Name: Jesse Kazemir Block: D Date: March 3rd Science 10 Digital
advertisement

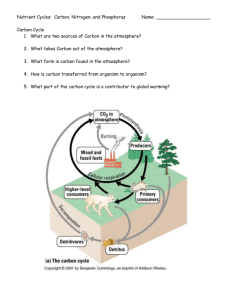
Name: Jesse Kazemir Block: D Date: March 3rd Science 10 Digital Immersion: Nutrient Cycles Read our e-textbook pages 68–87. Nutrient cycles - answer the questions below in sentences. 1. Where are nutrients accumulated or stored for short or long periods? Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, and land masses. 2. Name a biotic process and an abiotic process that allow nutrients to flow in and out of stores. Biotic – Decomposition Abiotic – river run-off 3. Photosynthesis is an important process in which carbon and oxygen are cycled through ecosystems. Describe this process. Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere enters plants through their leaves, and reacts with water – as long as there is sunlight. This produces oxygen and carbohydrates. 4. Cellular respiration is the process in which plants and animals make use of stored energy and release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Describe this process. Cellular respiration is pretty much the opposite of photosynthesis. The cells convert carbohydrates and oxygen into carbon dioxide and water. This process gives the cells energy to grow, reproduce, and repair itself. 5. How is decomposition related to the carbon cycle? Decomposers convert carbohydrates into carbon dioxide, and release it into the atmosphere. This is the same as cellular respiration 6. What is nitrogen fixation? Nitrogen fixation is the process in which nitrogen is converted into compounds that contain nitrate or ammonium. It can occur in three ways. In the atmosphere, in the soil, and in water bodies. 7. What is denitrification? Dentrification is the opposite of nitrogen fixation. In dentrification, nitrogen is returned to the atmosphere. 8. What is eutrophication? Eutrophication is the process by which excess nutrients result in increased plant production and decay. The cycling of nutrients in the biosphere Use the general model of a nutrient cycle to answer the questions below. Industrial Waste Run-off from mining etc. Using nutrients like fertilizer Human activities Mining Nutrients or Minerals 1. This diagram illustrates the general model of a nutrient cycle. What types of human activities can affect a nutrient cycle? Manufacturing, industrial waste, mining, etc. 2. How do these human activities affect a nutrient cycle? They contribute extra nutrients to the cycle, or they take away too many nutrients. Too much of a good thing can turn bad. Although the nutrients are critical parts of ecosystems, too much can negatively affect a species that are sensitive to an overload of the nutrient. 3. On the diagram above, add terms and arrows that could represent the effects of human activity on a nutrient cycle. 4. How do changes in nutrient cycles affect biodiversity? Any excess nutrients or lack of nutrients can alter the abiotic and biotic conditions necessary for supporting biodiversity. Any change in the amount of nutrients can greatly affect how an organism survives. 5. Reflect on your local community. Discuss a human activity that is affecting your local ecosystem. My local ecosystem is affected if people put out their garbage too early in the morning, or too late in the evening. This can affect bears, because they tend to eat the garbage, which might hurt them. This would also affect small animals that bears could eat. There would be way more of them, because less of them are being eaten off. The bears are full from eating garbage, and don’t eat as many small animals. Read our e-textbook pages 71–87 about the carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus cycles. The Carbon Cycle 1. Why is the carbon cycle important? Carbon is an essential component in the chemical reactions that sustain life, such as cellular respiration. 2. How is carbon stored? Short term stores can be in vegetation on land, plants in oceans, in land-based and marine animals, and in decaying organic matter in soil. It can also be stored in the air as CO2, and also dissolved in the top layers of the ocean. Long term stores can be in the middle, and/or at the bottom of the oceans. Coal, oil, and gas deposits are also long term stores of carbon. 3. How is carbon cycled? Photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, ocean processes, and events like large-scale forest fires and volcanic eruptions are all examples of carbon being moved through an ecosystem. 4. Name several human activities that affect the carbon cycle. Motorized transportation, land clearing, agriculture, and urban expansion The Nitrogen Cycle 1. Why is the nitrogen cycle important? Nitrogen is an important component of DNA and proteins, which are essential for the life processes that take place inside cells. 2. How is nitrogen stored? Nitrogen is mainly stored in the atmosphere (nitrogen gas). However, other major stores are in organic matter in soil, and in oceans. Living organisms, lakes and marshes also store small amounts of nitrogen. 3. How is nitrogen cycled? Nitrogen fixation, nitrification, and uptake are three of the processes that make nitrogen available to plants and eventually animals. Nitrogen gas is not usable by most organisms, so nitrogen goes through one of these three processes to make it useful. 4. Name several human activities that affect the nitrogen cycle. Human activities have doubled the available nitrogen in the biosphere in the past 50 years. This is from fossil fuel combustion in power plants and processes such as sewage treatment. The burning of fossil fuels in cars, trucks, and other vehicles also releases nitrogen. The Phosphorus Cycle 1. Why is the phosphorus cycle important? Phosphorus is an essential element in the molecule that carries energy to plant cells and animal cells. A lot of phosphorus is found in human bones, as well. 2. How is phosphorus stored? Phosphorus is never stored in the atmosphere. Instead, it is trapped in phosphate rock and the sediments of ocean floors. 3. How is phosphorus cycled? Weathering, the process in which phosphate rock gets broken into smaller fragments. There are two types of weathering. Chemical weathering, which Is when a chemical reaction causes the rock to break down, and physical weathering, where wind, rain, and freezing release particles of rock and phosphate into the soil. 4. Name several human activities that affect the phosphorus cycle. Phosphate is mined a fair bit for fertilizers and detergents. Run off from these mines add too much extra phosphorus into the ecosystems, causing problems. They have too much phosphorus, which can be harmful to certain organisms.