Tissues Student Notes
advertisement

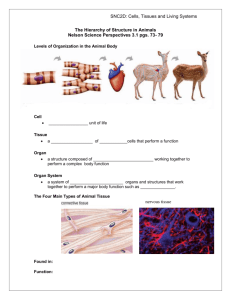
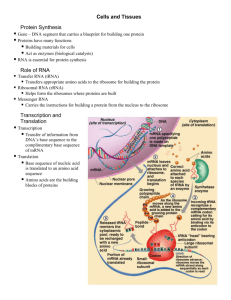
CHAPTER 5: TISSUES Tissues A tissue is composed of ____________ that are specialized to perform a _____________________ Four adult primary types of tissues form the "fabric" of the human organism: 1. 2. 3. 4. __________ tissues (ET; covering/lining); ___________ tissues (CT; support); ___________ tissues (MT; movement); ____________ tissues (NT; control). Surrounding all body cells is ____________________ Functions: Medium to _______________; ______________ Site of _______________. Epithelial Tissue Tissue that always faces a ____________; ___________________ Examples: __________________________ Cells are ___________________ of one another Part of cells opposite the free surface attaches to a __________ ________________________ Basement membrane membrane packed with ___________ ______________________ 5-1 CHAPTER 5: TISSUES Types of Epithelial Tissue 1. Simple _______________ of cells Used for ______________________________ 2. Stratified _________________ cell layers Used for ___________________ 3. Pseudostratified single, _______________________ Usually ______; _______________ across cell surface Shapes of Epithelial Cells 1. Squamous epithelial --> __________________ 2. Cuboidal epithelial ____________________ 3. Columnar epithelial ______________________ Putting It Together Simple Squamous cells lining of ____________________ Simple Cuboidal Cells __________________________ Simple Columnar Cells ___________________________ Stratified Squamous Cells _________________ Stratified Cuboidal Cells ducts of ___________________ Stratified Columnar Cells ducts of ___________________ Pseudostratified Columnar Cells ___________________ Epthelial Tissue contains_______________________. Regeneration: _____ regeneration capacity, due to _____cell division 5-2 CHAPTER 5: TISSUES Glands Glands cells that ___________; made from ______________ Exocrine Glands secrete substances to the _____________ ________________ cells through ducts Example: Goblet Cells secrete ________________ ___________________________ Endocrine Glands secrete substances _________________ Example: __________are released directly into ____________ _________________________________ Membranes Membranes ____________________ over organs Mucous Membranes line the ____________________ systems; have ducts that release mucous Serous Membranes _____________________Connective Tissues Connective Tissue Most ________________ in the body Small numbers of cells embedded with connective _______________________________________ Collagen structural protein fibers give __________ ____________________ Fibroblasts secrete _________ substance; gives __________________________ Elastin ________________ that allow for ________ 5-3 CHAPTER 5: TISSUES All connective tissue has the ____________, just in ________________________ Loose Connective Tissue Many Cells; few __________ ____________________ Fibers are _______ arranged ______________________ are the most common cells Surrounds _______________________ Dense Irregular Connective Tissue Lots of ____________________________ Deep regions of the _____________ Dense, Regular Connective Tissue Collagen fibers ________________________ Creates strong attachments _____________________ Found in ___________________________-Cartilage & Bone Cartilage type of connective tissue that ________________ ________________of body parts Structure of Cartilage Stretchable fibers similar in texture to ________. Newly divided cells are called _______________; mature into ______________________ Very few blood vessels _______________________________ 5-4 CHAPTER 5: TISSUES Types of Cartilage Hyaline Cartilage Consists of ______________. Found where ______________________ or at joints in the body Reduces __________________________ Found on either ___________________________________ Elastic Cartilage Consists of _____________________; also some _____________ Found in parts of the body where ______________is important Found in outer edge of ________________________________ Fibrocartilage ___________________________; can withstand ___________________________ Densely packed ________________________ Found in _________________________________Bone ____________________ tissue of body Bones are joined _______________to bring about movement Bones store ________ & produce some kinds of ________ 5-5 CHAPTER 5: TISSUES Bones made from densely packed ________________ and _______________________ Inside fibers are __________, cavities that contain the ___________________________________Bone is innervated by ______________________________ Types of Bone Compact Bone Found on the ____________________, embedded with lots of ___________________________ Spongy Bone Found at the _____________________, loosely packed _________________________________- Muscles & Nerves Muscles tissues that __________________ move body parts Fibers are arranged in ____________________________ Skeletal Muscle Muscle attached to ___________ Individual cells are called _________________ Each cell has _________________, caused from the fusion of juvenile muscle cells Proteins are embedded in the muscle fibers (called ______ ___________________ 5-6 CHAPTER 5: TISSUES Actin & Myosin form _____________________ that make it _____________ Fibers are bundled together in _____________ & wrapped in ________________________ Smooth Muscle muscle of ______________________, & internal organs _________Actin & Myosin fibers, _________________ Maintains ____________________________________ Often called __________________________Cardiac Muscle ____________like skeletal muscle _______________ like smooth muscle Muscle fibers are ____________________ by specialized fibers called ______________________Nerve Tissue Nerve Tissue exercises ____________over body’s activities Individual cells called _________________ Structure of Neurons Main Structure is cell body Dendrites __________________ that pick up incoming chemical information Axons “arms” that ___________ chemical information Nerve _______________________Sensory Neurons Used to detect ____________________ Examples _______________________________________ 5-7 CHAPTER 5: TISSUES 5-8