Pax Romana & Contributions of Ancient Rome
advertisement
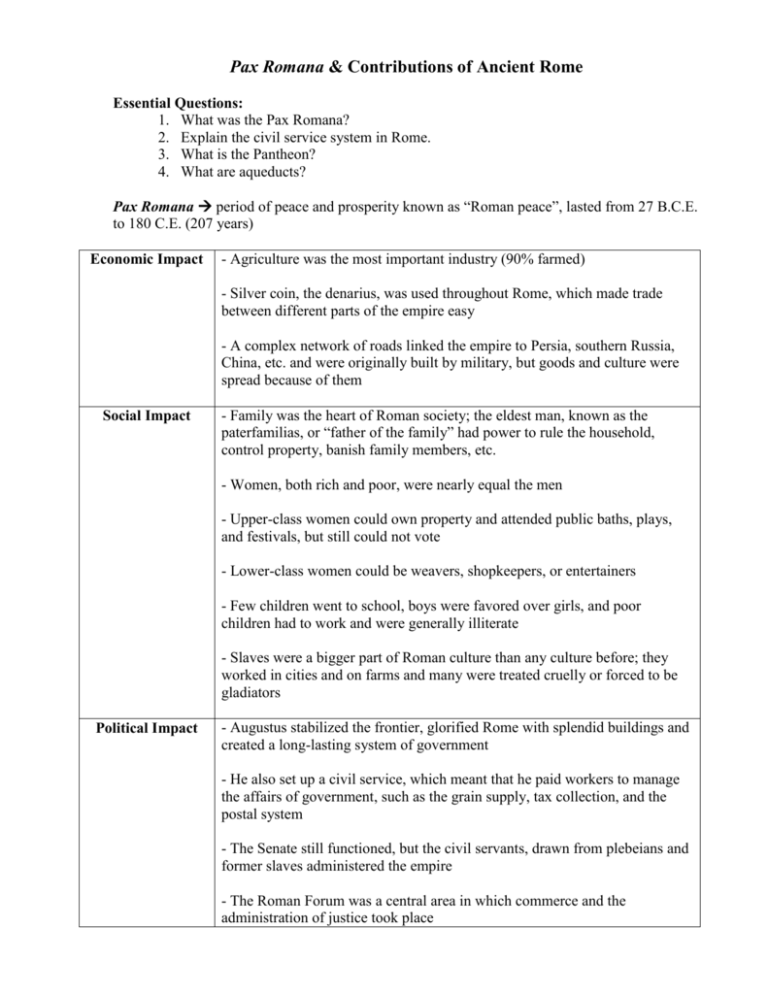
Pax Romana & Contributions of Ancient Rome Essential Questions: 1. What was the Pax Romana? 2. Explain the civil service system in Rome. 3. What is the Pantheon? 4. What are aqueducts? Pax Romana period of peace and prosperity known as “Roman peace”, lasted from 27 B.C.E. to 180 C.E. (207 years) Economic Impact - Agriculture was the most important industry (90% farmed) - Silver coin, the denarius, was used throughout Rome, which made trade between different parts of the empire easy - A complex network of roads linked the empire to Persia, southern Russia, China, etc. and were originally built by military, but goods and culture were spread because of them Social Impact - Family was the heart of Roman society; the eldest man, known as the paterfamilias, or “father of the family” had power to rule the household, control property, banish family members, etc. - Women, both rich and poor, were nearly equal the men - Upper-class women could own property and attended public baths, plays, and festivals, but still could not vote - Lower-class women could be weavers, shopkeepers, or entertainers - Few children went to school, boys were favored over girls, and poor children had to work and were generally illiterate - Slaves were a bigger part of Roman culture than any culture before; they worked in cities and on farms and many were treated cruelly or forced to be gladiators Political Impact - Augustus stabilized the frontier, glorified Rome with splendid buildings and created a long-lasting system of government - He also set up a civil service, which meant that he paid workers to manage the affairs of government, such as the grain supply, tax collection, and the postal system - The Senate still functioned, but the civil servants, drawn from plebeians and former slaves administered the empire - The Roman Forum was a central area in which commerce and the administration of justice took place Roman Contributions Art/Architecture - The Colossuem, a huge arena that could hold 50,000 and hosted gladiators contests, games, races, animal shows, etc. - The Pantheon was a temple for all the gods in Rome, had massive columns and domes, which were typical - Used bas-relief, where images project from a flat background - Where also skilled in mosaics, pictures or designs made by setting small pieces of stone, glass, or tile onto a surface Technology - Aqueducts were designed to bring water into cities and towns - Vast network of roads built of stone, concrete, and sand Languages - Latin was the official language of Rome - Latin influenced French, Spanish, Portuguese, Italian, and Romanian which became known as the Romance Languages Literature - Writers used Roman themes and ideas while following Greek forms and models - Virgil, a poet, wrote The Aeneid, which was a praise of Rome and Roman virtues; he believed government was Rome’s most important contribution to civilization Religion - Adopted the Greek gods, but changed their names - Most important were Jupiter (Zeus) – father of the gods, Juno (Hera) – his wife, who watched over marriage and women, and Minerva (Athena) – goddess of wisdom and war - Christianity spread throughout the Roman Empire and eventually became the official religion Law - All persons had the right to equal treatment under the law - A person was considered innocent until proven guilty - The burden of proof rested with the accuser, not the accused - A person should be punished only for actions, not thoughts - Any law that seemed unreasonable or unfair could be set aside