file - BioMed Central
advertisement

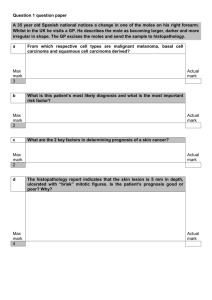
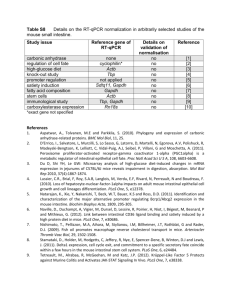
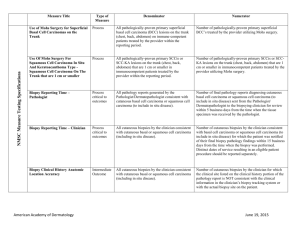
Identification of Importin 8 (IPO8) as the most accurate housekeeping gene for the clinicopathological analysis of lung specimens Paul A. Nguewa1 , Jackeline Agorreta 1 , David Blanco 1 , Maria Dolores Lozano2, Javier Gomez-Roman3, Blas A. Sanchez 4 , Iñaki Valles1, Maria J. Pajares 1, Ruben Pio1, Maria Jose Rodriguez 4 , Luis M. Montuenga 1#*, Alfonso Calvo 1# 1 Division of Oncology, Center for Applied Medical Research (CIMA), University of Navarra. Avda. Pio XII, 55. 31008 Pamplona, Spain. 2 Department of Pathology. University Hospital of Navarra. Avda. Pio XII, 36. 31008 Pamplona, Spain 3 Department of Anatomical Pathology, Marqués de Valdecilla University Hospital, Medical Faculty, University of Cantabria, Santander, Spain. 4 Research Department. Ingenasa #: Contributed equally to this paper Email addresses: PAN: panguewa@unav.es JA: jagorreta@unav.es DB: dblanco@unav.es MDL: mdlozano@unav.es JG-R: apagrj@humv.es BAS: bsanchez@ingenasa.es IV: ivalles@unav.es MJP: mpajares@unav.es RP: rpio@unav.es MJR: mjrodriguez@ingenasa.es LM*: lmontuenga@unav.es AC: acalvo@unav.es * Corresponding author: “Online Data Supplement” Sources of support: This work has been funded by “UTE project CIMA”, ISCIII-RETIC RD06/0020 grant; Cenit project ONCNOSIS, Government of Navarra. P.A.N. was supported by a Spanish Torres-Quevedo fellowship (PTQ05-01-01084) and J.A. by a fellowship from the “Instituto de Salud Carlos III”, Ministry of Health, Spain. Supplemental Table 1: Clinical characteristics of patients with lung cancer SET A SET B SET C No Sex Age (y) Diagnosis Stage Smoking 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 F F M M F F M M M F M M F M M M M M M M M M M F M M M M F M M M M M M M M 37 52 75 58 71 54 55 60 70 73 50 58 71 60 69 54 53 67 52 71 48 75 52 59 68 73 74 78 66 70 66 75 63 60 87 75 63 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Adenocarcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Adenocarcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Adenocarcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Adenocarcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Adenocarcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Adenocarcinoma IB IB IA IA IB IIIB IA IA IIB IIB IB IA IB IIIB IB IB IB IB IIIA IA IIA IB IB IB IIIA IIIA IIIA IB IB IB IB IIIA IB IB IB IIIA IB Yes No Yes Yes No No Yes Yes No No Yes Yes No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes Yes No Yes U Yes Yes Yes U Yes U Yes U: Unknown 1 Supplemental Table 2 Absolute values of ∆Ct (|∆Ct|=|Ct Normal-Ct Tumor|) of GAPDH and HPRT1 in paired lung clinical samples (Set A). Mean and Standard error of mean (SEM) were calculated. SET A No 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 GAPDH |∆Ct| 2.09 3.14 2.22 2.21 0.45* 1.17 1.97 1.12 4.99 0.83* 3.55 2.81 2.20 1.84 3.43 HPRT1 |∆Ct| 1.23 2.02 1.24 1.19 0.45* 1.59 2.22 1.75 4.37 0.06* 2.42 2.56 1.88 1.69 2.50 Mean SEM 2.27 0.31 1.81 0.26 *: Negative values 2 Supplemental Table 3 ANOVA test of three lung cancer patient microarrays (HuGene-FL, HG-U95A, HG-U133A). The raw datasets are publicly available at the website: www.affymetrix.com/products/arrays/index.affx. (*) p-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant. GAPDH