Chapter Four
advertisement

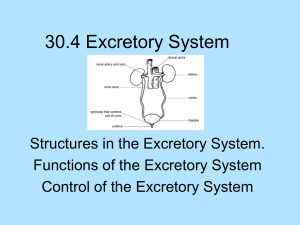
Chapter Four Respiration and Excretion I. The Respiratory System A. Functions1. Taking in Oxygena. Respiration-The process in which oxygen and glucose undergo a complex series of chemical reactions inside cells b. Breathing- The movement of air into and out of lungs. 2. Removing Carbon Dioxide and Water- respiration eliminates CO2 and H2O 3. Systems working togetherRespiration also requires Digestive and Circulatory system to move oxygen to the lungs and expel carbon dioxide B. The Path of Air 1. Nose- enters the body into the nasal cavities lined with mucus a. Cilia- hair like extensions that can move together to seep the mucus into the throat. 2. Pharynx- Air then enters the Throat, also in the digestive system 3. Trachea- Air then moves into the windpipe. Lined with mucus, cilia, and rings of cartilage. The epiglottis protects from trachea from food entering 4. Bronchi and Lungsa. Bronchi- Passages that direct air into the lungs b. Lungs- Main organ of the respiratory system. c. Alveoli- The end of the smallest tubes of bronchi are tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood. C. Gas Exchange 1. Air enters alveolus 2. Oxygen passes through the wall of the alveoli into the blood. 3. Carbon Dioxide and Water move from the blood to the alveoli (backwards) 4. How Gas Exchange Occurs- Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide attach to the Hemoglobin on the red blood cells and transfers 5. Surface Area for Gas Exchange-The larger the surface area, the more efficient the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. D. How you Breathe- more than 20,000 times a day. 1. Muscles for Breathing- ribs and diaphram a. Diaphragm- dome shaped muscle that plays an important role in breathing 2. The Process of Breathing- a. When you inhale, the diaphragm moves downward and pressure in the lung decreases causing air to flow in b. When you exhale, the diaphragm moves upward and the pressure in the lungs increases, pushing the air out. 3. Relating Breathing and Speaking a. Larynx- Voice Box contains two folds of tissue that stretch across the opening (vocal cords). b. Vocal Cord-contract from muscles and vibration contains sounds II. The Excretory System- excretion- removal of waste A. The Excretory System- The system in the body that collects wastes produced by cells and removes the wastes from the body 1. Kidneys- Major organs that remove urea (chemical coming from the breakdown of protein). Filter 2. Ureters- Carry urine from the kidneys through these narrow tubes to the urinary bladder 3. Urinary Bladder- Sack like Muscular organ that stores urine 4. Urethra- Small tube that carries urine out of the body B. Filtration of Wastes 1. Nephrons- Tiny filtering factories that remove wastes in stages a. Filtering out waste- First waste and needed materials such as glucose are filtered out of the blood. b. Formation of Urine- The needed material is returned to the blood and the waste are eliminated in urine. 2. Analyzing Urine for Signs of Disease- If urine contains glucose or protein it may indicate a medical problem. C. Excretion and Homeostasis- (review section 1-1) Excretion maintains homeostasis by keeping the body’s internal environment stable and free of chemicals. 1. Kidneys- Filter blood and regulate the amount of water in the body. 2. Lungs and Skin- Remove some waste by exhaling or perspiring. 3. Liver- Breaks down waste and even converts hemoglobin to bile D. Diagram of the Excretory System (p 129)