Goals and Objectives powerpoint
advertisement

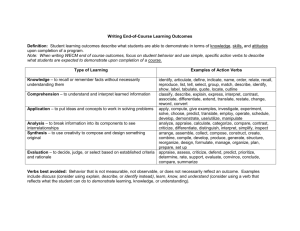
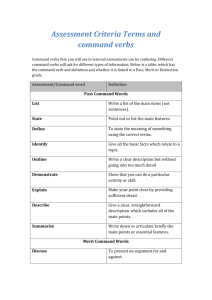
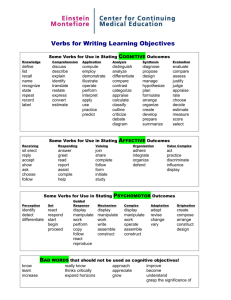
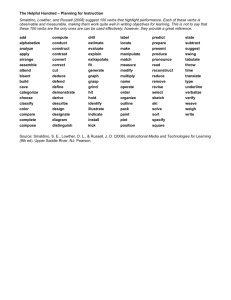
RUST COLLEGE MODEL FOR DEMONSTRATING INSTITUTIONAL EFFECTIVENESS GOAL AND OBJECTIVES I THE TERMS “GOALS AND OBJECTIVES” CAN BE CONFUSING! LET US TRY TO EXPLAIN THE DIFFERENCES. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN GOALS AND OBJECTIVES GOALS Broad Statements General Intentions Intangible Abstract Generally hard to measure OBJECTIVES Specific Precise Tangible Concrete Measurable GOAL The goal of a learning activity is like a target OBJECTIVES The objectives are the arrows that help the institution, student reach the target and demonstrate mastery IDENTIFYING GOALS A. B. C. D. State the definition of a Historically Black College or HBCU. Provide the student with current information about the criminal justice major. Introduce the student to a new development in material science. Be exposed to a new way of organizing paperwork. Answer Only one is not a broad based goal. A. State the definition of a Historically Black College or HBCU. Remember this about a GOAL Every educational activity should have a goal The goal focuses on what the student will experience, rather than what the instructor, the VPs, directors, staff will share or do It is a broad statement of purpose What is the purpose of the educational activity? What is the main intention EXAMPLE The purpose of this presentation is to provide Rust College students with new information on career paths. Introduce students to modes of satiric writing in the eighteenth century Introduce students to healthy nutritious meals. Become acquainted with the top educational donors and their support of HBCUs. Explain the loan management program and deferment. OBJECTIVES The ABCD APPROACH Always begin with the end result in mind! Who is this activity intended for? Be specific At the end of the activity the students will be able to….. At graduation the students will be able to….. A A= Audience (the students, not the instructors, administrator or staff) What exactly is it that you want the student to be able to do as a result of your….. Blackboard assignment Seminar Hands on Workshop Webinar B B= Behavior (what the students will do) States what conditions the instructor/staff will impose when the students are demonstrating mastery of a skill. Usually a WHEN or WHILE statement “when given a set of five unlabeled slides” “when given a list of common over the counter drugs” “while working independently” C C= Condition (imposed by the instructor/staff) The standard or criterion for judging behavioral performance. What has to happen for the student to succeed? It might be: Speed Accuracy Quality Quantity D D= Degree What is “Good Enough”? ACTION VERBS MATCH LIST DEFINE ARRANGE LABEL NAME ORDER REMEMBER MEMORIZE RECOGNIZE RELATE RECALL REPEAT REPRODUCE REMEMBERING Recall of Information ACTION VERBS Classify Report Discuss Review Express Sort Indicate Translate Recognize Explain Identify Locate Restate Select Tell Describe UNDERSTANDING Interpret Information in One’s Own Words Action Verb Demonstrate Dramatize Apply Choose Employ Illustrate Interpret Operate Prepare Practice Schedule Sketch Solve Use APPLYING Use knowledge or generalization in a new situation ACTION VERBS Discriminate Differentiate Analyze Appraise Calculate Categorize Compare Contrast Criticize Diagram Distinguish Examine Inventory Question Experiment Test ANALYSING Break down knowledge into parts and show relationships among parts ACTION VERBS Appraise Argue Assess Attack Choose Compare Defend Estimate Evaluate Judge Predict Rate Score Select Support Value ASSESSING Making judgments based on criteria and standards ACTION VERBS Arrange Assemble Collect Compose Construct Create Design Formulate Manage Organize Plan Prepare Propose Set –up Synthesize Write CREATING Bring together parts of knowledge to form a whole and build relationships for new situations CONGRATULATIONS Best Wishes and Thank you for your Attention. Please go to our link and call us to conduct small group workshops. Sandra C. Vaughn, Ph.D. Vice President for Assessment and Accreditation Mrs. Monique McKoy Lewis, Administrative Assistant