Unpacking Outcomes - North East School Division
advertisement

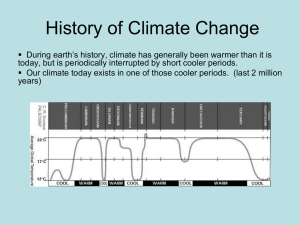
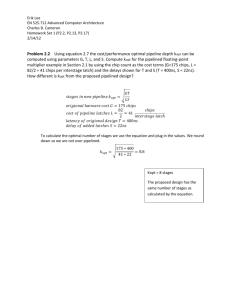
North East School Division Unpacking Outcomes Unpacking the Outcome growth Analyze familiar animals life cycles development Outcome (circle the verb and underline the qualifiers) AN2.1 Analyze the growth and development of familiar animals, including birds, fish, insects, reptiles, amphibians, and mammals, during their life cycles. KNOW Life cycles of living things Animals Types Resources to find information about life cycles of living things. Offspring names of animals Seasonal behaviors of animals Characteristics of life cycles Animal traits Development of animals UNDERSTAND Every animal has life cycle. Animal life cycles differ but there are common characteristics. Different cultures interpret lifecycles in their own ways Some aspects of animals change depending on the stage in their life cycle and some aspects stay the same. We can make predictions based on patterns. BE ABLE TO DO a. Pose questions about the growth and development of familiar animals. b. Use a variety of resources (e.g., Elder, naturalist, zookeeper, park warden, pet store, books, pictures, and videos) to find information about the life cycles of living things. c. Identify the names of the offspring (e.g., cub, pup, calf, kitten, chick, fawn, fingerling, maggot, tadpole, gosling, and infant) of familiar animals. d. Recognize the cyclic nature of mother Earth expressed by the Medicine Wheel, including life cycles and seasonal behaviors of animals. e. Compare the length and stages of life cycles of familiar animals. f. Describe the characteristics common to each stage (e.g., birth, youth, adulthood, and old age) of the life cycle of familiar animals (e.g., dog, cat, beaver, frog, fish, bird, ant, wasp, and chicken). g. Analyze which traits (e.g., body size, head size to body ratio, and number of limbs) remain relatively constant and which change in specific animals as they grow and develop. h. Create a physical, visual, or dramatic representation of the growth and development of familiar animals during their life cycles. i. Predict how big a specific animal will grow based on observed patterns of animal growth and changes. j. Design an animal suited for life in a particular environment (real or imaginary) and represent its growth and changes throughout its life cycle. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How do animals grow and develop? How are life cycles of animals the same? How are they different? What traits of animals remain constant when they grow and develop? What animal traits change as they grow and develop? How can patterns (life cycles) help us make predictions and why is this important? How do various cultures interpret life cycles?