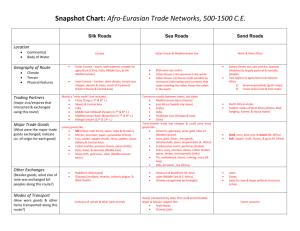
Trade Routes & their Connections
advertisement
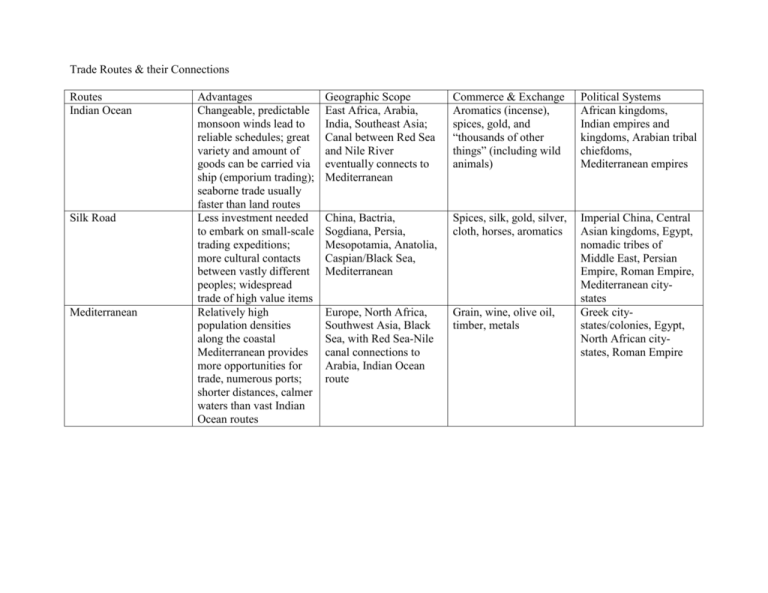
Trade Routes & their Connections Routes Indian Ocean Silk Road Mediterranean Advantages Changeable, predictable monsoon winds lead to reliable schedules; great variety and amount of goods can be carried via ship (emporium trading); seaborne trade usually faster than land routes Less investment needed to embark on small-scale trading expeditions; more cultural contacts between vastly different peoples; widespread trade of high value items Relatively high population densities along the coastal Mediterranean provides more opportunities for trade, numerous ports; shorter distances, calmer waters than vast Indian Ocean routes Geographic Scope East Africa, Arabia, India, Southeast Asia; Canal between Red Sea and Nile River eventually connects to Mediterranean Commerce & Exchange Aromatics (incense), spices, gold, and “thousands of other things” (including wild animals) Political Systems African kingdoms, Indian empires and kingdoms, Arabian tribal chiefdoms, Mediterranean empires China, Bactria, Sogdiana, Persia, Mesopotamia, Anatolia, Caspian/Black Sea, Mediterranean Spices, silk, gold, silver, cloth, horses, aromatics Europe, North Africa, Southwest Asia, Black Sea, with Red Sea-Nile canal connections to Arabia, Indian Ocean route Grain, wine, olive oil, timber, metals Imperial China, Central Asian kingdoms, Egypt, nomadic tribes of Middle East, Persian Empire, Roman Empire, Mediterranean citystates Greek citystates/colonies, Egypt, North African citystates, Roman Empire