Nutrient Cycles Worksheet: Science 10 Answer Key
advertisement

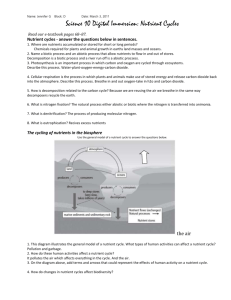
Bob Zhang Science 10 (Blk 2-3) Oct 17, 2011 2.2 – Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems P91 # 1 Question Use the following nutrient cycle diagram to answer questions (a) to (d). Diagram on P91. Answer (a) Land, atmosphere, oceans, marine sediments and sedimentary rock, nutrient stores. (a) Identify the abiotic components (b) Producers, composers, decomposers (b) Identify the biotic components (c) Some arrows are thicker than others because they show the amount and speed in which nutrients move into and out of stores. (c) Why are some arrows thicker than others (d) What would you add to this diagram to show the processes by which nutrients naturally leave stores in rock? 2 Describe the importance to living organisms of each of the following? (a) Carbon is an essential nutrient that is required to sustain life. (a) Carbon (b) Nitrogen is an important part of DNA and proteins, which are needed to sustain life. (b) Nitrogen (c) Phosphorus 3 (d) I would add weathering and the specific nutrient cycled. Explain how each of the following is stored in the biosphere. (a) Carbon (b) Nitrogen (c) Phosphorus (c) Phosphorus is essential for life as it mixes with carbon to strengthen bones, and assist in root development, stems, and seed production. (a) Carbon is stored in the atmosphere, in oceans, in organisms, and mainly in sedimentary rock. (b) Nitrogen is stored mainly in the atmosphere, but exists in organisms and oceans as well. (c) Phosphorus is stored in phosphate rock, oceans, and in organisms. It is not stored in the atmosphere as gas. 4 In what form is carbon stored in the ocean? Carbon is stored in aquatic plants, and is stored as dissolved carbon dioxide. 5 Explain how human activities have influenced: (a) Mining for carbon, burning of fossil fuels, agriculture, industry, domesticated plants (a) Carbon (b) Clearing forests by burning, and by burning grasslands. Chemical fertilizers and fossil fuel burning also contributes. Affects via acid rain (b) Nitrogen (c) Phosphorus (c) Mining of phosphate rock and guano. Fertilizers detergents and improperly treated wastes, including human sewage. Burning forests 6 How does geologic uplift contribute to the phosphorus cycle? During geologic uplift, phosphate rock is exposed, and weathering begins to release the phosphorus from the phosphate. 7 The following processes circulate carbon in an ecosystem. Identify which processes circulate carbon and which processes circulate carbon very slowly. (a)The process of photosynthesis is fast, but the amount per round is little. (a) Photosynthesis (c) The process of sedimentation is slow, but the amount per round is a lot (b) Volcanic activity (c) Sedimentation and rock formation (b) The process of volcanic is can be fast or slow, and the amount per round is a lot. (d) The process of respiration is fast, but the amount per round is little. (d) Respiration 8 Explain the term “leaching”. Leaching is when water runs over soil, and picks up nutrients, and carries it into rivers or lakes. 9 List three ways in which plants influence the cycling of nutrients. Plants influence the cycling of nutrients by: (a) photosynthesis (b) cellular respiration (c) acting as a nutrient store 10 Match the following processes with the descriptions. (a) Nitrogen Fixation (i) Nitrate is converted to nitrogen gas (b) Nitrification (ii) Ammonium is converted to nitrate (c) Denitrification (iii) Nitrogen gas is converted to nitrate (a) matches with (iii) (b) matches into (ii) (c) matches into (i) 11 Explain the relationship between Rhizobium bacteria and plants Rhizobium fixes bacteria and converts N2 into NH4+, a form of nitrogen usable by plants. 12 How can lightning benefit an ecosystem? Lightning is a form of nitrogen fixation.