Name_______________ ______ Date______________ Per_____
advertisement

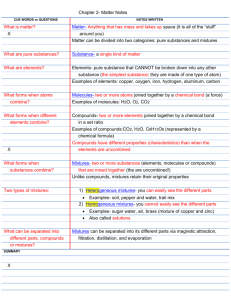
Name____________________________________________ Date________________ Per_____ Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures Elements Over time, scientists discovered that some matter is composed of pure chemicals. Pure substances are homogeneous and have certain unchanging chemical compositions. For example, a pure sample of highly condensed carbon, diamond, will always have the same crystalline structure. The repeating structural unit of diamond consists of eight atoms in cubic shapes. Using this cubic form and its highly symmetrical arrangement of atoms, diamond crystals form several different shapes. We will discuss this in more detail in Chapter 15. This cubic form and its light reflectivity make diamond one of the most desired substances on Earth. Chemicals that have the same type of matter all through the sample are said to be pure elements . Oxygen, potassium, mercury, and nickel are pure elements. During his research in 1789, Antoine Lavoisier defined an element as a substance that could not be decomposed by a chemical reaction into simpler substances. Lavoisier identified 33 elements that he thought were pure and indivisible. Of those 33, 20 of the 109 elements currently identified, are still considered pure elements. An element is made up of a pure sample with all of the same kinds of atoms and cannot be further separated into simpler elements. Mixtures Mixtures can be separated into two or more substances manually. No chemical reaction is needed. In nature, salt water can be separated into its components of water and salt by allowing the water to evaporate. Mixtures are found in two forms: heterogeneous and homogeneous . A heterogeneous mixture is one with physically separate parts that have different properties. An easy example is salt and pepper. A heterogeneous mixture has separate phases . A phase represents the number of different homogeneous materials in a sample. Salt is all one phase and pepper is one phase. They do not have a wide variety of characteristics, but are physically separate. A homogeneous solution has one phase (liquid) but may have more than one component within the sample. Again, salt water is an example of a homogeneous mixture. It is the same throughout, but has two parts: water and salt. Figure 3.3 compares matter and its different parts. Fig. 3.3. Matter can be further broken down into different divisions. Compounds Pure chemicals that can be broken down into simpler chemicals are known as compounds . Commonly, chemical compounds are made up of two elements in set proportions to each other. Water provides an easy example of a compound. It is composed of the elements hydrogen and oxygen. There are always two parts of hydrogen to one part oxygen in every molecule of water. If the water sample is from the sea or polluted, there may be other chemicals added, but basic water always has the same proportion of hydrogen to oxygen by mass. Elements Compounds Mixtures