Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis Vocabulary - Biology 12
advertisement

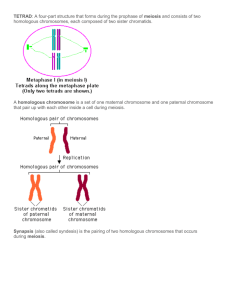
Vocabulary-Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis Biology 12 Allen Cell cycle Centromere Crossing over Cytokinesis Chiasmata Chromatid (G1, S, G2, M) a region on a chromosome that joins two sister chromatids when segments of homologous chromosomes are exchange (AKA homologous recombination) The cytoplasmic division of a cell at the end of mitosis or meiosis The point at which paired chromosomes remain in contact after crossing over during meiosis Each of the two threadlike strands into which a chromosome divides longitudinally during cell division. Each contains a double helix of DNA Diploid Containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent. Equatorial plate The plane located midway between the poles of a dividing cell during the metaphase stage of mitosis or meiosis Haploid The number of chromosomes in a sperm or egg. Interphase The phase between successive mitotic divisions of a cell. Includes G1, S, G2 Kinetochore proteins located at the centromere to which kinetochore microtubules attach during mitosis and meiosis Kinetochore microtubule a microtubule that attaches to kenetochores. Responsible for allighing replicated chromosomes and separating sister chromatids. Meiosis A type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each with half the chromosome number (n) of the parent cell Mitosis A type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each the same as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth p arm The short arm of a chromosome ploidy The number of sets of chromosomes in a cell q arm The long arm of a chromosome recombinant chromosomes chromosomes that have exchanged material with their homologous counterparts. Sister chromatid Two identical copies of a chromatin connected by a centromere Somatic cell Any cell of a living organism other than the reproductive cells Synapsis The side-by-side association of homologous paternal and maternal chromosomes during the prophase I of meiosis Tetrad A four-part structure that forms during the prophase I of meiosis and consists of two homologous chromosomes, each composed of two sister chromatids Zygote A diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum