3.1 eukaryotic vs. prokaryotic LP
advertisement

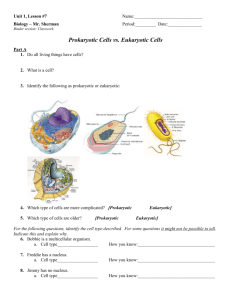
FIVE-STEP LESSON PLAN TEMPLATE Callie Roth 10/10/10 FIVE-STEP LESSON PLAN OBJECTIVE. KEY POINTS. SWBAT identify that scientists classify things based on patterns, similarity, and diversity. SWBAT explain that a eukaryotic cell has a nucleus and a prokaryotic cell does not. Scientists classify things based on patterns, similarity, and diversity. In nature, some things occur repeatedly creating a pattern. Similarity means that things are alike in some way. Diversity means that things are different in some way. Prokaryotic cells are very simple and do not have a nucleus. Instead of a nucleus, prokaryotic cells have a nucleiod. The only organelles that prokaryotic cells have are ribosomes. Eukaryotic cells are more complex and have a nucleus. They have a lot of organelles including ribosomes. 1. How are eukaryotic cells different from prokaryotic cells? (DOK 2) A. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, and prokaryotic cells do not. B. Eukaryotic cells have cell walls, and prokaryotic cells do not. C. Eukaryotic cells contain genetic material, and prokaryotic cells do not. D. Eukaryotic cells contain ribosomes, and prokaryotic cells do not. 2. Is the cell in the diagram to the right a eukaryotic cell? (DOK 3) A. Yes, because there are complex organelles like a nucleus. B. Yes, because it is very small. C. No, because there are complex organelles like a nucleus. D. No, because it is a plant cell. 3. A scientist discovered a new organism while looking through a microscope. The scientist observed that the cell contained a nucleus, cell membrane, and mitochondria. How should this organism be classified? (DOK 2) A. It cannot be classified. B. It should be classified as prokaryotic. C. It should be classified as eukaryotic. D. It should be classified as zookaryotic. 4. OPENING MATERIALS. 1. Anticipatory Set (5 minutes) – TSW enter the classroom silently. TTW call on a student to read and answer the bellringer – what are all living things made of? TSW answer the do now. TTW connect the bellringer to the daily lesson. TTW go over agenda, announcements, and big goal connection. 3. INTRODUCTION OF NEW MATERIAL 2. Input, Modeling, and Check for Understandings (15 minutes) – TTW present a power point on the big idea of patterns, similarity, and diversity and the difference between a eukaryotic cell and prokaryotic cell. TSW take notes from the power point. TTW conduct CFU’s. TSW answer cfu’s. 2. GUIDED PRACTICE 3. Guided Practice (15 minutes) – TTW ask teams questions and classify pictures of cells. TSW answer questions. TTW award points. 1. INDEPENDENT PRACTICE 4. Independent Practice (15 minutes) – TSW complete worksheet on the cell types. TTW call on students to share their answers. TSW share answers. TTW correct and clarify misunderstandings. TTW award team points. 5. CLOSING 5. Closing (5 minutes) – TSW write a reflection on the day’s lesson in their journal. TTW assign weekly homework. TSW begin homework. FIVE-STEP LESSON PLAN TEMPLATE 3.1 Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic Cells – Make-up Notes Scientists classify things based on patterns, similarity, and diversity. In nature, some things occur repeatedly creating a pattern. Similarity means that things are alike in some way. Diversity means that things are different in some way. Prokaryotic cells are very simple and do not have a nucleus. Instead of a nucleus, prokaryotic cells have a nucleoid. The only organelles that prokaryotic cells have are ribosomes. Eukaryotic cells are more complex and have a nucleus. They have a lot of organelles including ribosomes. 3.1 Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic Cells Independent Practice 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What are patterns? What does it mean if two things are similar? What does it meant if two things are different? What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells similar? Is the cell in the diagram to the right a prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell? 7. A scientist discovered a new organism while looking through a microscope. The scientist observed that the cell contained a nucleoid, cell wall, and ribosomes. How should this organism be classified (as prokaryotic or eukaryotic)? 3.1 Challenge (If you finish early, you should complete this section.) 8. Write a short paragraph comparing and contrasting prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.