VERTEBRATES
advertisement

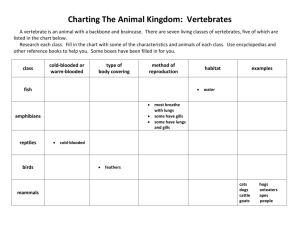
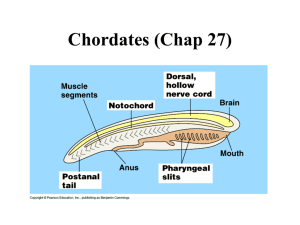
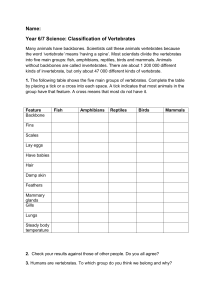
VERTEBRATES Ch. 25 & 26 Life Birds Mammals What are vertebrates? Animals with a backbone Examples: fishes, frogs, turtles, snakes, birds, alligators, mammals, etc. Vetebra comes from the Latin word vertere, meaning “to turn” Phylum Chordata Chordates are named for an embryonic structure – The notochord is a flexible rod that extends through much of the length of the body Most chordates are vertebrates, but There are two groups of invertebrates that are chordates (tunicates & lancelets) Vertebrates are Chordates Vertebrates are animals with a skull and a backbone – An endoskeleton In vertebrates, only remnants of the notochord remain Example: the cartilage discs in your backbone Most vertebrates have paired limbs What is the importance of: Skull? Backbone? Other important features Hinged Jaws – Importance? Vertebrates Hagfish and lampreys Do not have hinged jaws or paired limbs Vertebrates Fishes – Have hinged jaws – aquatic Tetrapods: Amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals Tetrapods (“four footed”) have 2 sets of paired limbs This allowed them to?? Snakes are tetrapods! They evolved to become legless Activities 1) Finish grasshopper dissection & turn in. 2) pHSuccessnet.com – Ch. 25 webquest – Activity 25.1 FISHES The 1st jawed vertebrates. 2 Categories: Cartilaginous fishes – Chondrichthyes Skeletons are flexible and made entirely of cartilage Sharks and rays Bony fishes Skeletons contain bone hardened by calcium deposits Bony Fishes Stiff skeleton made of calcium Gills to extract O2 from water – Operculum- flap that covers the gills - pumps water over the gills Lateral line system Bony Fishes Stiff scales made of bone The outer mucus allows fish to glide more easily through the water Most are carnivores Some feed upon plankton or algae (seaweed) Bony Fishes Air Sac – “swim bladder” makes fish more buoyant – Also aids in hearing by transmitting vibrations Heart ---> 2 Chambers The ventricle (1) pumps blood to the gills The atrium (2) receives blood returning from the body 2 Chamber Heart One way circuit Very basic Much slower than land vertebrates Video Life Science: Fish and Amphibians Review 1) What is the major difference between cartilaginous and bony fishes? 2) Describe the function of the lateral line system. 3) List the general characteristics of bony fishes. 4) List and contrast the 3 classes of bony fishes. Perch Dissection Perch Dissection The First Tetrapods Amphibians are descendants of four limbed ancestors that were fully aquatic 400 mya – Limbs and legs evolved in fishes– moved to land (50 million years) Leg-like limbs allowed for movement through dense marine vegetation The First Tetrapods Acanthostega have gill structures, but amphibian-like limbs Amphibians Amphibios= “living a double life” in Greek Many live in their larval stage in water and adult stage on land Eggs do not have shells so are easily dried out Water is often necessary for laying eggs Adults generally: Have Lungs Have moist skin without scales Stage of Development Tadpoles --> the larvae of amphibians Legless aquatic plant-eaters with: Gills, lateral line system, long tail Metamorphosis into adult form leads to: Lungs in place of gills Eardrums No lateral line system 4 legs ***Some amphibians do not have a terrestrial stage, some amphibians do not have an aquatic stage Other characteristics Moist skin often assists lungs with gas exchange May also contain poison glands Amphibians have a 3-chambered heart Remember fish have 2 chambered heart Allows for 2 pathways of blood flow One to the lungs and skin for gas exchange One to the other tissues Advantage?? The Atria collect blood returning to heart Ventricle pumps blood out Amphibian Diversity about 8% of vertebrates Frogs – insect eaters – Toads are terrestrial frogs Salamanders – insect eaters Caecilians Legless & blind; burrow in soil Video Life Science: Fish and Amphibians General Characteristics of Amphibians? 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) What if they were forced to live on land and have no access to water? AMNIOTES Amniotes- reptiles, birds, mammals General Characteristics: – Live on land (do not need water) – Amniotic egg – Internal fertilization – Water-tight skin Amniotic Egg Waterproof egg with a shell Amnion- protects embryo from drying out Water-tight Skin Enriched with keratin – Prevents dehydration Reptiles- scales Birds- feathers Mammals- nails, hair, horns Reptiles Reptile Characteristics Water-tight, scaly skin that molts Lungs Lay eggs Cold-blooded (ectotherms) Komodo Dragon Hunting a Water Buffalo http://dsc.discovery.com/tv/life/episodes.h tml BIRDS Ancestor- dinosaur Endothermic amniotes Adaptations for flight: – Wing shape – Feathers (also for insulation) – Several weight-reducing features Review of Frog Dissection Where is the tympanic membrane? How can you tell a male from a female? What is the cloaca? What is the purpose of the fat bodies? What are 3 differences between reptiles and amphibians? Wing Shape Airfoil-shaped wings Air-sac System Function with lungs for respiration Helps supply high level of O2 that supports a high metabolism. Also reduces density of bird Weight-Reducing Features Air-sacs Honey-combed bones Absence of some internal organs Circulatory System Efficient oxygen delivery 4-chambered heart – Adaptation for active, endothermic lifestyle MAMMALS Mesozoic era- evolved from mammal-like reptiles, therapsids Mammal Characteristics Endothermic Mammary glands- milk Hair- insulation Lungs with diaphragm 4-chambered heart Internal fertilization Mammal Diversity Monotremes- lay eggs, cloaca Mammal Diversity Marsupials- “pouched mammals” Mammal Diversity Placental Mammals- Embryo completes development within the uterus; placenta forms & feeds embryo