Writing learning objectives
advertisement

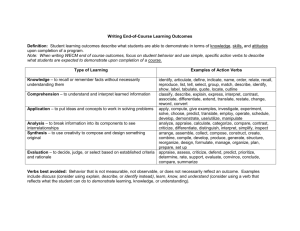
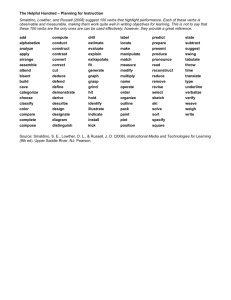
Writing learning objectives Beginning with the end in mind Definition of learning objectives Learning objectives are statements which describe what the learner is expected to achieve as a result of instruction. Whether you are teaching in a classroom, or training staff to do a particular task on an assembly line, learning objectives set a standard for the level of competence expected. There are a number of purposes of learning objectives: By knowing where you intend to go, you increase the chances of you and the learner ending up there They guide the teacher relative to the planning of instruction, delivery of instruction and evaluation of student achievement The guide the learner; helping him/her focus and set priorities They allow for analysis in terms of the levels and the outcomes of teaching and learning Well formed learning objectives are an important initial step in planning any training or instructional activities. They help the trainer to plan and prepare content that is appropriate and supportive of the desired learning outcomes. They are also essential in evaluating the outcomes of any learning. Writing learning objectives does take time and effort. It is time well spent though and some simple steps and guides can help make the process easier. Simple steps to writing learning objectives Generally, learning objectives are written in terms of learning outcomes: What do you want your students to learn as a result of the lesson? Follow the threestep process below for creating learning objectives. 1. Create a stem. Stem examples: After completing the module, the student will be able to… After this unit, the student will have… By completing the activities, the student will…. At the conclusion of the course/unit/study the student will… 2. After you create the stem, add a verb: Describe, recognize, compare, provide, list, write, etc. For a list of action verbs see below – choose your verbs carefully! 3. Once you have a stem and a verb, determine the actual product, process, or outcome: After completing the module, the student will be able to describe the purpose of learning objectives. Reference: action verbs Comprehension Cite Clarify Discuss Explain Express Extrapolate Generalize Give examples Illustrate Interpret Locate Paraphrase Rearrange Recombine Reconstruct Regroup Rename Reorganize Reorder Report Reproduce Restate Restructure Retell Rewrite State Summarize Tell Translate Verbalize Repeat Recall State Tell Discriminate Distinguish Identify Indicate Isolate List Match Omit Order Place Point Select Employ Find Operate Schedule Search Sketch Memorization Define Duplicate Imitate Discriminative Choose Collect Define Describe Detect Differentiate Application Apply Classify Compute Demonstrate Determine Dramatize Perform Predict Record Solve Use Write Criticize Debate Deduce Defend Diagram Differentiate Dissect Distinguish Examine Experiment Induce Infer Inspect Inventory Relate Separate Solve Test Criticize Evaluate Judge Mark Rate Score Select Sort Value Design Formulate Gather Generate Itemize Invent Manage Organize Plan Prepare Propose Set up Synthesize Systematize Outline Print Pronounce Punctuate Read Recite Say Sign Speak State Summarize Syllabicate Translate Verbalize Whisper Write Get Give Relate Repeat Analysis Analyze Appraise Breakdown Calculate Categorize Compare Conclude Contract Contrast Evaluation Appraise Approve Assess Change Chose Synthesis Arrange Assemble Collect Combine Compose Compile Construct Create Language Abbreviate Accent Alphabetize Articulate Call Capitalize Hyphenate Indent Miscellaneous Attempt Attend Begin Bring Buy Chart Circle Complete Consider Copy Correct Crush Designate Develop Discover Distribute Document End Erase Expand Extend Find Finish Fit Fix Follow Grind Guide Hold Include Inform Label Lead Lend Light Make Map Mend Miss Name Note Offer Position Present Produce Propose Provide Put Quote Raise Return Save Send Serve Sew Share Sharpen Shorten Shut Signify Start Store Strike Suggest Supply Support Switch Take Tear Touch Type Use Vote Watch Phrases and Verbs to Avoid The following tired phrases are commonly misunderstood to represent accurate and clear objective writing. They are in fact vague and lead to dull teaching because the participants do not understand what they are supposed to be able to accomplish. Avoid these and their brethren at all costs. To become Acquainted with... Adjusted to... Capable of... Cognizant of... Conscious of... Familiar with... Knowledgeable about... Knowledge of... Interested in... Evidence of a(n) Appreciation for... Attitude of... Awareness of... Comprehension of... Enjoyment of... Feeling of... Self-confident in... Understanding of... Interest in... Avoid These Weak Verbs Conceptualize Memorize Comprehend Recognize Feel Self-actualize Capacity Perceive Experience Thank Believe Listen Depth See Hear Understand Intelligence Know Sources and references This document was prepared using content from the following resources. All online resources were retrieved 17 March 2009. Writing Learning Objectives: Beginning With The End In Mind, Ohio University, College of Osteopathic Medicine http://www.oucom.ohiou.edu/FD/writingobjectives.pdf Train the Trainer: Developing Learning Objectives, Purdue University Libraries http://gemini.lib.purdue.edu/staffdev/handouts/developing%20learning %20objectives%20handout.doc Learning Objectives: Stems and Samples, Education Oasis http://www.educationoasis.com/curriculum/LP/LP_resources/lesson_ob jectives.htm Bloom's Taxonomy for Behavioural Objectives, Georgia State University, Department: Kinesiology & Health http://www.gsu.edu/~wwwche/bloom's.htm