`A` Level - The Forest Academy
‘A’ Level Sociology
Examining Body
AQA
Specification
2190
Entry Requirements
5+ A*-C GCSE grades including English and Mathematics.
Outline
Sociology comes from two words: “SOCIO” referring to society and “-LOGY” meaning science. Therefore,
Sociology is the study and explanation of people, groups and societies. Sociology prepares one for a lifetime of change, developing one’s appreciation of diversity, love of learning, as well as a knowledge base about human behaviour, social organisation and culture. If you are fascinated about why people behave the way they do or are interested in what is going on around the world, then Sociology is a subject for you.
Sociology will also allow you to explore how society has changed over time, touching on topics such as crime, globalisation and poverty. ‘A’ Level Sociology develops critical thinking skills, oral, visual and written communication, being able to work collaboratively with others and creative thinking skills.
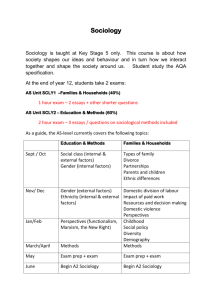
Year Units Learning Assessment
12 Families &
Households
Changing patterns of marriage, cohabitation, divorce, child bearing and separation.
The nature and extent of changes within the family, with reference to gender roles and power relation
The nature of childhood, and changes in the status of children in the family and society.
1 hour exam
20%
12
13
Education with research methods
Beliefs in Society
The role and purpose of education
Differential educational achievement of social groups by gender, ethnicity and social class.
Relationships and processes within schools.
The significance of educational policies.
The application of research methods to the study of education.
2 hour exam
30%
Different theories of ideology, science and religion.
The relationship between religious beliefs and social change and stability.
Religious organisation, including cults, sects and denominations.
The significance of religion and the capture and extent of secularisation.
1 hour 30 minutes exam
20%
13 Crime and Deviance with Theory and methods
Different theories of crime, social order and social control.
The distribution of crime by age, ethnicity, gender and social class.
Crime control, prevention and punishment, victims and the role of the CJS.
2 hours exam
30%
Progression Opportunities
Sociology is particularly relevant to any job that involves working directly with people (such as counselling, journalism, teaching, youth services, social work, public relations or human resources) or any job that requires researching skills. Sociologists work in many areas of society such as politics, education, mass media and the criminal justice system. This course provides a good grounding for students wanting to enter employment or higher education courses to degree level.