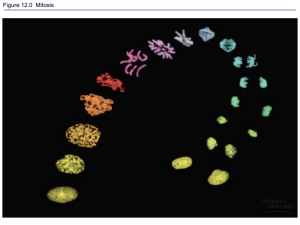
Describe/model meiosis and explain its role in sexual reproduction
advertisement
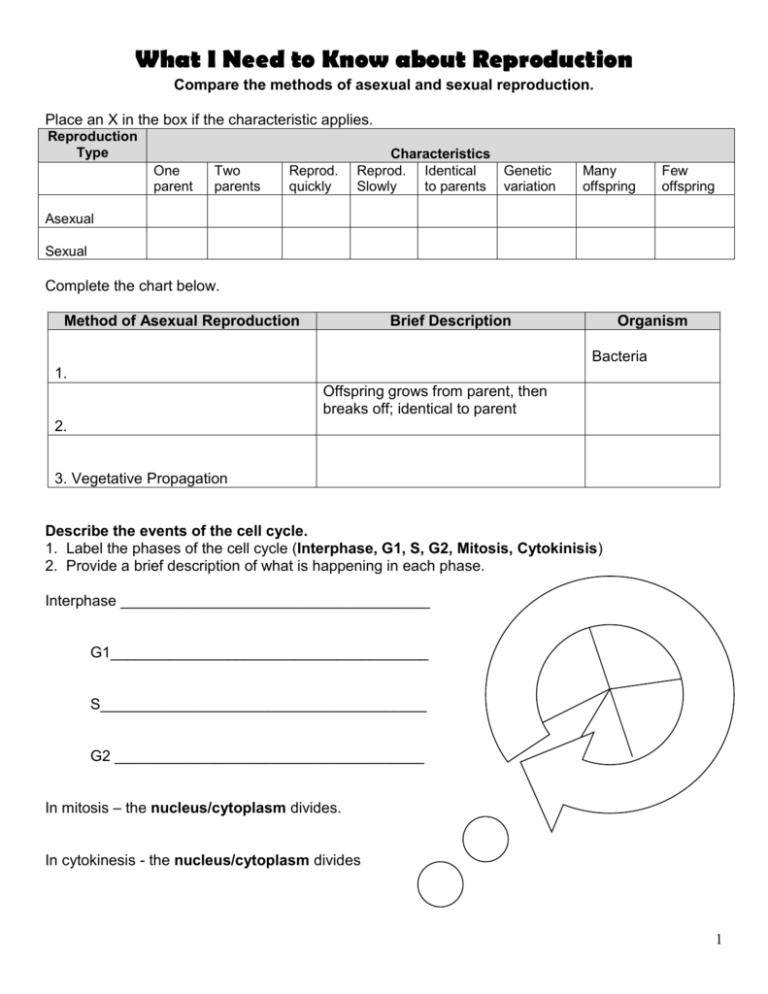
What I Need to Know about Reproduction Compare the methods of asexual and sexual reproduction. Place an X in the box if the characteristic applies. Reproduction Type One parent Two parents Reprod. quickly Characteristics Reprod. Identical Genetic Slowly to parents variation Many offspring Few offspring Asexual Sexual Complete the chart below. Method of Asexual Reproduction Brief Description Organism Bacteria 1. Offspring grows from parent, then breaks off; identical to parent 2. 3. Vegetative Propagation Describe the events of the cell cycle. 1. Label the phases of the cell cycle (Interphase, G1, S, G2, Mitosis, Cytokinisis) 2. Provide a brief description of what is happening in each phase. Interphase _____________________________________ G1______________________________________ S_______________________________________ G2 _____________________________________ In mitosis – the nucleus/cytoplasm divides. In cytokinesis - the nucleus/cytoplasm divides 1 Describe the relationship between DNA, genes, and chromosomes. Create a thinking map to show the relationship between DNA, Genes, and chromosomes or draw pictures with labels. Describe/model mitosis and explain why it is a critical part of the cell cycle (chromosome number, limit variation) Explain how you know that the diagram below is the process of mitosis. ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Purpose – Why do cells go through mitosis? (HINT: Remember the three Rs) 1. ___________________________________________ 2. ___________________________________________ 3. __________________________________________ Chromosome number before mitosis and after mitosis: ___n ___n Number of cell divisions: two or four (underline one) How many new cells are produced? Two or four (draw a box around the correct choice) Type of cell produced? Haploid or diploid (underline one from each group) Somatic or sex Mitosis is critical because… _______________________________________________________________________________ 2 Describe/model meiosis and explain its role in sexual reproduction (chromosome number, increase variation). Purpose – Why do cells go through meiosis? HINT: What is being produced (made)? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ Chromosome number before and after: ___n ___n Number of cell divisions: two or four (underline one) How many cells are produced? Two or four (draw a box around the correct choice) Type of cell produced? Haploid or diploid (underline one from each group) Somatic (body) or sex cell Describe two ways genetic variation is increased during meiosis 1. ________________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________________________ Describe how crossing over increases the chance for gene variation. Use the following words to complete the paragraph: not, homologous, chromosome, genetic, change, Meiosis, traits, offspring, chromosome Crossing-over is the exchange of ______________ material. It occurs when _________________ chromosomes pair up with one another. It happens when segments of one __________________ break off and _____________ places with another __________________. Crossing-over occurs in the first phase of ___________. This process can result in many new combinations of __________. Some ____________________ may have combinations of features that are _______ seen in either parent. 3 Compare mitosis and meiosis. Characteristics Mitosis Where it occurs in the organism Meiosis Sex organs Number of cells produced from parent cell Chromosome number of parent cell 2n Chromosome number in daughter cells Somatic Type of cell produced Function 1. Examine the table below. Fill in the missing information based on the numbers that are given. Organism Human Cat Somatic (Body Cell) Cell Chromosome Number 46 38 Onion 8 Rye 14 Guinea pig 26 Chicken Gamete (egg & sperm) Chromosome Number 23 39 4 2. Using the information from the previous table, complete the following. The first one is done for you. Organism Human Gamete Gamete (Egg) (Sperm) Chromosome Chromosome Number Number 23 23 Zygote Chromosome Number (Fertilized Egg) 46 Somatic Cell Chromosome Number 46 Cat Onion Rye Guinea pig Chicken Explain fertilization and how it results in genetic variation. What is fertilization? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ How does fertilization result in genetic variation? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ What is produced (made) as a result of fertilization (This is when egg and sperm come together)? ________________________________________________________________________________ Explain what a karyotype is and how what it can help determine. What is a karyotype? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ What can a karyotype be used for? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 5 Circle the abnormality in the following karyotype. Does this karyotype represent a male or female? Describe reproduction in angiosperms (flowering plants). Use the diagram to complete the chart and corresponding questions. The male gamete is called ___________________, which is made in letter ____. The female gamete is called __________________, which is made in letter ____. Flower Part Petals Matching Letter Function ____ Stamen ____ + ____ Anther ____ Pistil ____ Ovary ____ 6