RBC Morphology on a Peripheral Smear
advertisement

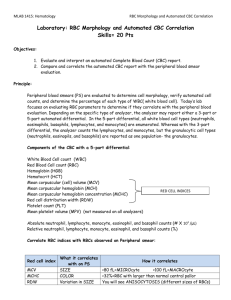
MLAB 1415: Hematology RBC Morphology on a Peripheral Blood Smear Laboratory: RBC Morphology on a Peripheral Blood Smear Skills= 20 pts Objectives: 1. Identify examples of abnormal red blood cell (RBC) morphology and inclusions. 2. To determine within one qualitative unit the abnormal red blood cell morphology observed on a peripheral blood smear. Principle: Peripheral blood smears are evaluated to determine cell morphology, verify automated cell counts, and determine the percentage of each type of WBC. Today’s lab focuses on identifying red blood cell inclusions and abnormal RBC morphology. Reagents, Supplies, and Equipment: 1. Prepared slides 2. Microscope, immersion oil and lens paper Procedure: 1. Place a Wright stained slide on stage. 2. Using the 10X objective, find an area where 50% of the RBCs are slightly overlapping and 50% of the RBCs are not touching (toward the feathered edge). The red blood cells should have a central pallor. Avoid areas where holes in the blood smear are seen or the RBCs look flat, large and distorted. Also, avoid thicker areas of the smear where the RBCs appear to have rouleaux. 3. Using the turret, switch to the 100X oil objective, add oil, and focus on the red blood cells. 4. In at least 10 consecutive fields, observe the number of inclusions, and/or examples of abnormal RBC morphology. If abnormalities are observed, calculate the average number observed per field. 5. Semi-quantitate any variation from normal morphology using the tables below. 6. If no significant RBC morphology is seen, report RBC morphology as “Normal”. 7. Record results on results form below. 8. Repeat with a second slide. MLAB 1415: Hematology RBC Morphology on a Peripheral Blood Smear Procedural notes: RBC inclusions and morphology definitions Variation Abnormality Description Anisocytosis Variation in RBC size Poikilocytosis Variation in RBC shape (clarify particular variation such as 1+schistocytes, 2+ codocytes) Abnormal Size Description Microcytosis Abnormally small RBC with MCV <80fL and diameter less than 7.0 µm Macrocytosis Abnormally large RBC with MCV >100fL. Abnormal Color Hypochromia Polychromasia Abnormal Shape Echinocyte or Burr Cell (Crenated RBC) Drepanocyte (Sickle cell) Schistocyte or schizocyte (cell fragment) Description Enlarged area of pallor due to cell’s decreased hemoglobin content Bluish/purple hue in young RBCs due to residual RNA Description RBCs with many blunt spicules. This can be caused by biologic reasons (uremia, Vit. E deficiency abetalipoproteinemia, postsplenectomy) or artifactual (slow drying, old RBCs, in thick area of slide). Do not grade these cells in the thick area of the slide. Elongated cell with point on each end; may be curved or S-shaped. Fragmented erythrocyte in many shapes and sizes; can display pointed extremities HELMET CELL (bite cell) Special schistocyte; Results from RES taking a “bite” out of RBC. Looks like 1920s football helmet. Codocyte (target cell) Bull’s eye looking RBC. Central concentration of hemoglobin surrounded by colorless area with peripheral ring of hemoglobin. May also be bell or cup shaped. See atlas. MLAB 1415: Hematology Dacryocyte (Tear drop cell) Stomatocyte RBC Morphology on a Peripheral Blood Smear RBC shaped like a tear or pear. Before reporting make sure that they are not artifactual due to slide preparation (all pointing same direction) RBC with slitlike (smile) area of central pallor. Acanthocyte (spur cell) RBC with irregularly spaced projections that vary in width, length and number. Elliptocyte or Ovalocyte Ellipto: cigar-shapped RBC Ovalo: egg-shaped RBC Spherocyte Inclusions Hemoglobin C crystal Small, globular, completely hemoglobinated