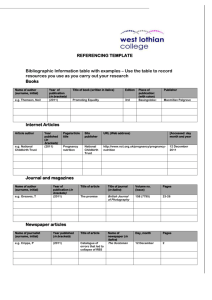
Referencing In The Reference List
advertisement

SSPSSR GUIDE TO CITING REFERENCES THE IMPORTANCE OF CITING REFERENCES The aim of this handout is to outline the academic conventions for citing references so that you can apply them to your own essays and dissertations. Your essays should contain references to published literature because it is necessary to acknowledge the work of others and to state the sources of ideas and information. If you cite someone else’s work without attribution you may fail the essay on the grounds of plagiarism. You should also use references to demonstrate your knowledge of the field. Whoever is marking your work will want to see evidence of wide reading, thoroughness, attention to detail and a familiarity with the relevant literature. Finally, references enable the reader to trace your sources if they want further information. You need to give a reference when you draw on a source for: your general inspiration a particular theory, argument or viewpoint specific information e.g. statistics and case studies direct quotations text you paraphrase rather than quote directly. SYSTEMS OF CITING REFERENCES There are three distinct systems for citing references: 1. Author-Date system, also referred to as the Harvard system 2. Notes system (footnotes or endnotes) 3. Numbered list system In addition, there exist many styles of citing references. Most journals and publishers have their own unique ‘house style’. Within a style, the layout of references for books, journal articles and book chapters will be different. This handout explains how to use the Author-Date system and the ‘Kent Harvard’ style. This is the recommended style to use in SSPSSR modules. LCEM Last updated February 16 REFERENCING IN THE TEXT In your text you never mention the titles of books or articles, or URL of websites. You only mention the author(s) and the date of publication. Never use footnotes for references. Never use Latin abbreviations. Make sure you use the author’s name in the text, not the editor’s. Avoid citations from lectures. Books and journal articles Where you have paraphrased an argument or drawn a piece of evidence from a cited work put the author’s name and the year of the work in parentheses. You should identify the page numbers too: … The ‘social democratic’ welfare state was sought and brought about from the bottom up by those who stood to benefit most - the working class (Van Kersbergen, 1995, p.66). … Where there are more than two authors use et al (Smith et al, 2003) but write authors out in full in the reference list. If the author’s name occurs naturally in the text, the year follows in parentheses: … Thus Gomulka (1999) concludes that the low level of service provision urgently needs to be addressed. … Direct quotations If you are giving a direct quotation you must identify the page numbers: Campaigners argue that as “it is women who will live with the consequences of these decisions, women need to be at the centre of decision-making” (Green, 1996, p.25). For a long quotation indent the text like this: Norman and Verhulst noted that: Few other disciplines relate quite as closely to everyday life as Social Policy, which deals with issues relating to employment, income, health and education. The subject appeals to students who are interested in contemporary social and political issues that shape our lives (Norman and Verhulst, 2003, p.9). Long quotations should be avoided because they don’t count as your own work and the marker may suspect that you copied out the passage because you don’t understand it! 2 ‘Quoted in’ citations Try to avoid second hand quotes. Only use them when the original source is unavailable. Hence, “to reach the goal of halving child poverty by 2010 will require substantially more redistribution to the poorest families” (Newburn, in Brewer, 2003, p.101). List the book by Brewer in the reference list. Web sites Do not give the URL in the text, but the organisation or author: Insurance benefits were raised by 22 per cent just before the 1955 election (Institute for Fiscal Studies, 2001). Other points Use letters to distinguish between works by one author in a single year. Hay (1977a, 1977b) argued that business had an interest in economic efficiency and containment of working class demands. Use initials to distinguish between two authors with the same surname. This kind of theory has been elaborated by neo-Marxists (Hall, R., 1977). In extreme cases welfare policy is regarded as a form of social control (Hall, A., 2000). 3 REFERENCING IN THE REFERENCE LIST The reference list is a list of works referred to in your essay. Put it at the end of the essay. Begin each source on a new line. List the references in alphabetical order by the first author’s surname. It is important that the author surname and date of publication are listed first, as this enables the reader to move between the text and reference list easily. List the references by date order if you have more than one text by the same author. Books Include the following information. The order is: Author(s), surname first Date of publication (in brackets) Title and subtitle (if any) underlined or highlighted or in italics but be consistent. The title has the main words capitalized Place of publication if known Publisher Baldock, J. and C. Ungerson (1994). Becoming Consumers of Community Care: Households within the Mixed Economy of Welfare. York: Joseph Rowntree Foundation. Chapter in a book Include the following information. The order is: Author of chapter, surname first Date of publication (in brackets) Title of chapter. The chapter title may be put in single quotation marks. “in” followed by Editor(s) or author(s) of collected work, surname first Title of collected work, underlined or highlighted or in italics but be consistent Place of publication if known Publisher Barry, N. (1999). Neoclassicism, the New Right and British Social Welfare. in: Page, R. M. and R. Silburn eds. British Social Welfare in the Twentieth Century. London: Macmillan. Use the abbreviations “ed” or “eds” for edited works. You must distinguish between authors and editors. For instance, in the above example, the in-text citation would mention Barry (1999), NOT the book’s editors. 4 Article in a journal Include the following information. The order is: Author(s) Year of publication (in brackets) Title of the article. The article title may be put in single quotation marks. Title of the journal. The journal name is treated as a book, underlined or highlighted or in italics but be consistent Volume and part number, month or season Page numbers of the article Clasen, J. (2002). Modern Social Democracy and European Welfare State Reform. Social Policy & Society, 1(3), 67-76. Include the volume and part number and page numbers of journal articles. In the above example: 1 is the volume number, 3 is the part number, 67-76 are the page numbers. Web site Include the following information. The order is: Author/editor/organisation Year, if known (in brackets) Title, underlined or highlighted or in italics but be consistent [Internet site] Available: <URL>. Note the common convention of using < and > to delineate the start and end of a URL Accessed date Institute for Fiscal Studies. Fiscal Facts: Unemployment Benefit Rates. [internet site]. Available: <www.ifs.org.uk/taxsystem/unempben.shtml> Accessed 11 May 2001. You can shorten the URL as long as you give enough information for the reader to locate the citation. You must give the date accessed, as web pages can change. 5