sense of hope and pride? African Americans created art that reflected their own experiences and presented it to the world with pride. Jazz and African American literature were known around the world, and African Americans demanded recognition for their cultural contributions.