24. Sex & Sex Linkage
advertisement

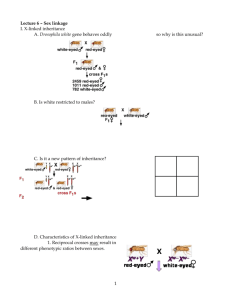
D’YOUVILLE COLLEGE BIOLOGY 102 - INTRODUCTORY BIOLOGY II LECTURE # 24 CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE 1. Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance: • discovery of meiosis & parallel behavior of meiotic chromosomes with Mendel’s laws for heritable factors (gene alleles) (fig. 15 – 2 & ppt. 1); conclusion: genes are on chromosomes (= chromosomal theory of inheritance) • Morgan’s discovery of sex linkage (X linkage): white-eyed mutants in Drosophila (fig. 15 – 3): white-eyed male x red-eyed female produces F2 with 3:1 ratio but only males with white eyes (fig. 15 – 4 & ppt. 2); concluded gene alleles were carried on X chromosome (further analysis below) 2. Chromosomal Basis of Sex Inheritance: • sex chromosomes & autosomes: humans have 1 pair of sex chromosomes + 22 pairs of autosomes (44A, XX for females or 44A, XY for males) (fig. 15 – 5) • X-Y system: males heterogametic; e.g., Drosophila & mammals; Y does not carry genes that match those on X, but does carry gene for maleness (SRY = sexdetermining region of Y) in humans (codes for DNA binding protein that activates autosomal genes for maleness during development) • Z-W system: females heterogametic; e.g. birds, butterflies, moths, some fish • X-O system: males have single X (XO), females are diploid for X (XX); e.g. grasshoppers, many insects Bio 102, spr. 13 lec. 24 - p. 2 • haplo-diploid system: males haploid, females diploid, e.g., honeybees; drones = males; workers = sterile females; queen = fertile female (fig. 15 – 6 & ppts. 3 &. 4) Bio 102, spr. 13 3. lec. 24 - p. 3 Sex-linked (usually X-linked) traits: • different pattern from autosomal inheritance (fig. 15 – 7 & ppt. 5) • males (hemizygous for X-linked genes) show all recessive traits (no masking by heterozygous condition), e.g., color blindness, hemophilia & Duchenne muscular dystrophy • sex chromatin (Barr body): dense-staining chromatin in interphase nuclei - one X chromosome inactivated in all cells: one-half of cells X1, one-half of cells X2, e.g., tortoise-shell pattern in cats (fig. 15 – 8 & ppt. 6)