09/10 Sem I
advertisement

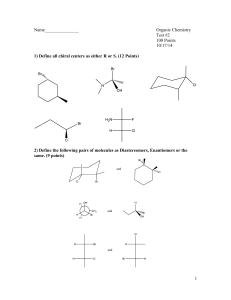
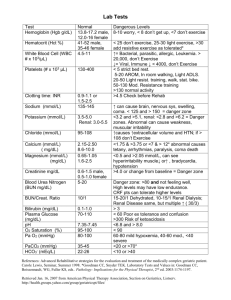
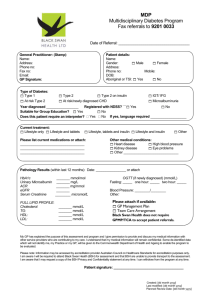
Sem 1 09/10 Nov 09 1 (a) (i) (ii) (b) (i) x = NaH z = (CH3)2CHNH2 (ii) (c) 2.(a) (i) + (ii) (b) 3<2<1 Carbon (2) is allylic from both directions, making it’s base conjugate more stable through more resonance contributors, less acidic then carbon (1) which has the same number of resonance contributors but with a more stable conjugate base due to the higher electronegativity of the oxygen atom.. (c) (d) (i) 7,7-diethyl-5-isopropyl-2,3-dimethyldecane (ii) 4-ethyl-6-(1,2-dimethylpropyl)decane (iii) 1-ethyl-2-(2,2-dimethylpentyl)cyclopentane 3. (a) The compound contains only one chirality center. Accordingly, the compound might be either of R or S assignment. Chiral center. CH 3 Cl H H H *C C C C H H CH2 CH 3 The compound also contains a carbon-carbon double bond, which may be the compound either of E or of Z assignment. Thus the four stereoisomers can be designated: Z,R; compounds are as follows H Cl Z, R CH 3 H *C C H H E,R CH 3 (b) H *C C H H E,R; C C Z,S CH2CH3 CH 3 H H *C C Cl H C H H C C CH2CH3 H CH 2CH3 C E,S. The four H H H Cl Z,S; E,S CH 3 H H *C C Cl H CH 2CH3 C C H No. Because: R/S assignment is purely a convention of nomenclature and is completely independent of the direction in which plane-polarized light is rotated by the compound. (c ) One (10.0 mL 0.10 M) millimole (mmol) of the R eneantiomer is mixed with (30.0 mL 0.10 M) mmol of the S enantiomer. ((Note: No. moles = M V)). 1 mmol of the R enantiomer plus 1 mmol of the S enantiomer will form 2 mmol of a racemic mixture. There will be 2 mmol of S enantiomer left over. Therefore, 2 mmol out of 4 mmol is excess S enantiomer (2/4 = 0.50). The solution is 50% optically pure. Optical purity = (observed specific rotation) / (specific rotation of the pure enantiomer) Optical purity = 0.50 = (+4.8) / X where X= specific rotation of the pure enantiomer Then X = (+4.8) / 0.50 = +9.6 Therefore, the S enantiomer has a specific rotation of +9.6 and the R enantiomer has a specific rotation of -9.6. (d) (i) For the first step, two bonds are broken “One bond from the cyclohexene ring and one bond from HCl” and one bond is formed. (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) The H for this step should be positive since more bonds are broken than formed. For the second step, only one bond formed “CringCl” The H for this step should be negative since one bond is formed and non is broken. Step 1 is rate determining since it is more difficult. Transition state for: H H Step1: H H 4. (a) Cl H Step 2: Cl H (b) (c ) (i) (ii) (d) Since both the 2nd and 3rd carbons are equal, hydroboration-oxidation can give both 2penten-2-ol and 2-penten-3-ol which can tautomer to the 2-pentanone and 3-pentanone respectively.