Artificial Selection and Biotechnology
advertisement

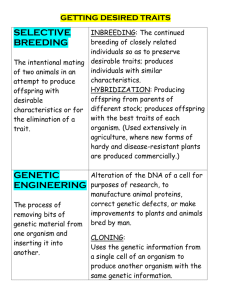
Artificial Selection and Genetic Engineering Summary Table Definition Examples Artificial Selection: The - breeding of certain dogs for protection process of selecting and - breeding dairy cattle to produce the most milk breeding animals or plants with - breeding wheat that matures quickly or resists frost desired traits to produce - Canadian Western Amber Durum wheat – good cooking qualities and yellow offspring with those traits. colour makes it ideal for pasta Biotechnology: Technology or procedures that are used to speed up or enhance artificial selection. Artificial Reproduction: - Cloning: Making an identical copy of a molecule, gene, cell or entire organism. Creation of new life by other - Artificial Insemination: Sperm is harvested from a male and inserted into than natural means. females to fertilize eggs. - In Vitro Fertilization: Sperm and eggs are harvested from male and female; the eggs are fertilized in a Petri dish; the embryo is then place into a female. Genetic Engineering: - Transgenics: Adding human genes to the fertilized egg of an animal so it will Technology that is used to produce offspring with human genes. The offspring can then produce human move the DNA from one proteins which can be used by humans organism into another, thus o e.g. insulin produced by bacteria with human gene for insulin altering the genetic makeup o e.g. iron-rich milk produced by cows with human gene lactoferrin of the 2nd organism. - Acquaculture: genes are added to fish eggs to improve offspring… such as by increasing grown rate and size, improving disease resistance, etc o e.g. ‘antifreeze’ gene is added to Atlantic salmon and halibut to allow winter fish farming - Genetically Modified Crops: crops such as wheat, corn, tomatoes and potatoes are genetically altered to improve production, reduce allergic reactions, have longer shelf life, increase nutrition, etc.