Relative Humidity
advertisement

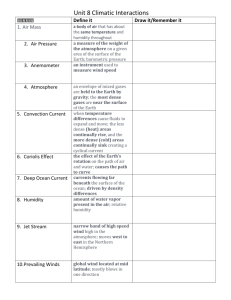
Name ______________________________________________ Date_______________ Per__________ Lab#_________ Relative Humidity Lab Objective – to use a psychrometer to measure relative humidity. Background Information Have you ever heard the word “muggy” used to describe the weather? How about the phrase “hazy, hot and humid”? These phrases are used to describe times when there is a considerable amount of moisture in the air. Of course, there is always moisture in the air, but the amount varies. If the air is warm and dry, it is easier for water to evaporate and enter the air as water vapor. If the air is cold and already holds a lot of water vapor, much less will evaporate into the air At every temperature there is a limit to the amount of water vapor that the air can hold. The warmer the air is, the higher the limit is. When air is holding all the water vapor it can, it is said to be saturated. Usually the air is unsaturated. Relative humidity is a measure of how much water vapor present compared to how much it can hold at that temperature. On a muggy day relative humidity can be high, as much as 80 – 90%. When the relative humidity is high, perspiration does not easily evaporate. This means our bodies’ cooling mechanisms are less effective. As a result, we feel uncomfortable. Saturated air has a relative humidity of 100%. Clouds or fog form when, and where, is saturated. In desert areas there is little water to enter the air and relative humidity is low. In this lab, we will measure the relative humidity using an instrument called a sling psychrometer. Data Table Location Time Of Day Dry Bulb Temp. (°C) Wet Bulb Temp. (°C) Difference (°C) Relative Humidity (%) Calculating Relative Humidity A sample of air ar 25C has 15 g/m3. The maximum capcity for air at 25C is 22 g/m3. What is the relative humidity of the air? (Show Work, Box Answer) Determining Relative Humidity Measuring the amount of water is not the only way to determine relative humidity. The relative humidity can be determined by using a sling psychrometer. 2 thermometers (one wet and one dry) are needed. The wet thermometer will evaporate water until the air is saturated. Because evaporation is a cooling process the temperature of this thermometer will decrease proportionally to the amount of water that evaporated. The difference between these thermometers is then compared to determine the relative humidity. If the wet bulb had a reading of 15C and the dry thermometer had a reading of 20C then what is the relative humidity? 1. Find the difference of the two thermometers. (Show Work, Box Answer) 2. Refer to Table 1 to use the differences from above and the dry bulb temperature to determine the relative humidity. (This # should be a %, Box Answer) Materials - 1 Sling Psycrometer Room temperature water Procedure Inside: 1. Put a drop or two of water on the sock wrapped thermometer. 2. Swing the psychrometer in circles 50 times 4. Record the wet bulb and dry bulb temperatures on the data table. 5. Complete the data table. Relative humidity can be determined by using the Relative Humidity Chart. Outside: Repeat the procedures above outside of the classroom. Questions and Conclusions 1. What did you notice about the wet bulb temperature as you swung the psychorometer? Explain this observation. 2. Is evaporation a cooling process or a heating process? Explain. 3. Was there a difference between the classroom and the outside relative humidity? If there was, how can you explain the difference? 4. Which do you think is more stable the inside relative humidity or the outside? Explain your reasoning. 5. Do water puddles evaporate faster when the humidity is high or low? Explain your reasoning. 6. Sometimes people say, “It’s the humidity that makes us feel so hot, not the heat?” What do you think they mean? (Think about your answer to # 2 and #5 in relation to sweating) 7. What would the relative humidity be if the wet and dry bulb thermometers were the same temperature? Explain why there is no change in temperature in this situation.