Outcome parameter
advertisement

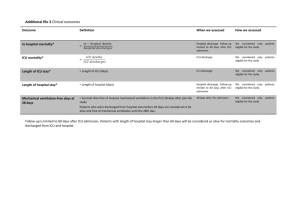
Methods Outcome parameter Duration of mechanical ventilation and of ICU stay, frequency and cause of readmission to the ICU and length of hospital stay were recorded. Extubation was performed at the discretion of the attending physician when hemodynamics were stable for half an hour, temperature was higher than 36 °C, and the patients breathed spontaneously reaching adequate blood gases and were cooperative. Patients were transferred from the ICU to the intermediate care unit when they met the following criteria: Extubated, SpO2 higher than 94% with oxygen insufflation up to 6 l min-1, stable hemodynamics with only minor doses of inotropes, i.e. dobutamine 5 mg kg-1 min-1 and milrinon 0.3 mg kg-1 min-1. ICU discharge decisions were made by the consultant intensivist on-duty. Readmission was defined as admission to the ICU of a patient who had previously been admitted to the ICU during the same hospitalisation period. Causes of readmission were defined as follows: cardiovascular = cardiac arrest needing cardiopulmonary resuscitation prior to ICU admission, shock requiring vasopressor/inotropic drugs, chest pain, arrhythmia, cardiac failure; respiratory = acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome, acuteon-chronic respiratory failure and impaired respiratory function requiring non-invasive or invasive mechanical ventilation; renal = acute renal failure requiring renal replacement therapy; reoperation = reoperation with the need of postoperative intensive care treatment. Patients were discharged from the hospital at the discretion of the department of cardiac surgery. Statistics Differences in ventilation and discharge times between the four groups were analysed using one-factorial ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s honestly significant difference test. Differences in times between group A and group B were analysed using the T-test. Results No significant differences between the four groups could be detected for duration of ventilation, duration of ICU time, readmission to the ICU, or length of hospital stay (see Supplemental Table 1). When looking post-hoc at group A and group B, i.e. patients with or without alveolar derecruitment after OS, a trend to more readmissions to the ICU and longer hospital stay in group B could be detected. No significant differences could be detected for ICU duration (see Supplemental Table 2). The reasons for readmission to the ICU were three times pulmonary, one time cardiovascular, and one time reoperation in group B compared to one time cardiovascular in group A. Supplemental Table 1 Group A_RM A_NRM B_RM B_NRM P Ventilation time [h] 17 (13) 14 (4) 18 (19) 64 (198) 0.458 ICU time [h] 44 (37) 37 (39) 57 (54) 112 (244) 0.536 8 (4) 8 (4) 10 (5) 12 (9) 0.230 Hospital discharge time [d] ICU, intensive care unit; p, ANOVA. Data are presented as mean (SD). Supplemental Table 2 Group A B p Ventilation time (h) 16 (9) 41 (140) 0.307 ICU duration (h) 41 (38) 61 (73) 0.638 1 5 0.063 8.1 (3.5) 10.8 (7.1) 0.078 ICU readmission (n) Length of hospital stay [d] p, t-test or χ2-test, as appropriate. Data are presented as mean (SD) or n.