Meteorology Assessment
advertisement

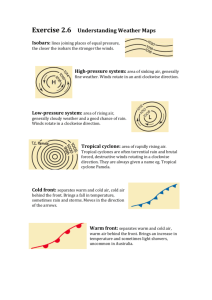
Study guide for Meteorology Assessment Study the composition of Earth’s Atmosphere. Be able to identify the most abundant gases. Study the layers of the atmosphere and know how the temperature changes within each. Also be able to place the ionosphere and ozone layer in the proper layer. Describe the process of creating a cloud. Including: Relative Humidity, CCN, Temperature, Dew Point, Coalescence, etc. Describe the temperature profile that produces rain, snow, sleet, freezing rain. Define orographic lifting and explain the effects on climate due to rain shadows. Explain the Coriolis Effect and differentiate between the results in the northern and southern hemisphere. Compare and Contrast high and low pressure areas. How do the winds blow around each? What type of weather is produced by each? How is weather information gathered? Temp, Humidity, Dew Point, Wind, Upper Air, Pressure Understand the symbols on a weather map: Fronts, Isobars, Isotherms, H, L, Describe the wind patterns associated with H/L pressure systems as indicated by isobars. Severe Weather: Thunderstorm, Severe Thunderstorm, Supercell Thunderstorms, Hurricanes, Floods, Winter Storm, Watches / Warnings Describe hurricanes: where they form, where the strongest winds are located, how the wind flows, where the storm surge is, how they are categorized. Name a greenhouse gas released by the burning of fossil fuels. Know the four factors that affect climate. Know the three major divisions of climate and what latitudes they cover. Know the conditions required to produce a thunderstorm. Be able to interpret a weather map. Using fronts, wind barbs, isobars, etc.