Collins Maths Frameworking Year 7
advertisement
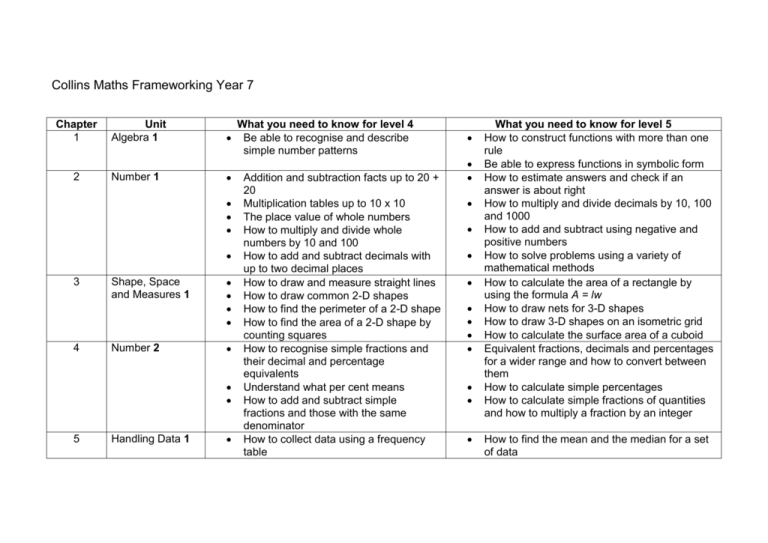
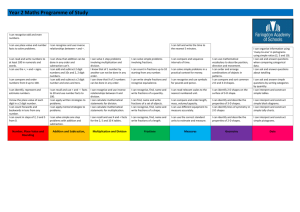
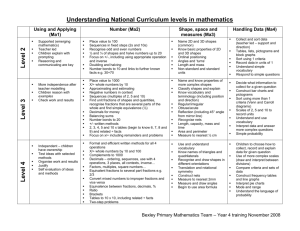
Collins Maths Frameworking Year 7 Chapter 1 2 Unit Algebra 1 Number 1 3 4 Shape, Space and Measures 1 Number 2 5 Handling Data 1 What you need to know for level 4 Be able to recognise and describe simple number patterns Addition and subtraction facts up to 20 + 20 Multiplication tables up to 10 x 10 The place value of whole numbers How to multiply and divide whole numbers by 10 and 100 How to add and subtract decimals with up to two decimal places How to draw and measure straight lines How to draw common 2-D shapes How to find the perimeter of a 2-D shape How to find the area of a 2-D shape by counting squares How to recognise simple fractions and their decimal and percentage equivalents Understand what per cent means How to add and subtract simple fractions and those with the same denominator How to collect data using a frequency table What you need to know for level 5 How to construct functions with more than one rule Be able to express functions in symbolic form How to estimate answers and check if an answer is about right How to multiply and divide decimals by 10, 100 and 1000 How to add and subtract using negative and positive numbers How to solve problems using a variety of mathematical methods How to calculate the area of a rectangle by using the formula A = lw How to draw nets for 3-D shapes How to draw 3-D shapes on an isometric grid How to calculate the surface area of a cuboid Equivalent fractions, decimals and percentages for a wider range and how to convert between them How to calculate simple percentages How to calculate simple fractions of quantities and how to multiply a fraction by an integer How to find the mean and the median for a set of data How to find the mode and range for a set of data How to read and interpret statistical diagrams 6 Algebra 2 7 Shape, Space and Measures 2 How to use simple formulae expressed in words How to solve simple equations Understand the rules (conventions) of algebra Use and interpret coordinates in the first quadrant 8 Handling Data 2 9 Number and Measures 3 How to collect discrete data and record them using frequency tables How to group data, where appropriate, into equal class intervals How to represent collected data in frequency diagrams, and interpret them The order in which the four operations must be used How to round numbers to the nearest 10, 100 and 1000 The names and abbreviations of units in everyday use and how to solve How to find the mean from a frequency table How to interpret pie charts How to calculate probability using equally likely outcomes How to calculate probability from experimental data How to construct, express in symbolic form and use simple formulae, involving one or two operations How to simplify expressions and expand brackets How to solve equations The language associated with angle The sum of the angles in a triangle and of angles around a point Use and interpret coordinates in all four quadrants How to compare two simple distributions How to interpret graphs and diagrams, and draw conclusions Recognise the need for care when setting class boundaries How to multiply and divide a three-digit whole number by a two-digit whole number The order in which the four operations must be used How to round numbers to one decimal place How to make estimates of calculations 10 Algebra 3 11 Shape, Space and Measures 3 12 13 Number 4 Algebra 4 Shape, Space and Measures 4 Handling Data 3 How to work out simple fractions How to work out simple percentages Recognise simple proportions of a whole How to solve simple problems with some algebraic content How to use simple formulae and rules expressed in words How to find the order of rotational symmetry of a shape How to reflect simple shapes in a mirror line How to collect data and record it in a frequency table Understand and be able to use the range to describe a set of data 15 14 problems using these Be able to recognise the square numbers up to at least 12 x 12 Be able to recognise the first few triangle numbers How to find square roots using a calculator Be able to recognise the different types of angle The names of the different types of triangle and quadrilateral How to generate coordinates from a simple linear rule How to plot the graphs of simple linear functions, where y is given in terms of x How to draw and measure angles How to construct triangles from given information Understand the geometrical properties of 2-D shapes How to solve simple problems using ratio and direct proportion The link between a proportion and the equivalent decimal, fraction and percentage How to construct simple formulae from problems How to express simple problems algebraically How to use algebra to help to solve problems Be able to recognise and visualise transformations of 2-D shapes: o Reflections o Rotations o Translations How to compare two distributions using the mean and the range, and to draw conclusions How to construct and interpret pie charts How to calculate probabilities based on 16 Number 5 17 Algebra 5 18 Shape, Space and Measures 5 How to solve problems and apply mathematics to practical contexts How to present results in a clear and organised way How to use simple fractions and percentages to describe proportions of a whole How to use a simple formula expressed in words How to use and interpret coordinates in a simple graph How to solve simple equations The names of and how to draw common 2-D shapes How to construct simple 3-D shapes experimental evidence How to carry through a task and solve mathematical problems, and identify and obtain the necessary information How to check results and describe situations using mathematical symbols, words and diagrams How to calculate fractions and percentages of quantities and of measurements How to construct and use simple formulae How to use and interpret coordinates derived from real-life situations How to solve equations involving two stages How to solve simple problems using algebra Be able to identify the symmetry of 2-D shapes How to use the geometrical properties of 2-D shapes How to construct more complex 3-D shapes