BACTERIAL CATALASE AND CYTOCHROME OXIDASE TESTS
advertisement

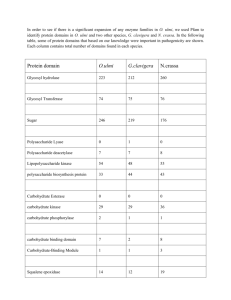
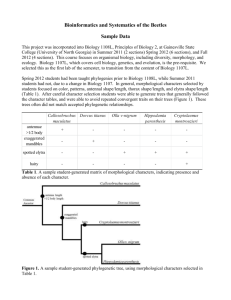
BACTERIAL CATALASE AND CYTOCHROME OXIDASE TESTS— IDENTIFYING MICROBIAL ABILITY TO USE RESPIRATORY METABOLISM Respiratory metabolism results in the conversion of glucose into energy in the form of ATP by the processes of glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. In the process of respiratory metabolism, most of the ATP is generated as a result of the activity of the electron transport system. The electron transport system is composed of membrane associated molecules (cytochromes or flavoproteins) that accept and donate electrons. Reduced NADH and FADH from glycolysis and Kreb’s cycle enter at or near the top of the electron transport chain and reduce the first molecule in the chain as they are concurrently re-oxidized. As electrons are passed down the chain of the electron transport system, each molecule in the chain alternate between reduced and oxidized forms. Cytochrome oxidase is found at the bottom of this chain, cytochrome oxidase catalyzes the re-oxidation of the last cytochrome molecule in the chain by molecular oxygen. This final process results in the reduction of molecular oxygen to water. At times, the incomplete reduction of oxygen leads to the production of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) or the superoxide free radical (O2-) that are both toxic to the cell. Many aerobic or facultatively anaerobic cells produce enzymes that remove these toxic byproducts. Superoxide dismutase removes the superoxide free radical in the following reaction (2H+ + 2 O2- - H2O2 + O2). Catalase removes hydrogen peroxide in the following reaction (2 H2O2 - 2 H2O + O2). Strict anaerobes usually lack these enzymes and therefore are restricted to an oxygen free environment. As only a subset of all the bacterial species produce cytochrome oxidase and catalase, one can test for the presence of these enzymes in bacteria to determine the oxygen tolerance of an individual bacterium and also to identify the bacterium. In this laboratory exercise you will be testing Enterococcus faecalis and Staphylococcus aureus for the presence of cytochrome oxidase and catalase. Catalase test: In the previous exercise you isolated Enterococcus faecalis and Staphylococcus aureus from a mixed culture using the streak plate method. Divide a clean microscope slide in half using a wax pencil; label one half EF and the other half SA. Use a sterile loop to transfer a small amount of culture from the plate to the microscope slide. Add one drop of a H2O2 solution to each culture sample and watch for the production of bubbles in the suspension. The bubbles result from oxygen gas that is released as a result of catalase activity that has converted the externally supplied hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water. If no bubbles are produced the test is negative for catalase activity. Cytochrome oxidase test: Divide a clean piece of filter paper in half using a wax pencil; label one half EF and the other half SA. Use a sterile loop to transfer a small amount of culture from the plate to the microscope slide. Use a sterile wooden applicator to rube the sample into the paper without tearing the paper. This acts to remove capsule (glycocalx, mucin) from the surface of the bacteria so the substrate can interact with the bacteria. Add one drop of tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine to each sample and record the results immediately after 20 seconds. Tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine is a chromogenic reducing reagent. In its reduced state tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine is colorless; in its oxidized state it is deep purple or blue. Therefore, if the bacteria produce cytochrome oxidase, the reagent will be oxidized and will turn blue. The reaction is described below. In a negative test for cytochrome oxidase the sample will remain clear, turn yellow or light gray. [Tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine (reduced) + 2 Cytochrome oxidase (oxidized)- Tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine (oxidized) + 2 Cytochrome oxidase (reduced)]. As this reagent is unstable in the presence of water and oxidizes quickly you should observe your results immediately!!!!! Record your results for the catalase and the cytochrome oxidase tests in the table below. Using a (+) for a positive test and a (-) for a negative test. What constitutes a positive or negative reaction for each test? Organism Staphylococcus aureus Enterococcus faecalis Catalase activity Cytochrome oxidase activity