Controls on the Stratigraphic record

Controls on the Stratigraphic record
• Episodic sedimentation (Ager’s Catastrophic Uniformitarianism)
•
Correlation
• The nature of the control
•
Event stratigraphy
•
Sequence stratigraphy
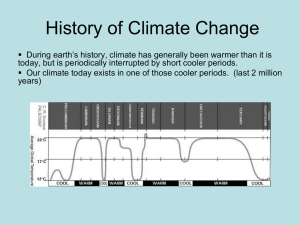
Ager’s view of the record
•
More gaps than record
• Obvious unconformities
•
Variable thickness and “pinch outs” of like-aged strata in different locations
•
Incredibly slow estimates for accumulation rates
•
The myth of the type section
• The “true” nature of bedding surfaces: breaks in sedimentation, and thus unconformable surfaces!
•
Episodic sedimentation
• “Catastrophic Uniformitarianism”
•
Chance preservation
Cautions to keep in mind
• Ager’s bias
•
View from above base level
•
Predisposed to questions of preservation rather than depositional process
•
Worked during the beginning of the Plate Tectonics Revolution
•
Gaps in the record vary with
•
Environment
•
Process
• Age
Correlation
•
Early workers incorrectly viewed matching lithologies as equal in age
(“Layer cake thinkers”)
• Lithostratigraphic correlation - matching similarly placed formations in different sections (Result is almost always diacronous!)
• Temporal correlation - matching strata of equal ages in different sections
(Result almost always cuts across facies of lithologies!)
Methods of correlation
• “Walking the section”
•
Mapping sections
• Identification of marker beds
• Positional equivalence of differing facies
• Matching of unconformity surfaces or deformed and metamorphosed
formations
Correlation by positional equivalence
Vagaries and Limitations
• Boundary offsets (“State-line faults”)
• Stratigraphic cutoffs (arbitrary boundaries between units)
Diacronous Facies of the Devonian Catskill sequence
Diacronous facies and
Lateral migration
• Persian Gulf coast
• Coast of France
•
•
Sandy Hook, NJ
LI spit complex
•
Mississippi Delta
2 m/yr
10 m/yr
12 m/yr
65 m/yr
75 m/yr
Event correlation of transgressive/regressive inflections
Event stratigraphy and golden spikes
•
Ideal stratigraphic age markers are instaneous and global
•
Approximated by
• Ash falls
•
Impact events
•
Magnetic reversals
• Some evolutionary events
•
Transgression/regression inflection points
•
Records of certain climatic cycles
Capitalizing on gaps and diacronous facies
•
Unconformities can be viewed as natural breaks in the record
•
They separate packets of diacronous, transgressive/regressive sedimentary strata
• These define “Sequence” boundaries in the sense of Sloss et al.
(1949); Sloss (1963)
•
Many of these sequences are global in scale and may span
system boundaries
Sloss diagram for
North America
Sequence Stratigraphy
• Framework for division and understanding of the stratigraphic record
•
Concepts formulated by Peter Vail, Bilal Haq, and other.
• Formations can be grouped into “sequences” bounded by unconformities arising from global changes in sea level
•
These global eustatic changes in sea level occur on a variety of time-scale associated with specific processes
Pros and Cons of the approach
• Provides an overarching framework with which to approach the record
• Process based
•
Identification of truly global eustatic events can be challenging
• Conversion from relative to absolute
SL can be difficult
•
Inadequate time control can led to process related misconceptions
Nested cyclicity
•
Sequence approach postulates that global SL can changes on a variety of time scales in response to processes with different time constants
• Vail et al. (1977) and Haq et al. (1977) identified four orders of cycles
•
Other works have defined higher order cycles
•
Confusion arises because various scientists ascribe different time scales and processes to similarly named cycles
Sequence Stratigraphic cycles
•
First Order: 200-400 myr
•
Second Order:
•
Third Order:
•
Fourth Order:
•
Fifth Order:
•
Sixth Order:
10-100 myr
1-10 myr
200-500 kyr
20- 400 kyr
1-10 kyr
First Order Cycles
•
Equal to the Supercycles of Fischer (1981)
•
Duration: 200-400 m.y.
•
Hypothesized Cause:
–
Major eustatic cycles caused by the formation and breakup of supercontinents
First
Order
Cycles
Second Order Cycles
Equal to
•
Sequences of Sloss
•
Synthems of Chang (1975), Ramsbottom (1979)
•
Duration: 10-100 m.y.
•
Hypothesized Cause: Eustatic cycles induced by volume changes in global mid-ocean ridge system (mantle convection cycles?)
Changes in
Sea floor spreading
• Sea floor spreading rates can range from 1-12 cm/y resulting in large changes in ocean basin volume and continental flooding (example shows changes from 2 to 6 cm/yr
Third Order Cycles
•
Equal to Mesothems of Ramsbottom (1979)
•
Duration of 1-10 m.y.
•
Hypothesized Cause: Crustal flexures or changes in the Geoid
(regional uplift?)
•
Short duration relative to biostratigraphic contraints makes determing global extent and driving process difficult
Fourth Order Cycles
•
Cyclothems of Wanless and Weller (1932)
•
Duration of 200-500 k.y.
•
Hypothesized Cause: Eustatic changes driven by growth and decay of ice sheets; growth and abandonment of deltas
•
Problem - While there is a 400 ka cycle associated with the
Pleistocene ice ages, it has no eustatic expression!
Fifth and Sixth Order Cycles
• Orbital, or Croll/Milankovitch cycles
• Eccentricity: 95, 125, 400 kyr
•
Tilt: 41 kyr
• Precession: 19, 23 kyr
• Sub-Orbital:1-10 kyr
• Cause still active area of research