Chapter 2 & 3: States of Matter
advertisement

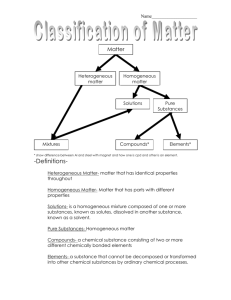
Chapter 2 & 3: States of Matter I can explain the relationship between matter, atoms, and elements I can distinguish between elements and compounds I can write chemical formulas I can distinguish between pure substances and mixtures I can identify chemical and physical properties I can compare and contrast physical changes and chemical changes I can describe four common states of matter I can list the different changes of state of matter I can state the law of conservation of mass and conservation of energy I can explain how gases differ from solids and liquids I can describe what density is and how to calculate density using an equation or graph CHAPTER 2, SECTIONS 1-3 Matter Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space Matter: Everything is Made of! There are two types of matter: • 1. Pure Substances Elements Compounds • 2. Mixtures Homogeneous (same all the way throughout) Heterogeneous (different throughout) Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space! Pure substances (can not be broken into simpler compounds and still maintain the same properties) All pure substances are homogeneous Elements Compounds (1 – simple) (2 or more) Examples: Silver Gold Oxygen Hydrogen Carbon Examples: Salt: NaCl Carbon dioxide Water MgBr2 Mixtures (made of two or more substances that can easily be separated) Homogeneous Heterogeneous (same throughout) (not same throughout) Examples: Kool-Aid Coffee Salt water The air we breathe Hershey bar Examples: Hershey bar (with almonds) Pizza Vegetable soup Salad Blood Classify the Following Examples as Heterogeneous or Homogeneous: • Hershey Bar?Homogeneous ______________________ • Snickers Bar?Heterogeneous ______________________ • Pizza? Heterogeneous ____________________________ • Italian Dressing? Heterogeneous ___________________ • Hot Chocolate? Homogeneous ____________________ Properties of Matter Used to describe or identify matter • • • • • • • • Color Shape Texture Size Melting point Boiling point Malleability Density Density A measurement of how much matter is in a certain volume of a substance • Low density = “light” • High density = “heavy” Determines if an object will sink or float Density = Mass / Volume Practice Problem #1 (density = mass/volume) List items which will float on the particular sample of ice from the previous problem: • ____________ Air • ____________ Wood Methanol • ____________ Chemical Properties Used to describe how matter reacts • • • • • Flammability Toxicity Heat of combustion Oxidation state(s) Half-Life Chemical Change vs. Physical Change Chemical Change: A change that occurs to produce new substances (cannot be reversed) Physical Change: a change that does not produce a new substance (can be reversed) Color Change Tearing Production of Heat/Light Cutting Formation of precipitate Folding Formation of a gas Painting Example: rust Melting Example: baking Freezing Example: food digestion Boiling Example: rotting Dissolving Example: leaves changing color Example: ice cube melting Classify the Following Examples as Physical or Chemical Change: • Tearing paper? Physical ____________________ • Boiling Water? Physical ____________________ • Making Kool-Aid? __________________ Physical • Teeth Rotting? ___________________ Chemical Ways to Separate a Mixture Stir with a magnet to separate magnetic from nonmagnetic materials A centrifuge is a device that separates solid from a liquid by spinning tubes in a circle like a washing machine spins. The solid particles settle to the bottom of the tube. Filtration is the removal of a solid from a liquid by the liquid passing through the pores of the filter paper, and the paper trapping the solid. CHAPTER 3, SECTION 1 Matter Changes by Adding or Removing Energy (aka heat) Matter Can NEVER be Created or Destroyed Law of Conservation of Mass • States that matter can be changed from one form into another, but the total amount of mass remains constant