RBC without central pallor Descriptions Dark red hexagonal RBC inclusion Basophilic stippling Bluish-black granules (Wright’s stain) in RBCs from precipitating ribonucleoproteins and mitochondrial remnants in toxic states (lead poisoning) Howell-Jolly bodies Dark purple spherical granule near periphery of RBC composed of remnants of DNA Pappenheimer bodies Cluster of iron-containing particles usually found at the periphery of mature RBCs Malaria Arrangement Rouleaux Agglutination Can appear as rings within RBC Descriptions Stacked coin appearance of RBCs (in the examining area of the smear) Clusters of RBCs due to presence of a coldacting antibody against red cells MLAB 1415: Hematology RBC Morphology on a Peripheral Blood Smear RBC Morphology Grading System/hpf (100X oil) Abnormality Anisocytosis Poikilocytosis Slight 1+ 2+ 3+ <15% Variation Abnormality 15-25% 26-49% <1 If > SLT, Grade each type of abnormal shape 50-89% Abnormal Size OCC/Few Without CBC: 25% smaller than nucleus of small lymph Without CBC: 26-49% smaller than nucleus of small lymph Without CBC: ≥50% smaller than nucleus of small lymph MCV 75-79 MCV 70-75 MCV <70 Without CBC: 25% larger than nucleus of small lymph Without CBC: 26-49% larger than nucleus of small lymph Without CBC: ≥50% larger than nucleus of small lymph MCV 100-150 MCV 105-110 MCV >110 Without CBC: 25% larger area of central pallor Without CBC: 26-49% larger area of central pallor Without CBC: ≥50% larger area of central pallor 2 MCHC 28-31 3-4 MCHC 24-27 5-7 <24 >8 <1 Abnormal Shape 1-3 4-5 >5 1-2 3-4 5-7 ≥8 <1 1-3 4-5 >5 <1 1-3 4-5 >5 <1 1-3 4-5 >5 <1 1-3 4-5 >5 <1 <1 1-3 1-3 4-5 4-5 >5 >5 2 3-4 5-7 >8 Microcytosis OCC/Few Macrocytosis 4+ Reserved for extreme cases where 90-100% of the cells are abnormal Abnormal Color Few Hypochromia Polychromasia Echinocyte or Burr Cell (Crenated RBC) Codocyte (target cell) Schistocyte or schizocyte (cell fragment) Helmet cell (bite cell) Drepanocyte (Sickle cell) Dacryocyte (Tear drop cell) Stomatocyte Acanthocyte (spur cell) Elliptocyte or Ovalocyte Reserved for extreme cases where 90-100% of the cells are abnormal MLAB 1415: Hematology Spherocyte 2 RBC Morphology on a Peripheral Blood Smear 3-4 5-7 >8 Inclusions <1 1-3 4-5 >5 Basophilic stippling <1 1-3 4-5 >5 Howell-Jolly bodies <1 1-3 4-5 >5 <1 1-3 4-5 >5 Rouleaux <10% Agglutination <10% Arrangement 10 -25% 10 -25% 25%-50% 25%-50% ≥50% ≥50% Hemoglobin C crystal Pappenheimer bodies MLAB 1415: Hematology RBC Morphology on a Peripheral Blood Smear Name: _________________ Date:__________________ Laboratory: RBC Morphology on a Peripheral Smear Report Form 20 pts Slide # or Patient Name Abnormal variation (aniso/ poik) Abnormal Size Abnormal Shapes Inclusions/ RBC Color MLAB 1415: Hematology RBC Morphology on a Peripheral Blood Smear Name: _________________ Date:__________________ Laboratory: RBC Morphology on a Peripheral Smear Study Questions 11 pts. 1. Poikilocytosis is the term for variation in _________________. 2. Microcytes are defined as having an MCV less than ____________. 3. Howell-Jolly bodies are composed of ________________. 4. According to the ACC RBC morphology grading scheme, if an average of 7 bluish-purple young RBCs were observed in 10 100x/oil fields, what morphology abnormality would you document and how would you grade it? (2pts) 5. According to the ACC RBC morphology grading scheme, if an average of 40% of the RBCS in 10 100x/oil fields had a significantly larger than normal central pallor, what morphology abnormality would you document, and how would you grade it? (2pts) 6. Pappenheimer bodies are composed of __________. 7. A schistocyte is also known as a cell ______________. 8. A sickle cell is also known as a ____________. 9. What causes agglutination on the blood smear?