HPRT1 HG-U95A (Tumor vs. Normal) Probe p-value 35905_s_at 0.000000 (*) AFFX-HUMGAPDH/M33197_3_at 0.000000 (*) AFFX-HUMGAPDH/M33197_5_at 0.000000 (*) AFFX-HUMGAPDH/M33197_5_st 0.004315 (*) AFFX-HUMGAPDH/M33197_M_at 0.000000 (*) AFFX-HUMGAPDH/M33197_M_st 0.048685 (*) AFFX-HUMGAPDH/M33197_3_st > 0.05 37640_at 0.000025 (*) 3 HuGene-FL (Tumor vs. Normal) Probe p-value AFFX-HUMGAPDH/M33197_3_at 0.000106 (*) AFFX-HUMGAPDH/M33197_3_st 0.040188 (*) AFFX-HUMGAPDH/M33197_5_at 0.000010 (*) AFFX-HUMGAPDH/M33197_5_st 0.043371 (*) AFFX-HUMGAPDH/M33197_M_at 0.000178 (*) AFFX-HUMGAPDH/M33197_M_st > 0.05 X01677_f_at 0.000010 (*) M31642_at 0.009939 (*) HG-U133A (Tumor vs. Normal) Probe p-value 212581_x_at 0.000014 (*) 213453_x_at 0.000015 (*) 217398_x_at 0.000015 (*) AFFX-HUMGAPDH/M33197_3_at 0.000075 (*) AFFX-HUMGAPDH/M33197_5_at 0.000152 (*) AFFX-HUMGAPDH/M33197_M_at 0.000005 (*) 202854_at 0.000432 (*) Supplemental Text 1. Correlation between endogenous control genes in lung tumor cell lines The four strongest correlations (**p<0.01) (See supplemental Table 4, in bold) were found between RPLPO and ACTB (r=0.970), PPIA and ACTB (r=0.969), PPIA and HPRT (r=0.949), and GAPDH and POLR2A (r=0.944). In addition, we also evaluated the number of significant correlations (**p<0.01) of each gene among the sixteen others, in lung cell lines (See supplemental Table 5). We then classified the genes in three groups depending on the number of significant correlation (NC). The ones with very good and good numbers of significant correlation were: PPIA and ACTB (NC=11/16); HPRT1, GAPDH, RPLPO (NC=9/16); and 18S (NC=8/16). Those with bad significant correlation were: UBC (NC=7/16); PGK1, POLR2A (NC=6/16), GUSB, TBP (NC=5/16), and HMBS (NC=4/16). The last group included genes with the lowest NC, thus indicating the worse correlations with other reference genes: YWHAZ (NC=3/16); B2M (NC=2/16); IPO8 and TFRC (NC=1/16). 4 A HKG 18S ACTB B2M GAPDH GUSB HMBS HPRT1 IPO8 PGK1 POLR2A PPIA RPLPO TBP TFRC UBC YWHAZ Supplemental Table 4 Correlation between sixteen reference genes in lung cancer cell lines. 18S ACTB 0.883(**) B2M 0.797 0.662 GAPDH 0.882(**) 0.933(**) 0.578 GUSB 0.808(**) 0.804(**) 0.446 0.716 HMBS 0.665 0.770 0.222 0.729 0.778 HPRT1 0.828(**) 0.906(**) 0.466 0.814(**) 0.913(**) 0.919(**) IPO8 0.574 0.363 0.239 0.498 0.657 0.288 0.388 PGK1 0.628 0.880(**) 0.423 0.807(**) 0.558 0.704 0.744 0.054 POLR2A 0.723 0.836(**) 0.317 0.944(**) 0.595 0.750 0.754 0.387 0.820(**) PPIA 0.929(**) 0.969(**) 0.641 0.931(**) 0.869(**) 0.835(**) 0.949(**) 0.479 0.765 0.826(**) RPLPO 0.869(**) 0.970(**) 0.653 0.933(**) 0.705 0.779 0.855(**) 0.307 0.895(**) 0.866(**) 0.937(**) TBP 0.607 0.826(**) 0.406 0.701 0.679 0.803(**) 0.862(**) 0.052 0.714 0.644 0.831(**) 0.757 TFRC 0.248 0.263 0.289 0.110 0.285 0.523 0.424 -0.199 0.122 -0.004 0.358 0.274 0.590 UBC 0.796 0.861(**) 0.759 0.805(**) 0.580 0.648 0.697 0.201 0.798(**) 0.656 0.817(**) 0.892(**) 0.682 0.449 Data are represented as coefficients (r-value) between each two housekeeping genes. HKG: housekeeping genes. (**) p-Values are considered significant when p<0.01. 