Biology Note Guide
advertisement

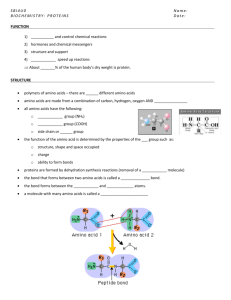
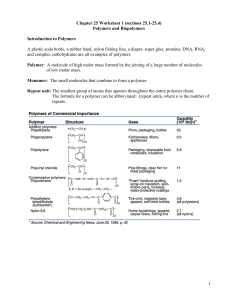
Biology Note Guide Chapter 6 Section 3 Life Substances The Role of Carbon in Organisms Carbon has ___ valence electrons. Forms ___ covalent bonds to become stable. Carbon can bond with __________________ as well as other elements. _______________ bond = share __________ electron _______________ bond = shares ___________ electrons ______________ bond = shares ____________ electrons Carbon atoms bond to make ___________________________, ___________________________, or ____________________. These structures can have almost any number of _______________________ as well as other__________________. Huge number of carbon structures possible. Isomers Compounds that have the same chemical formula but different ____________________________________ structures. Fructose and glucose = C6H12O6 Molecular Chains Carbon compounds vary greatly in size. Some contain one carbon while other have__________________. Large organic compounds are called_________________________. (Proteins) Cells build biomolecules by bonding small molecules together to form chains called______________________. Many polymers are formed by a chemical reaction known as _________________________. Polymers In condensation, the small molecules that are bonded together to make a polymer have a ___________ and an ____________ group that can be removed to form H-OH, a ______________ molecule. The subunits become bonded by a ________________ bond. These polymers can be broken apart by _______________________. Hydrolysis – Hydrogen and hydroxyl group from water attach to the bonds between subunits that make up the polymer, thus __________________the polymer. The Structure of Carbohydrates “carbohydrate loading” – eating large quantities of __________________ before vigorous activity. It works because carbohydrates are used by cells to provide __________________. Carbohydrate – biomolecule composed of ________________, _________________, and _____________________ with a ration of about ______________ hydrogen atoms and __________ oxygen atom for every ___________________ atom. Continued… Simplest type of carbohydrate is a _____________________________. (glucose and fructose) Two monosaccharides = ______________________(two-sugar carbohydrate. glucose + fructose = (____________________________) = sucrose molecule known as table sugar (disaccharide) Largest carbohydrate molecules are________________________. (many mono subunits) Polysaccharides Starch – branched chains of glucose units used as energy stored by _______________ cells and as food reservoirs in seeds and bulbs. Mammals store energy in the liver in the form of ____________________. Cellulose is another glucose polymer that forms the cell walls of plants and give plants _____________________ support. __________________ is made of long chains of glucose units linked together is arrangements somewhat like a chain-link fence. The Structure of Lipids __________________ – large biomolecules that are made mostly of carbon and hydrogen with a small amount of oxygen. Fats, oils, waxes, and steroids are all lipids. ____________________ in water because the molecules are __________________. Lipids are very important for the proper functioning of organisms. Cells use lipids for storage of ______________, ___________________, and protective _____________________. Main component of the cell __________________________ Fatty Acid fatty acid – long chain of ___________________ and __________________ A common type of lipid is linked with a molecule of glycerol. ________________________________________– each carbon chain is bonded to other carbons by ______________________ bonds. Unsaturated –____________________is present in the chain Polyunsaturated –_______________________double bond. The Structure of Proteins ____________________– large, complex polymer composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur. Proteins are essential to all life. Provide structure for tissues and organs and carry out cell___________________. _____________________ are the basic building blocks of proteins. Amino Acids _________________ common amino acids These building blocks in various combination make thousands of proteins. Amino acids are linked together when an –H from the amino group of one amino acid and an –OH from the carboxyl group of another amino amino acid are removed to form a water _______________________ . Peptide bond = covalent bond formed between the __________________ The number and sequence of amino acids that make up a protein are important to determine its shape. Some amino acids are______________________, some are basic, and some are not charged. This cause them to _______________and attract in different ways. The amino acid chain that make up proteins twists and turns as the amino acids interact. Many proteins consists of two or more amino acid chains held together by hydrogen bonds. The ultimate 3-D shape the protein folds into is extremely important to the functioning of the protein. If the sequence of the amino acids were different the protein might not be able to carry out its function in the cell. Proteins are important in the contracting of muscle tissue, transporting oxygen in the bloodstream, providing immunity, regulating other proteins, and carrying out chemical reactions. Enzyme Protein that changes the rate of _____________________________. Involved in almost all ___________________ processes. Speed reaction in food digestion Activity of enzymes depend of temperature, ionic conditions, and the pH of the surroundings. The Structure of Nucleic Acids Complex biomolecule that stores cellular information in the form of a ______________. Nucleic acids are polymers made of smaller subunits called _________________. Nucleotides consist of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus atoms arranged in three groups, - a nitrogenous base, a simple sugar, and a phosphate group. DNA = _________________ = master copy of information DNA DNA contains the instructions used to form all of an organism’s enzymes and structural proteins. Forms the ________________________that determines how an organisms looks and acts. DNA’s instructions are passed on every time a cell divides to form a new cell. RNA Another nucleic acid Forms a copy of the ___________for use in making proteins. Chemical difference between DNA and RNA is minor but important.