Outline of Chapter 1, Sections 1 and 2
advertisement

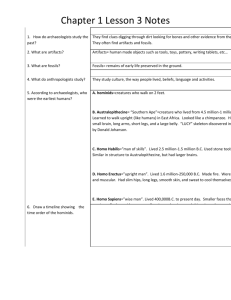
Name: Answer Key Period: ______ Honor Code: __________________ Outline of Chapter 1, Sections 1 and 2 1.1 Human Origins in Africa (pgs. 7-11) 1) Scientist Search for Human Origins a) Scientists Discover Clues i) Archaeologists are scientists who learn about early people by excavating and studying the traces of early settlements. ii) Bones reveal what people looked like, how tall they were, and how long they lived. iii) Artifacts are remains, such as tools, jewelry, and other human-made objects. iv) Anthropologists study culture, or people’s unique way of life and Paleontologists study fossils. b) Mary Leakey Finds Footprints i) In the mid-1970’s she led a scientific expedition to Tanzania, in East Africa. ii) In 1978, they discovered prehistoric footprints of humanlike beings called australopithecines. iii) Humans and other creatures that walk upright, like the australopithecines, are called hominids. c) Johanson Discovers “Lucy” i) An American anthropologist Donald Johanson was working in Ethiopia in 1974. ii) They found an unusually complete skeleton of an adult female hominid and named her Lucy. iii) She was the oldest hominid found to date and lived around 3.5 million years ago. d) Hominids in Motion i) Walking upright helped them travel distances more easily. ii) They were also able to spot threatening animals and carry food and children. iii) They had developed the opposable thumb, which let them pick up small objects and make tools. 2) Progress During the Old Stone Age i) Paleolithic Age, or Old Stone Age, lasted from 2.5 million to 8000 B.C.E. and the first stone tools date back to this era. ii) Neolithic Age, or New Stone Age, lasted from 8000 to about 3000 B.C.E. and people in this time learned to polish stone tools, make pottery, grow crops, and raise animals. a) Homo Habilis: The First Toolmaker? i) These hominids lived from 2.5 million to 1.5 million B.C.E. and were found in East Africa. ii) Their name means “man of skill” and this hominid was also called “Handy Man” iii) They were the first to make tools of lava rock to cut meat and crack open bones. b) Homo Erectus Is More Intelligent i) Another species of hominids found in East Africa, but lived from 1.6 million to 30,000 B.C.E. and were the first to migrate from Africa to India, China, Southeast Asia, and Europe. ii) They used their intelligence to develop technology - ways of applying knowledge, tools and inventions to meet their needs. iii) Homo erectus was the first to use fire to provide warmth, cook food, and scare attackers. 3) The Dawn of Modern Humans i) Homo sapiens, the species name for modern humans meaning “wise men”, possibly developed from Homo erectus. ii) They had larger brains and were classified as Neanderthals and Cro-Magnons. a) Neanderthals’ Way of Life i) This species lived from 200,000 to 30,000 B.C.E. and were found in Europe and Southwest Asia. ii) They were powerfully built and evidence suggests they tried to explain and control their world. iii) Neanderthals were resourceful and the first to develop religious beliefs and perform rituals. b) Cro-Magnons Emerge i) These hominids were found in Europe and lived from 40,000 to 8,000 B.C.E. ii) Their skeletal remains show that they are identical to modern humans. iii) They planned their hunts, which helped them survive more easily and replace the Neanderthals. c) Recent Findings Add New Knowledge i) In 1994, two fossil hunters in Ethiopia found a 2.33 million-year-old jaw and stone tools that date back before the time toolmakers were previously thought to exist. ii) In 1996, researchers dated a bone flute to the time of the Neanderthals, which hints at a new talent for that species, musical expression. 1.2 Humans Try to Control Nature (pgs. 12-16) 1) Achievements in Technology and Art a) A New Tool Kit i) People of the Paleolithic Age were nomads, those who wander from place to place instead of making permanent settlements. ii) Nomadic groups whose food supply depends on hunting animals and collecting plant foods are called hunter-gatherers. iii) Early modern humans used knives to kill game, fish hooks and harpoons to catch fish, digging sticks to pry plants loose, and special spears to kill game from a distance. b) Paleolithic Art i) Artistic creations show their world more accurately than their tools. ii) Examples are necklaces of seashells, lion teeth, and bear claws or realistic sculptures of animals. iii) The best-known examples are their cave paintings on the walls and ceilings of European caves. They drew lifelike images of wild animals using charcoal, mud, and animal blood. 2) The Neolithic Revolution i) About 10,000 years ago, people scattered seeds and the next season found new crops growing. ii) This brought about the Neolithic Revolution, or the agricultural revolution – the far-reaching changes in human life resulting from the beginnings of farming. a) Causes of the Agricultural Revolution i) Change in climate was probably a key factor with rising temperatures worldwide that provided longer growing seasons and drier land for growing wild grasses. ii) As populations rose, hunter-gatherers felt pressure to find new food sources and farming provided a steady source of food. b) Early Farming Methods i) Slash-and-burn farming, in which they cut trees or grasses and burned them to clear a field. ii) Farmers planted crops for a year or two then moved on to other areas. After the trees grew back, other farmers repeated the same process. c) Domestication of Animals i) Hunters’ expert knowledge of wild animals played a role in the domestication, or the taming of such animals as horses, dogs, goats, and pigs. ii) Farmers kept animals as a constant source of food and slowly trained them to help in the fields. d) Revolution in Jarmo i) An agricultural settlement in the Zagros Mountains of Iraq that began about 9,000 years ago. ii) This society thrived on wild wheat, barley, goats, pigs, sheep, and horses. 3) Villages Grow and Prosper a) Farming Develops in Many Places i) Africa - The Nile River Valley was important for the growth of wheat, barley, and other crops. ii) China – 8,000 years ago millet was grown and 1,000 years later they domesticated wild rice. iii) Mexico and Central America – Corm, beans, and squash were grown and developed. iv) Peru – Here, tomatoes, sweet potatoes, and white potatoes were first grown. b) Catal Huyuk i) This agricultural village was located on a fertile plain in south-central Turkey and it produced large crops of wheat, barley, and peas. ii) The people produced obsidian products, a dark volcanic rock that looks like glass. iii) Floods, fire, and drought could destroy villages. Disease and theft were other problems among wealthy villages where people lived close together.