Evolution Study Guide
advertisement

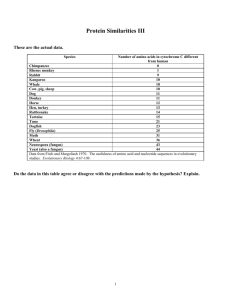
Evolution Study Guide Honors Name Period Date 1. What is population genetics? 2. A biologist analyzes the DNA sequences in three different primates. The biologist finds that primates A and B have nearly identical DNA sequences. The DNA sequences in primate C are significantly different from those of primate A. From this information, what could a biologist infer? 3. List three things that cause genetic variation in species. (Think back to meiosis and two parts that increase genetic variation during this.) 4. How are humans related to primates? 5. Describe the following types of predation selection. a. Mimicry- b. Camouflage- 6. What is the largest and most influential force driving evolution? 7. Describe the process of speciation. 8. Where did Darwin observe the many varieties of finches that helped support his theory of Natural Selection? 9. How did Darwin discover where the finches came and evolved from? 10. What phrase did Darwin use instead of evolution? Descent with _______________ 11. Sexual selection is important to choosing a mate, such as male peacocks with beautiful feathers use them to attract females. How does this relate to natural selection? (Explain in your own words. It’s not in the notes). 12. Compare and contrast vestigial, homologous, and analogous structures. Give examples of each. 13. How can biological molecules (like amino acid sequences, RNA, and DNA) show common ancestry between different organisms? 14. List the evidence for evolution? Cytochrome c is a protein that is involved in cellular respiration in all eukaryotic organisms. Human cytochrome c contains 104 amino acids. The following table compares human cytochrome c with cytochrome c from a number of other organisms Organism Pigs Duck Snake Tuna Moth Number of cytochrome c amino acids that differ from human cytochrome c amino acids 13 17 20 31 36 15. List the organisms above from most closely related to humans to least closely related. 16. Define and list examples of the following: a. coevolution – Ex. Predator vs. Prey If the prey adapts to blend in the environment better, then the predators need to evolve better senses to find the prey. b. convergent evolution c. divergent evolution 17. What is the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium used to do? 18. List/Describe the major part of Darwin's Theory of Natural Selection? 1) 2) 3) 4) 19. What type of population is most susceptible to loss of genetic variability as a result of genetic drift? Large, medium, or small? 20. Compare and contrast the following types of natural selection, include a drawing of what the graphs of each type: a. directional selection b. stabilizing selection c. disruptive selection 21. What is the difference between reproductive isolation and geographic isolation? How do these relate to allopatric and sympatric speciation? Be able to relate all four together, and provide examples. 22. What is gene flow? 23. Define the following words. Be sure to include how they relate to each other: evolution, natural selection, genetic variation, and adaptation.