5 YWHAZ 0.802(**) 0.712 0.815(**) 0.702 0.610 0.282 0.486 0.603 0.525 0.473 0.672 0.684 0.300 -0.009 0.768 Supplemental Table 5 Number of significant correlations (NC) (**p<0.01) of each gene over all the sixteen endogenous control genes in lung cancer cell lines. B Cell Lines (Pearson Correlation) 16 Genes NC (over 16) ACTB 11 PPIA 11 HPRT1 9 GAPDH 9 RPLPO 9 18S 8 UBC 6 PGK1 6 POLR2A 6 GUSB 5 TBP 5 HMBS 4 YWHAZ 3 B2M 2 IPO8 1 TFRC 1 6 Supplemental Text S2. Correlation between endogenous control genes in normal and tumoral lung tissues In Supplemental Table 6, correlations between endogenous control genes in lung tissues are represented as coefficients (r-value). Most of endogenous control genes were strongly correlated. The strongest correlations (**p<0.01) (Table S5, in bold) were between IPO8 and ACTB (r=0.981), PPIA and RPLPO (r=0.969), POLR2A and 18S (r=0.962), IPO8 and POLR2A, PPIA and HMBS, GAPDH and PGK1 (r=0.957), HPRT and GAPDH (r=0.956), PPIA and POLR2A (r=0.954), and PPIA and PGK1 (r=0.953). The evaluation of the numbers of significant correlation (**p<0.01) of each gene among the sixteen others in lung tissues (See Supplemental Table 7) revealed two groups of genes. Except for three genes, all the others exhibited very good or good NC, ranging from 14/16, to 11/16. The best one was IPO8 (NC=14/16). PPIA, ACTB, HMBS, POLR2A, 18S, and RPLPO had NC=13/16; HPRT, PGK1, TBP, and YWHAZ: NC=12/16; and finally, GAPDH and UBC, NC=11/16. However, the group with the worse numbers of significant correlation was: B2M and TFRC (NC=3/16), and GUSB (NC=1/16). Consequently, this analysis shows that IPO8, 18S, ACTB, POLR2A, PPIA, HMBS, and RPLPO exhibit a strong correlation expression among them (r=0.9810.953) as well as high numbers of significant correlations (NC=14-13 over the sixteen genes). 7 Supplemental Table 6 Correlation between sixteen reference genes in lung cancer tissues. HKG 18S ACTB B2M GAPDH GUSB HMBS HPRT1 IPO8 PGK1 POLR2A PPIA RPLPO TBP TFRC UBC YWHAZ 18S ACTB 0.857(**) B2M 0.644 0.802(**) GAPDH 0.756(**) 0.705 0.275 GUSB 0.486 0.616 0.268 0.520 HMBS 0.926(**) 0.819(**) 0.515 0.868(**) 0.627 HPRT1 0.715(**) 0.716(**) 0.320 0.956(**) 0.477 0.792(**) IPO8 0.908(**) 0.981(**) 0.779(**) 0.722(**) 0.581 0.848(**) 0.738(**) PGK1 0.836(**) 0.718(**) 0.281 0.957(**) 0.595 0.928(**) 0.921(**) 0.753(**) POLR2A 0.962(**) 0.945(**) 0.702 0.817(**) 0.561 0.924(**) 0.789(**) 0.957(**) 0.846(**) PPIA 0.922(**) 0.863(**) 0.485 0.932(**) 0.614 0.957(**) 0.889(**) 0.889(**) 0.953(**) 0.954(**) RPLPO 0.926(**) 0.821(**) 0.514 0.924(**) 0.421 0.923(**) 0.891(**) 0.866(**) 0.921(**) 0.941(**) 0.969(**) TBP 0.844(**) 0.721(**) 0.577 0.702 0.388 0.835(**) 0.725(**) 0.780(**) 0.757(**) 0.798(**) 0.811(**) 0.829(**) TFRC 0.526 0.441 0.096 0.746(**) 0.336 0.533 0.829(**) 0.512 0.700 0.552 0.680 0.701 0.640 UBC 0.846(**) 0.746(**) 0.715(**) 0.649 0.170 0.759(**) 0.701 0.780(**) 0.705 0.822(**) 0.741(**) 0.823(**) 0.810(**) 0.441 Data are represented as coefficients (r-value) between each two housekeeping genes. HKG: housekeeping genes. (**) p-Values are considered significant when p<0.01. 8 YWHAZ 0.894(**) 0.824(**) 0.680 0.777(**) 0.483 0.910(**) 0.698 0.863(**) 0.777(**) 0.895(**) 0.872(**) 0.884(**) 0.829(**) 0.458 0.778(**) Supplemental Table 7 Number of significant correlations (NC) (**p<0.01) of each gene over all the sixteen endogenous control genes in lung cancer tissues. Tissues (Pearson Correlation) 16 Genes NC (over 16) IPO8 14 18S 13 ACTB 13 HMBS 13 POLR2A 13 PPIA 13 RPLPO 13 HPRT1 12 PGK1 12 TBP 12 YWHAZ 12 GAPDH 11 UBC 10 B2M 4 TFRC 3 GUSB 1 9