file - European Urology
advertisement

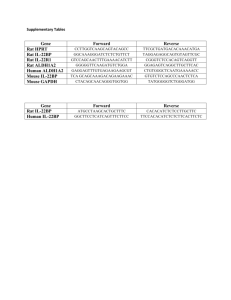
Supplementary Table 1 – Foundation Medicine gene content: 182 genes sequenced across entire coding sequence and 14 genes sequenced across selected introns Supplementary Table 2 – Bacterial artificial chromosome probes used for fluorescence in situ hybridization Supplementary Table 3 – Clinical characteristics Supplementary Table 4 – Summary of known somatic alterations and androgen receptor gene (AR) variation found by next-generation sequencing Supplementary Table 5 – Summary of the mutational spectrum of castration-resistant prostate cancer POS = positive; AMP = amplification; MUT = mutation; DEL = homozygous deletion; TRUNC = truncation. Supplementary Table 6 – Validation studies FISH = fluorescence in situ hybridization; T = translocation, T+D = translocation + deletion, D = deletion; T2ERG = TMPRSS2-ERG fusion; LOH = loss of heterozygosity, Homo Del = homozygous deletion; TRUNC = truncation; AMP = amplification; MUT = point mutation. Although the Foundation Medicine platform is capable of detecting LOH, only homozygous deletions are reported. Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1 Fluorescence in situ hybridization assay showing representative examples of tissue confirmation of ERG gene fusion using breakapart assay (upper left panel), copy number loss of PTEN (upper right panel) and BRCA2 (lower right panel), and copy number gain of AR (lower left panel) using methodology described in Materials and Methods. Green probes are centromeric reference probes. BAC probes are listed in Supplementary Table 2. Supplementary Figure 2 Matched primary tumor and metastasis from a patient. Next generation sequencing of the primary Gleason 5+4 tumor revealed TMPRSS2:ERG gene fusion and TP53 mutation. Soft tissue metastasis removed approximately 3 years later in the setting of metastatic CRPC revealed adenocarcinoma with neuroendocrine differentiation. The metastatic tumor (both neuroendocrine and adenocarcinoma foci) also harbored TMPRSS2:ERG gene fusion and the TP53 mutation, concordant with the original adenocarcinoma mutation profile. Supplementary Figure 3 A matched hormone naïve metastatic sample and CRPC metastasis (obtained three years later) demonstrated concordance in ERG gene fusion (both negative) and BRCA2 deletion (both positive) status, but RB loss and TP53 mutation were present only in the CRPC tumor suggesting that these were later events in this case.