CH332_2ndhour_exam_2008
advertisement

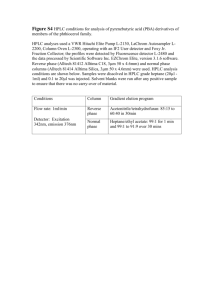
Chemistry 332 Second Hour Exam February 18, 2016 1. Which of the following is not an advantage of Fourier transform spectroscopy? (a) Fourier transform spectroscopy offers improved signal-to-noise ratio. (b) Fourier transform spectroscopy allows for the acquisition of spectra in a very short time. (c) Fourier transform spectroscopy is applicable to all important regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. 2. In GC, separation between two different solutes occurs because (a) the solutes have different solubilities in the mobile phase. (b) the solutes volatilize at different rates in the injector. (c) the solutes spend different amounts of time on the stationary phase. 3. Typical GC detectors include (a) flame ionization, thermal conductivity, electron capture, and mass spectrometer. (b) ultraviolet, fluorescence, amperometric, and conductivity. (c) spectrophotometer, refractive index, light scattering, and electrochemical. 4. A TCD or thermal conductivity detector measures the (a) ability of a substance to transport heat from a cold region to a hot region. (b) ability of a substance to transport heat from a hot region to a cold region. (c) ability of the detector to transport heat from a hot region to a cold region. 5. Normal-phase liquid chromatography refers to (a) the use of a nonpolar solvent as the eluent in HPLC. (b) the use of a polar material as the stationary phase in a chromatographic column. (c) the use of a nonpolar material as the stationary phase in a chromatographic column. 6. Reversed-phase HPLC of a multi-component solute usually uses (a) an isocratic polar solvent. (b) a gradient from more polar to less polar solvent. (c) a gradient from less polar to more polar solvent. 7. The use of smaller stationary phase particles in liquid chromatography (a) increases relative surface area, and therefore, improves resolution. (b) increases the magnitude of irregular flow paths. (c) decreases the resistance to solvent flow. 8. Which of the following statements is true for a refractive index detector in HPLC? (a) It is more sensitive than a UV detector. (b) It can only be used for isocratic elutions. (c) It does not respond to many solutes. Longer Answers 9. A single extraction with 100 mL of CHCl3 extracts or removes 88.5% of the weak acid, HA (Ka = 3.5 x 10-5), from 50 mL of aqueous solution at a pH = 3.00? If a student carries out the same extraction at a pH = 7.00 and reports that fraction remaining in the aqueous phase is 0.01, is this result is reasonable, explain? 10. You have just received a call from Rainin Instrument Company saying that they want to hire you as an instrument design specialist because of you extensive instrumental background. You accept the job, and on your first day you are asked to design an isocratic HPLC system with an IR detector. The IR detector should be able to rapidly scan the IR spectrum (4000-1000 cm-1) of the column effluent. a) Sketch the system you would build, describing each component. b) Please justify your selection of components. 11. A chromatogram of a standard test mixture produced the following results: ’ tr (min) W (min) b Peak 1 Peak 2 2.00 2.50 0.113 0.141 a) Calculate the effective number of plates for the column (Neff) from data for peak 1. b) Calculate the resolution factor (Rs) for the two peaks. 12. a) Describe how kinetic and thermodynamic processes influence chromatographic separation. b) Provide an example of a how you could change the kinetic properties of a chromatographic system. c) Provide an example of a how you could change the thermodynamic properties of a chromatographic system. 13. How is it possible to use Raman spectroscopy to measure the vibrational energy levels of a molecule using high-energy, visible light (a 632 nm laser in our case). 14. Describe how a GC thermal conductivity detector works. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this detector?