Sample Unit of Focus Lessons: Place Value Grade: Primary Monday
advertisement
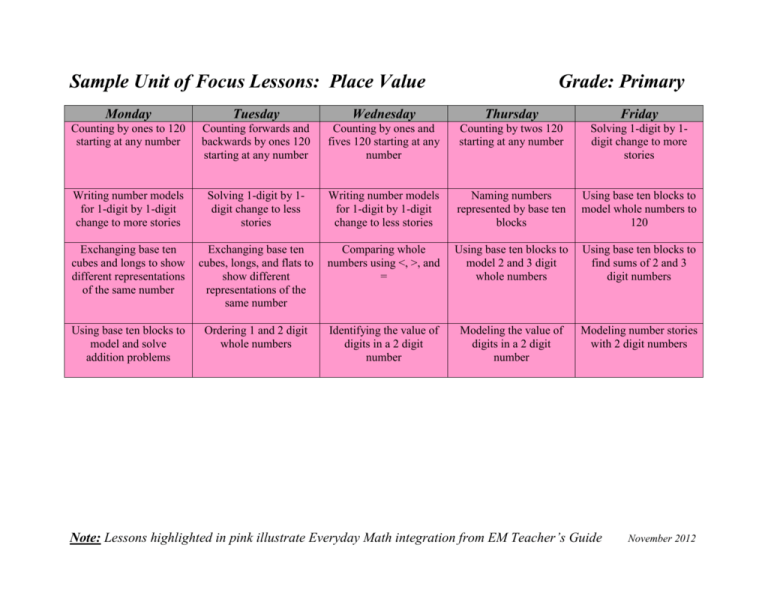
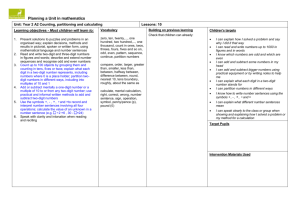
Sample Unit of Focus Lessons: Place Value Grade: Primary Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Counting by ones to 120 starting at any number Counting forwards and backwards by ones 120 starting at any number Counting by ones and fives 120 starting at any number Counting by twos 120 starting at any number Solving 1-digit by 1digit change to more stories Writing number models for 1-digit by 1-digit change to more stories Solving 1-digit by 1digit change to less stories Writing number models for 1-digit by 1-digit change to less stories Naming numbers represented by base ten blocks Using base ten blocks to model whole numbers to 120 Exchanging base ten cubes and longs to show different representations of the same number Exchanging base ten cubes, longs, and flats to show different representations of the same number Comparing whole numbers using <, >, and = Using base ten blocks to model 2 and 3 digit whole numbers Using base ten blocks to find sums of 2 and 3 digit numbers Using base ten blocks to model and solve addition problems Ordering 1 and 2 digit whole numbers Identifying the value of digits in a 2 digit number Modeling the value of digits in a 2 digit number Modeling number stories with 2 digit numbers Note: Lessons highlighted in pink illustrate Everyday Math integration from EM Teacher’s Guide November 2012 Unit Resources End of Unit Outcomes At end of this unit students will be able to: (2011 MA Curriculum Framework for Mathematics) Number and Operations in Base Ten 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Count to 120, starting at any number less than 120. In this range, read and write numerals and represent a number of objects with a written numeral. Understand that the two digits of a two-digit number represent amounts of tens and ones. Understand the following as special cases: a. 10 can be thought of as a bundle of ten ones—called a “ten.” b. The numbers from 11 to 19 are composed of a ten and one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, or nine ones. c. The numbers 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90 refer to one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, or nine tens (and 0 ones). Compare two two-digit numbers based on meanings of the tens and ones digits, recording the results of comparisons with the symbols >, =, and <. Add within 100, including adding a two-digit number and a one-digit number, and adding a two-digit number and a multiple of 10, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method and explain the reasoning used. Understand that in adding two-digit numbers, one adds tens and tens, ones and ones; and sometimes it is necessary to compose a ten. Given a two-digit number, mentally find 10 more or 10 less than the number, without having to count; explain the reasoning used. Subtract multiples of 10 in the range 10–90 from multiples of 10 in the range 10–90 (positive or zero differences), using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method and explain the reasoning used. Note: Lessons highlighted in pink illustrate Everyday Math integration from EM Teacher’s Guide November 2012 Mathematical Practices By the end of this unit, students will be able to: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4. Model with mathematics. 5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 6. Attend to precision. 7. Look for and make use of structure. 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Sample List of Integrated Everyday Math Lessons (From Grade 1 Teacher’s Guide) For adaptation as focus lessons in this unit Everyday Math Games For use during Independent Problem-Solving connected to this unit 1.1 Daily Routines 2.11 Number Models 2.12 Subtraction Number Models 5.1 Place Value: Tens and Ones 5.2 Place Value with Calculators 5.3 Relations: Greater Than, Less Than, Equal To 5.5 Animal Weights 5.6 More Than and Less Than Number Stories 5.8 Solving Number Stories 9.3 Number Grid Puzzles 1.2 Monster Squeeze 2.11 Nickel Penny Grab 2.12 High Roller 5.1 Digit Game: Top It 5.3 Base Ten Exchange 5.5 Shaker Addition Top It: Beat the Calculator Note: Lessons highlighted in pink illustrate Everyday Math integration from EM Teacher’s Guide November 2012