Answers - Afro-Eurasian Trade Networks, 500-1500
advertisement
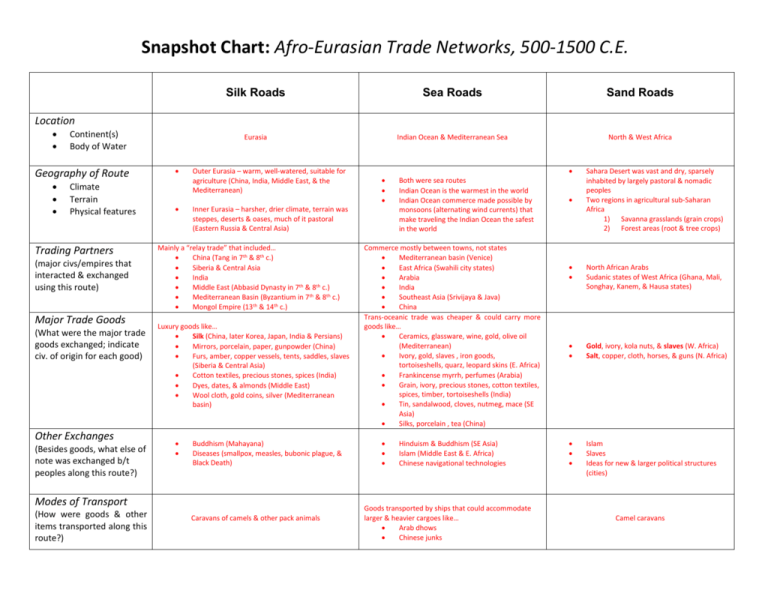
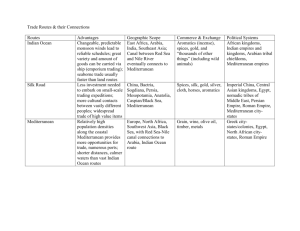
Snapshot Chart: Afro-Eurasian Trade Networks, 500-1500 C.E. Silk Roads Sea Roads Sand Roads Eurasia Indian Ocean & Mediterranean Sea North & West Africa Location Continent(s) Body of Water Geography of Route Climate Terrain Physical features Trading Partners (major civs/empires that interacted & exchanged using this route) Major Trade Goods (What were the major trade goods exchanged; indicate civ. of origin for each good) Other Exchanges (Besides goods, what else of note was exchanged b/t peoples along this route?) Outer Eurasia – warm, well-watered, suitable for agriculture (China, India, Middle East, & the Mediterranean) Inner Eurasia – harsher, drier climate, terrain was steppes, deserts & oases, much of it pastoral (Eastern Russia & Central Asia) Mainly a “relay trade” that included… China (Tang in 7th & 8th c.) Siberia & Central Asia India Middle East (Abbasid Dynasty in 7th & 8th c.) Mediterranean Basin (Byzantium in 7th & 8th c.) Mongol Empire (13th & 14th c.) Luxury goods like… Silk (China, later Korea, Japan, India & Persians) Mirrors, porcelain, paper, gunpowder (China) Furs, amber, copper vessels, tents, saddles, slaves (Siberia & Central Asia) Cotton textiles, precious stones, spices (India) Dyes, dates, & almonds (Middle East) Wool cloth, gold coins, silver (Mediterranean basin) Buddhism (Mahayana) Diseases (smallpox, measles, bubonic plague, & Black Death) Modes of Transport (How were goods & other items transported along this route?) Caravans of camels & other pack animals Both were sea routes Indian Ocean is the warmest in the world Indian Ocean commerce made possible by monsoons (alternating wind currents) that make traveling the Indian Ocean the safest in the world Commerce mostly between towns, not states Mediterranean basin (Venice) East Africa (Swahili city states) Arabia India Southeast Asia (Srivijaya & Java) China Trans-oceanic trade was cheaper & could carry more goods like… Ceramics, glassware, wine, gold, olive oil (Mediterranean) Ivory, gold, slaves , iron goods, tortoiseshells, quarz, leopard skins (E. Africa) Frankincense myrrh, perfumes (Arabia) Grain, ivory, precious stones, cotton textiles, spices, timber, tortoiseshells (India) Tin, sandalwood, cloves, nutmeg, mace (SE Asia) Silks, porcelain , tea (China) Hinduism & Buddhism (SE Asia) Islam (Middle East & E. Africa) Chinese navigational technologies Goods transported by ships that could accommodate larger & heavier cargoes like… Arab dhows Chinese junks Sahara Desert was vast and dry, sparsely inhabited by largely pastoral & nomadic peoples Two regions in agricultural sub-Saharan Africa 1) Savanna grasslands (grain crops) 2) Forest areas (root & tree crops) North African Arabs Sudanic states of West Africa (Ghana, Mali, Songhay, Kanem, & Hausa states) Gold, ivory, kola nuts, & slaves (W. Africa) Salt, copper, cloth, horses, & guns (N. Africa) Islam Slaves Ideas for new & larger political structures (cities) Camel caravans